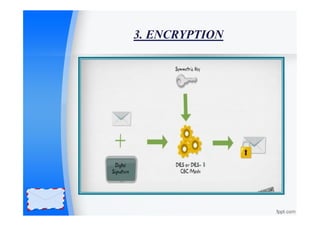
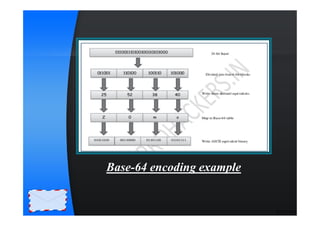
Privacy Enhanced Mail (PEM) is an internet standard designed for secure email communications, focusing on confidentiality, authentication, and message integrity. The process involves canonical conversion, digital signatures, encryption, and base-64 encoding to ensure messages are securely transmitted and received. PEM is outlined in four specifications (RFC 1421-1424) and employs mechanisms such as MD5 for digital signatures and a specific encoding scheme for secure data representation.