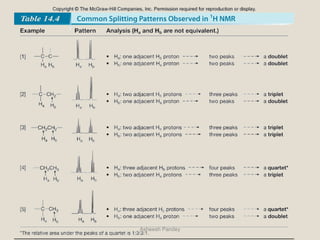
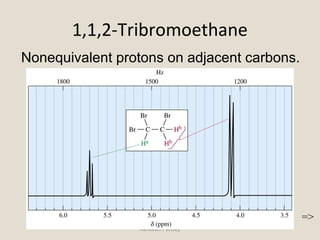
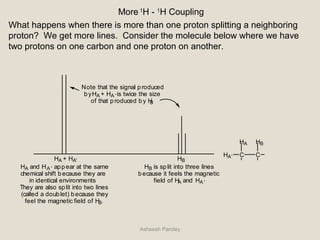
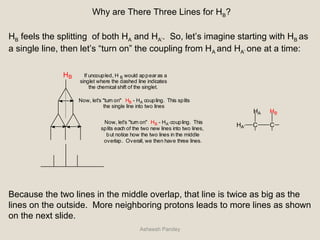
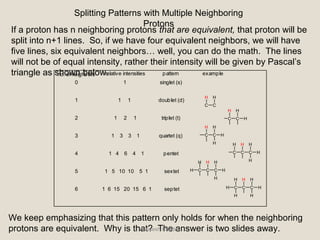
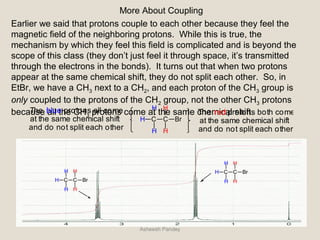
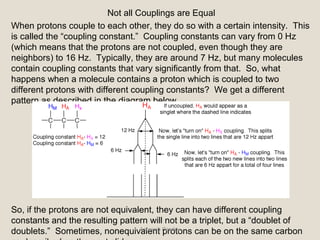
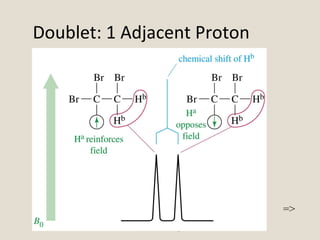
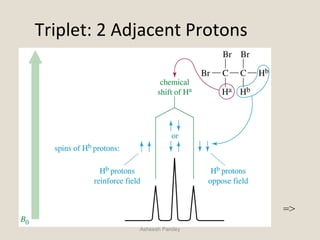
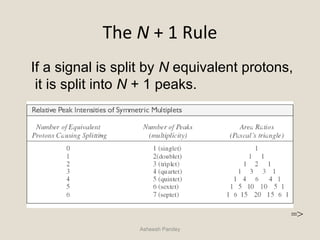
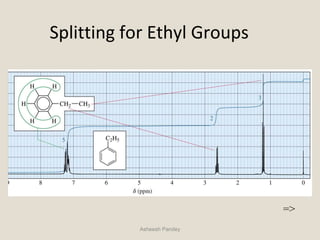
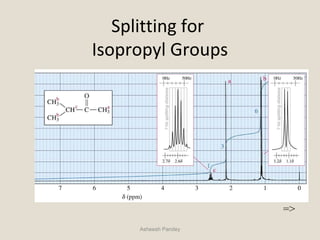
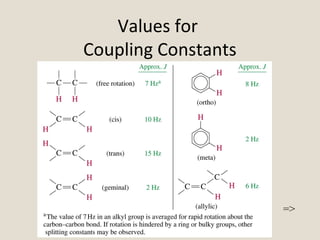
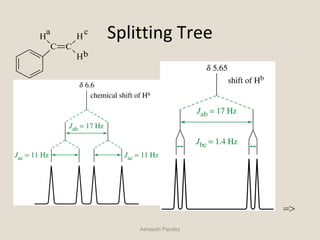
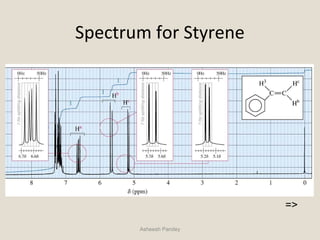
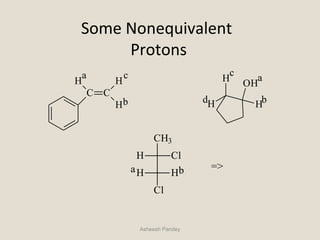
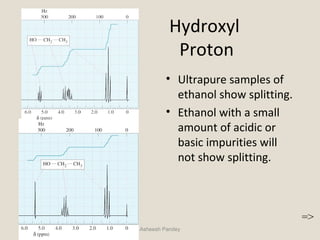
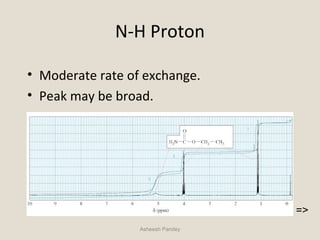
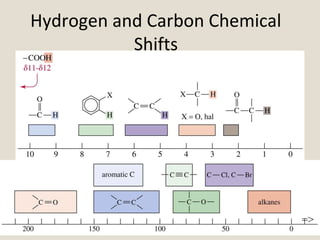
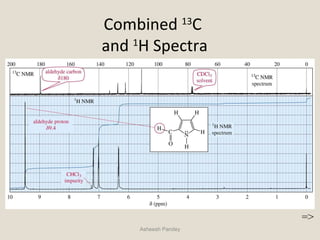
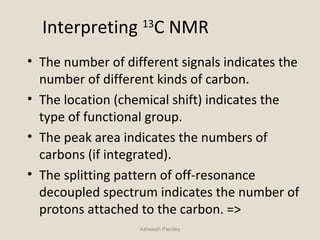
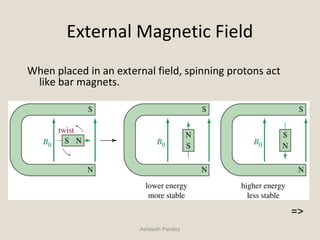
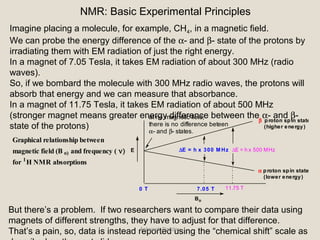
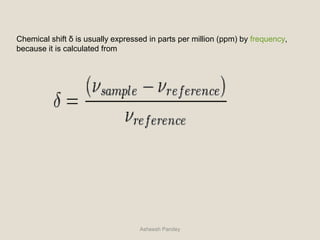
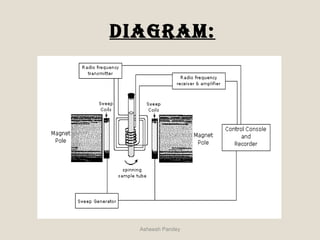
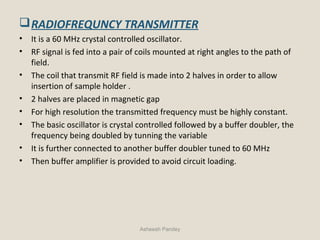
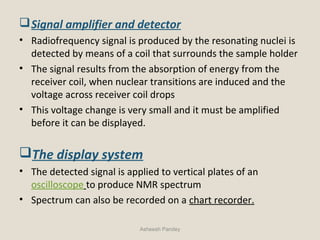
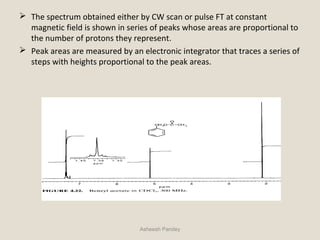
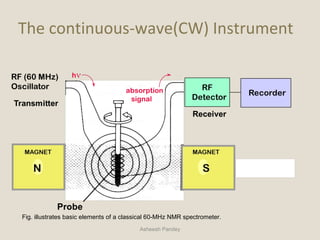
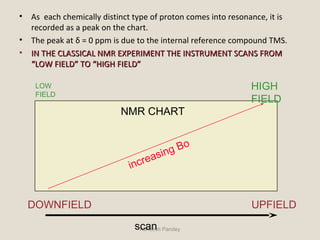
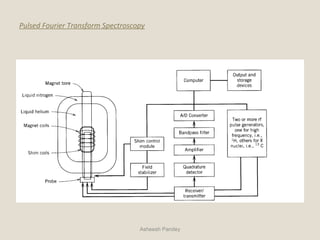
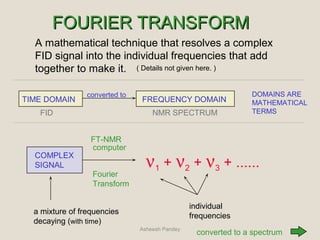
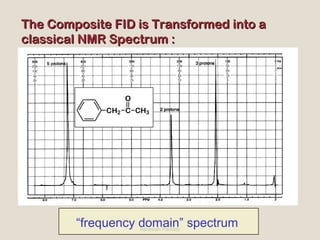
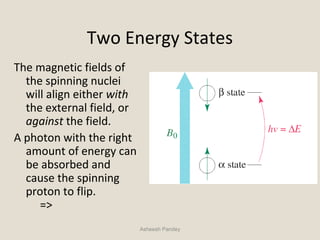
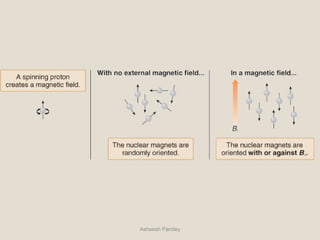
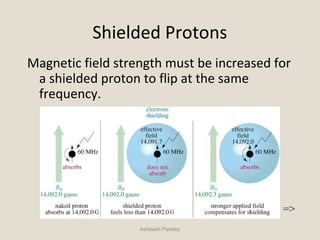
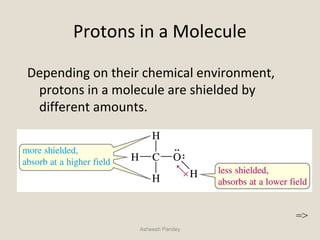
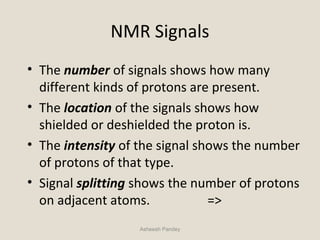
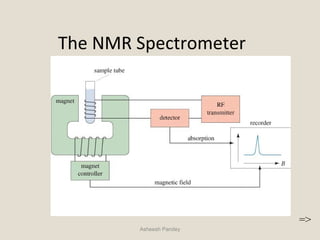
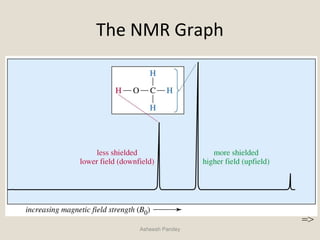
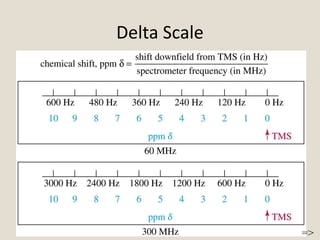
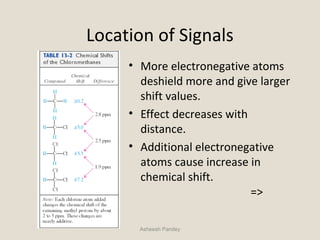
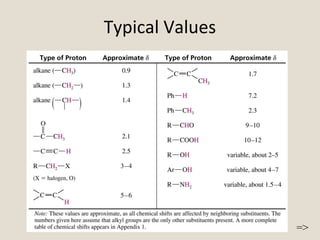
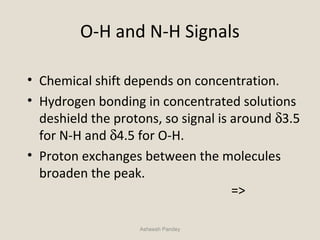
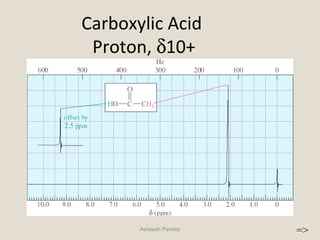
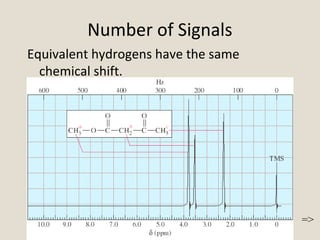
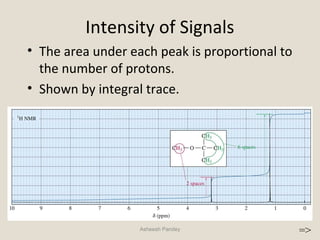
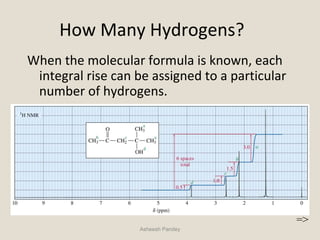
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR) is a technique used to analyze organic molecules. Certain nuclei, such as 1H and 13C, have nuclear spin and behave like tiny magnets when placed in an external magnetic field. NMR spectroscopy detects the absorption of radiofrequency energy by these nuclei as they transition between spin states. The frequency of absorption depends on the shielding of the nucleus by its chemical environment. NMR spectra provide information about a molecule's structure by revealing the number and types of nuclei present and their connectivity.



















![Calculating SHIFT VALUES:
Added Chemical Shifts
Substituent Type of Hydrogen -Shift -Shift
C C CH3 0.78 ---
CH2 0.75 -0.10
CH --- ---
RC C C
Y
[Y = C or O] CH3 1.08 ---
Aryl- CH3 1.40 0.35
CH2 1.45 0.53
CH 1.33 ---
Cl- CH3 2.43 0.63
CH2 2.30 0.53
CH 2.55 0.03
Br- CH3 1.80 0.83
CH2 2.18 0.60
CH 2.68 0.25
I- CH3 1.28 1.23
CH2 1.95 0.58
CH 2.75 0.00
OH- CH3 2.50 0.33
CH2 2.30 0.13
CH 2.20 ---
RO- (R is saturated) CH3 2.43 0.33
CH2 2.35 0.15
CH 2.00 ---
R–CO
O
or ArO CH3 2.88 0.38
CH2 2.98 0.43
CH 3.43 ---
(ester only)
R–C
O
CH3 1.23 0.18
where R is alkyl, aryl, OH, CH2 1.05 0.31
OR', H, CO, or N CH 1.05 ---
Asheesh Pandey
(Hydrogen under consideration)C C H
H
H
H
H
Cl
β α
Base Chemical Shift = 0.87 ppm
no α substituents = 0.00
one β -Cl (CH3) = 0.63
TOTAL = 1.50 ppm
(Hydrogen under consideration)C C H
H
H
H
H
Cl
βα
Base Chemical Shift = 1.20 ppm
one α -Cl (CH2) = 2.30
no β substituents = 0.00
TOTAL = 3.50 ppm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nmrbyasheeshpandey-160305220458/85/NMR-by-asheesh-pandey-49-320.jpg)