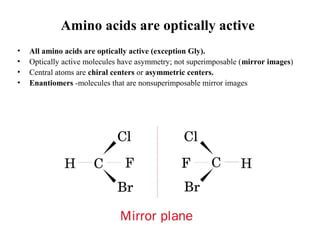
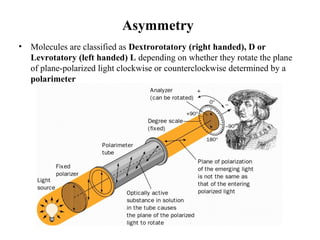
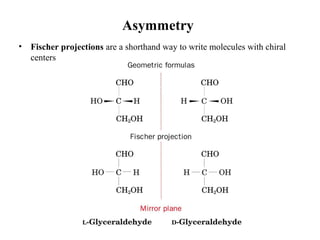
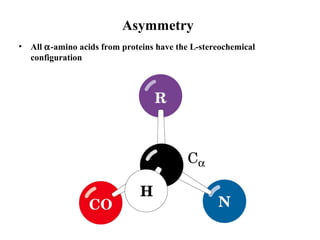
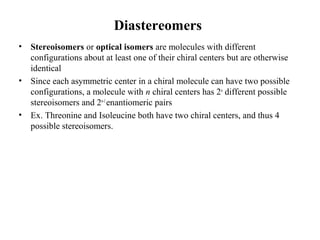
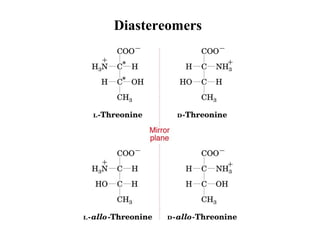
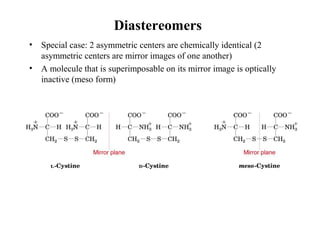
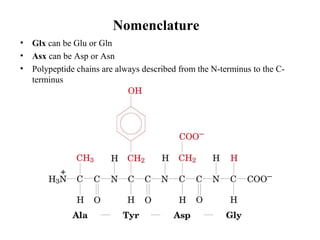
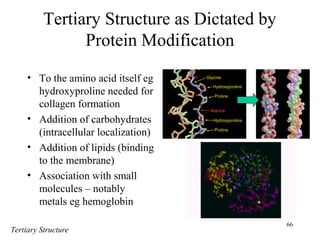
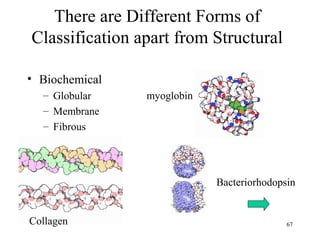
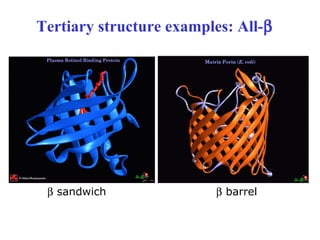
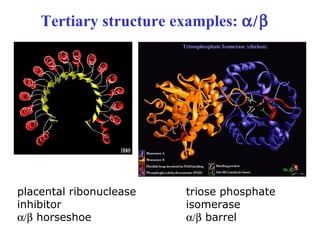
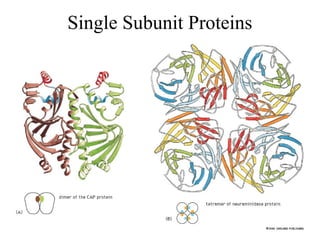
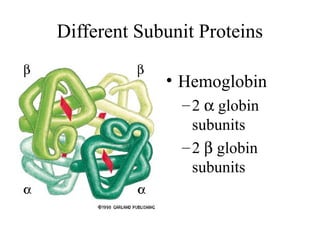
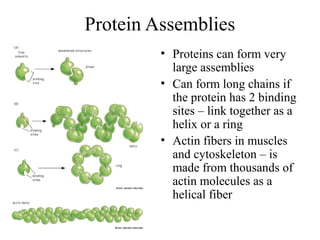
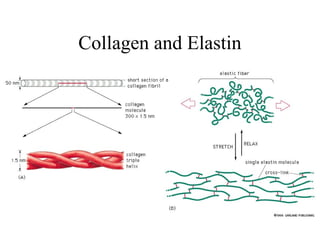
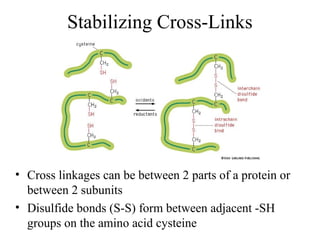
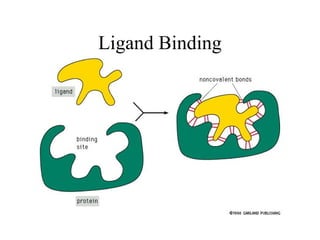
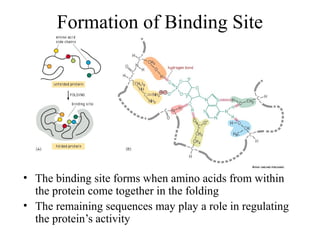
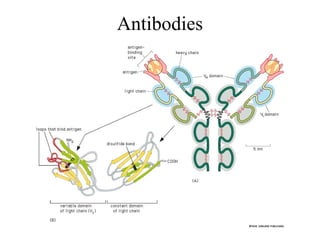
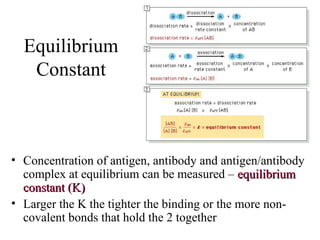
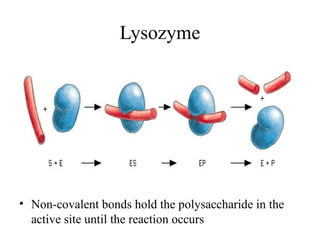
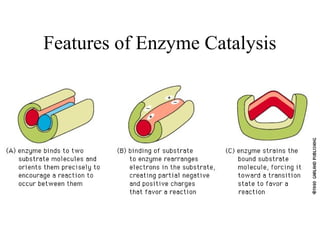
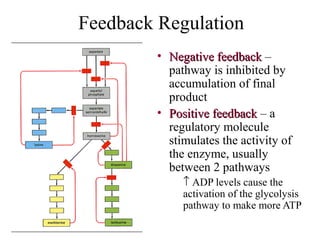
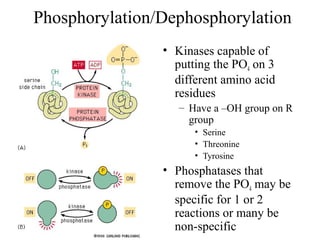
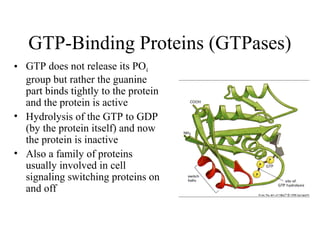
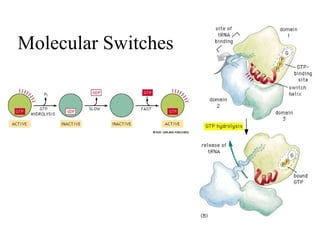
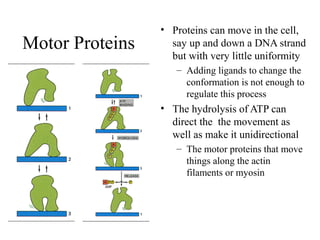
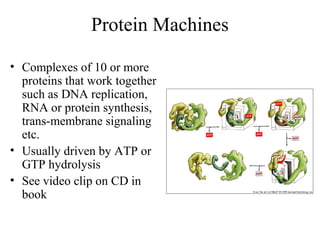
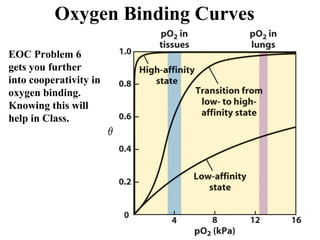
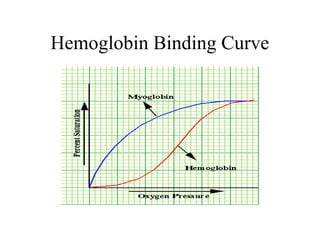
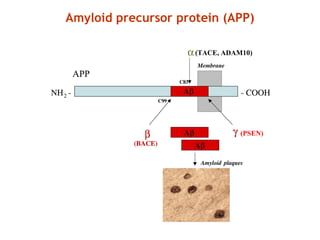
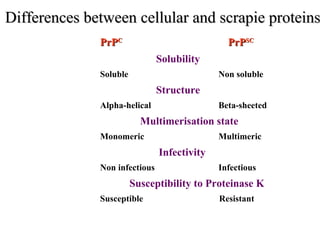
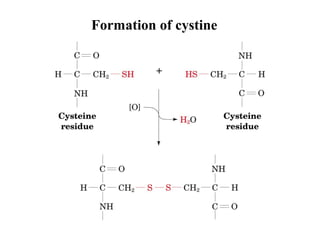
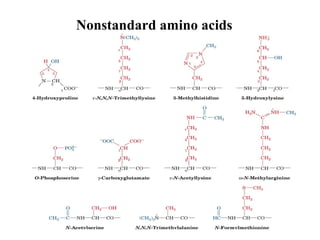
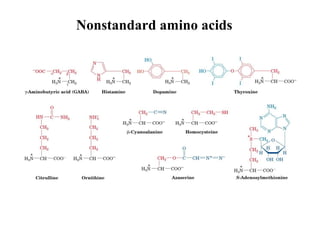
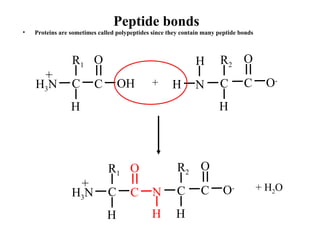
This document discusses principles of protein structure, including primary, secondary, and supersecondary structure. It covers the following key points:
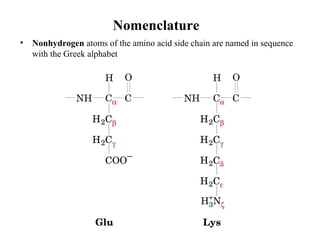
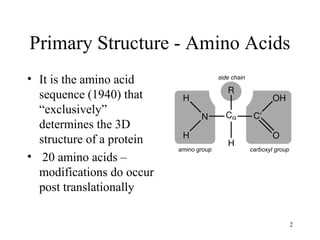
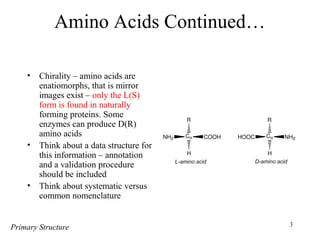
- Primary structure refers to the amino acid sequence of a protein. There are 20 common amino acids that make up protein sequences.
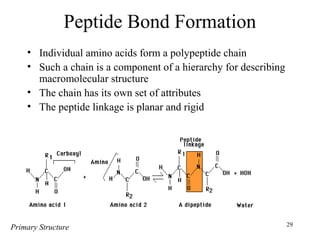
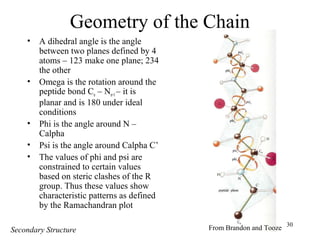
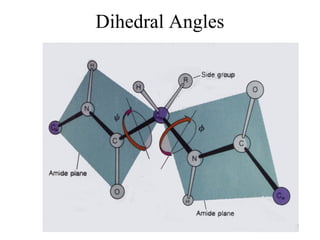
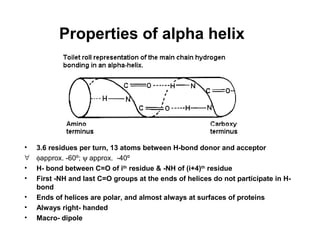
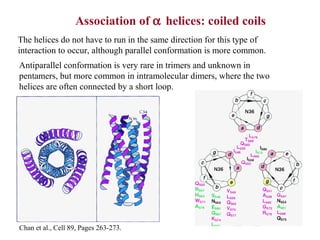
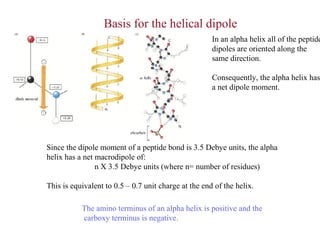
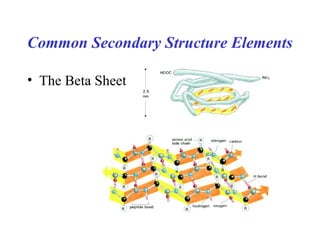
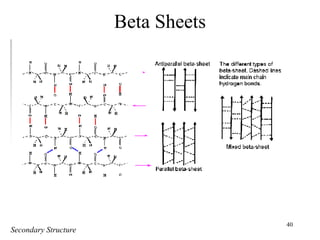
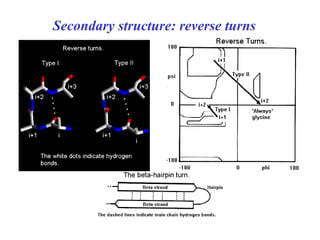
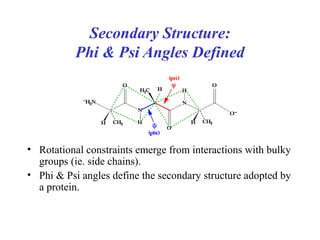
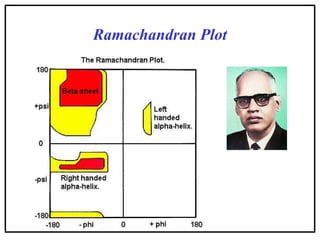
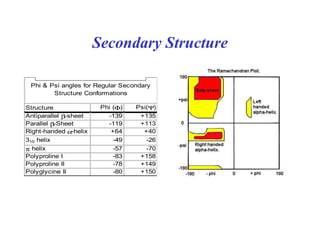
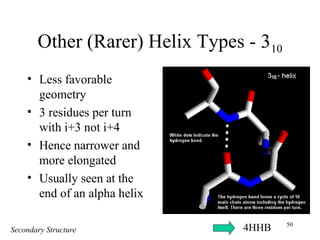
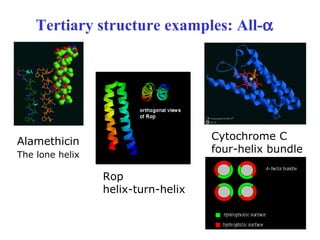
- Secondary structure includes common elements like alpha helices and beta sheets. Alpha helices are right-handed coils stabilized by hydrogen bonds between amino acids four positions apart in the sequence. Beta sheets consist of beta strands connected laterally or anti-parallel by hydrogen bonds.
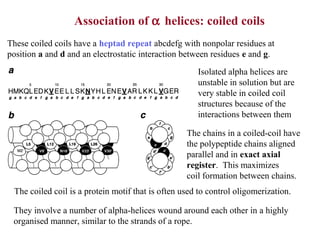
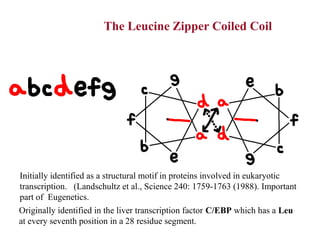
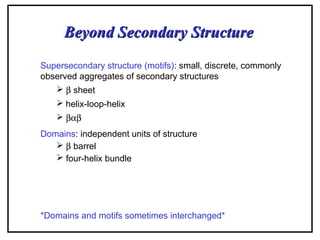
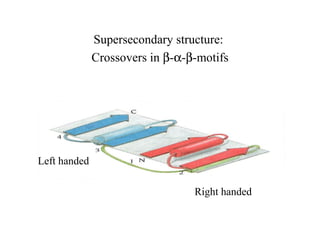
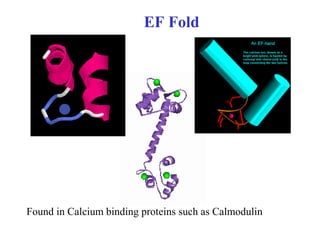
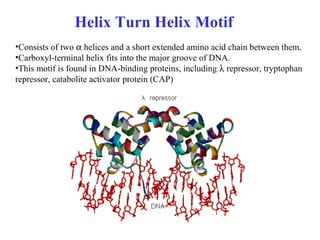
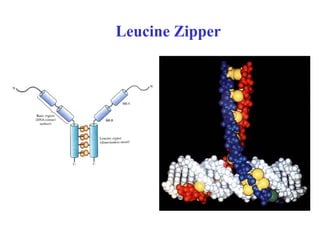
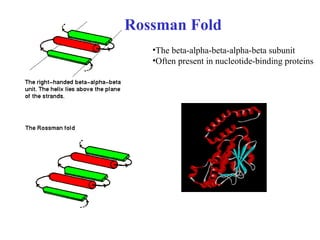
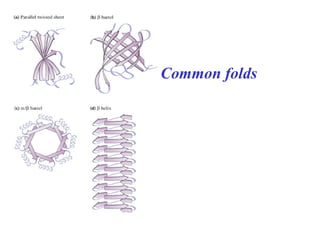
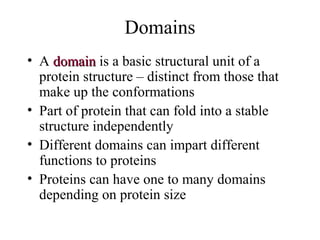
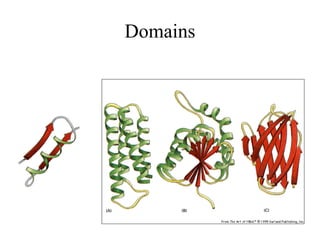
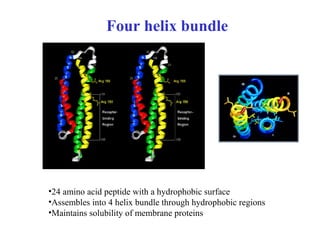
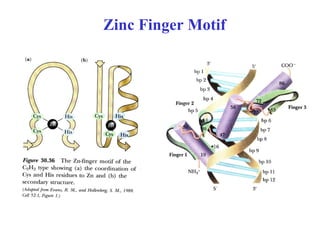
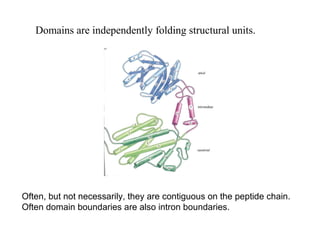
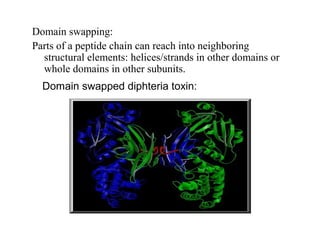
- Supersecondary structure refers to recurrent structural motifs formed by combinations of secondary structure elements, like beta-alpha-beta motifs or helix-loop-helix motifs. Larger domains





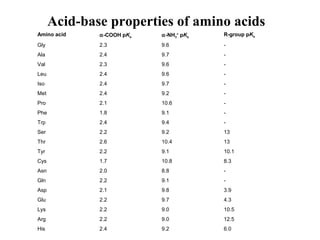
![Acid-base properties of amino acids
K1=
Gly+
+ H2O Gly0
+ H3O+
[Gly0
][H3O+
]
[Gly+
]
Gly0
+ H2O Gly-
+ H3O+
K2=
[Gly-
][H3O+
]
[Gly0
]
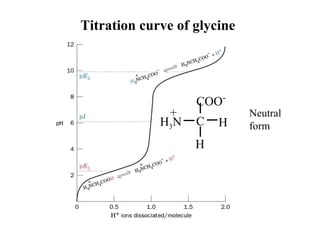
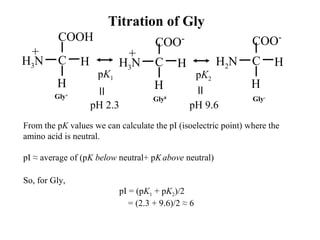
The dissociation of first proton
from the α-carboxyl group is
The dissociation of the second
proton from the α-amino group
The pKa’s of these two groups are far enough apart that they can be
approximated by Henderson-Hasselbalch
pK1 + logpH =
[Gly0
]
[Gly+
]
pK2 + logpH =
[Gly-
]
[Gly0
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/principlesofproteinstructure-160305212444/85/Principles-of-Protein-Structure-13-320.jpg)