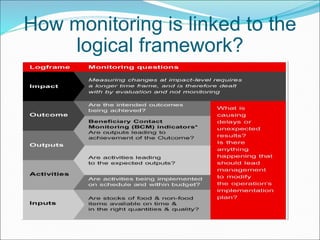
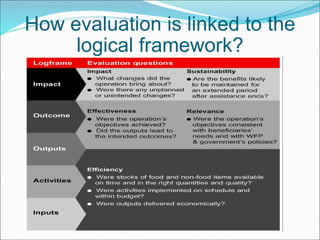
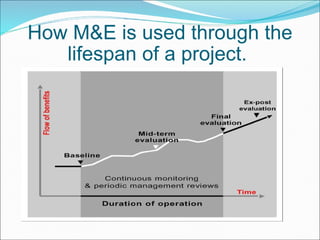
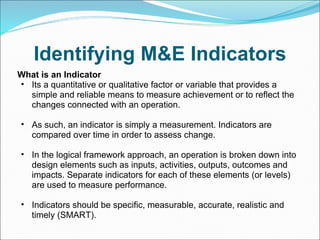
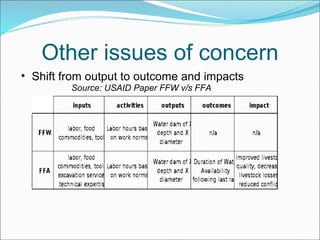
Result-based management (RBM) is an approach that focuses an organization's efforts and resources on expected results through improved accountability, effectiveness, and sustainability. Central to RBM is the results chain, which stipulates the necessary sequence to achieve desired objectives from inputs and activities to outcomes and impacts. Monitoring is the ongoing collection of data on indicators to track progress and inform management, focusing on lower results. Evaluation assesses overall performance through events like surveys and studies, focusing on outcomes and impacts. Well-defined indicators are needed to measure achievement at each level of the results chain throughout the lifespan of a project.