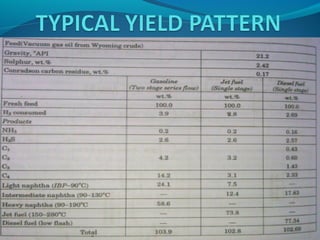
This document discusses catalytic reforming and hydrocracking processes. It provides details on:
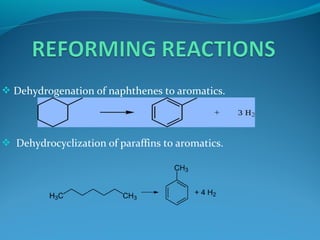
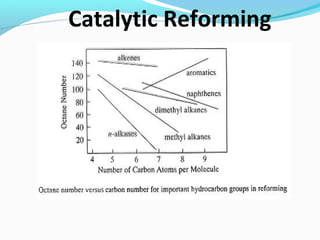
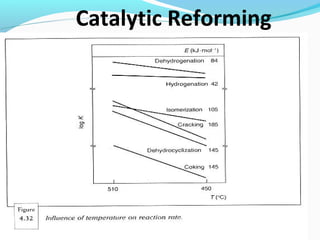
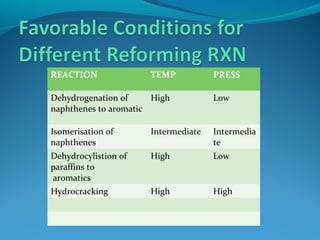
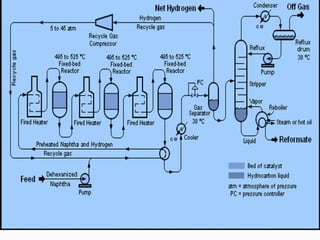
- Catalytic reforming converts low octane naphtha into high octane reformates through reactions like dehydrogenation and dehydrocyclization.
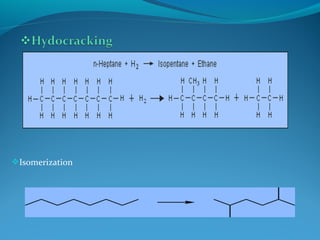
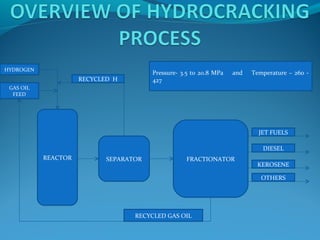
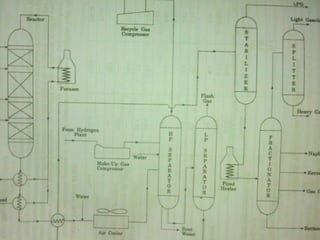
- Hydrocracking breaks down heavier hydrocarbon molecules into simpler molecules like gasoline and kerosene using hydrogen and catalysts at high pressures.
- Both processes upgrade petroleum fractions through chemical reactions like cracking, isomerization and hydrogenation to produce more valuable products like gasoline and jet fuel.