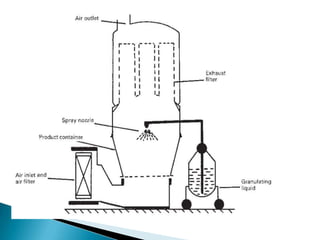
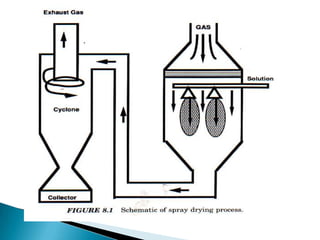
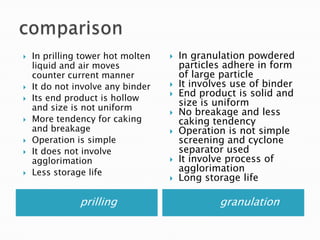
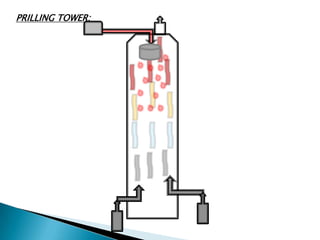
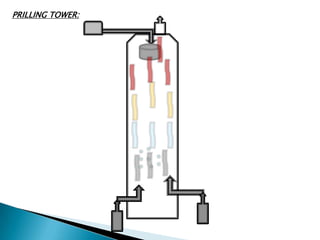
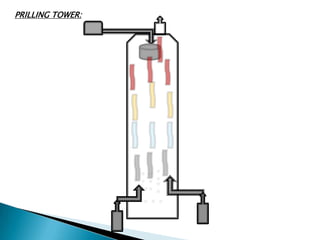
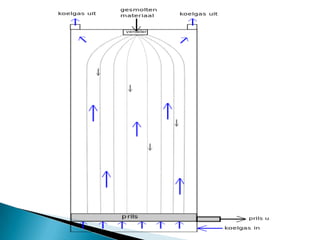
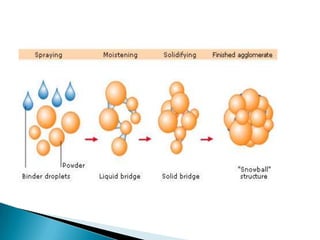
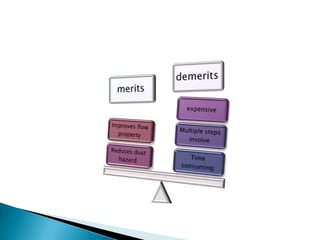
This document discusses prilling and granulation processes. Prilling involves spraying molten material into a prilling tower where it solidifies into spherical prills due to contact with upward air flow. Granulation converts fine particles into stronger, larger agglomerates using compression or a binding agent. The key difference is that prilling does not use a binder, produces hollow prills of varying sizes with more breakage, while granulation uses a binder to form solid, uniform size particles with less breakage and longer storage life. Granulation is commonly used in pharmaceuticals while prilling is used in fertilizer and explosive manufacturing.


























![
In this type of equipment, the particles
are set into movement by an impeller
rotating at a high speed (Approx 50100 rpm). Equipment also contains a
chopper which
rotates at around 1500 – 4000 rpm [10]. The
primary function of chopper is to cut large
lumps
into smaller fragments thus increases the
binder distribution into the blend.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-140112094513-phpapp02/85/prilling-tower-and-granulation-35-320.jpg)