The document summarizes three processes for producing phosphoric acid:
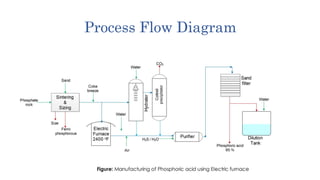
1) Direct conversion at plant sites which uses electric furnaces to reduce phosphate rock with coke and produce elemental phosphorus and carbon monoxide, then oxidizes and hydrates it to form phosphoric acid.
2) Oxidation and hydration of elemental phosphorus which produces phosphorus pentoxide by oxidizing phosphorus with air, then hydrates it to form phosphoric acid.
3) Blast furnace process which uses a blast furnace to reduce phosphate rock and coke to produce calcium silicate slag and phosphorus pentoxide gas, then condenses the gas to form phosphoric acid.












![Phosphoric acid [CHEMICAL PROCESSS INDUSTRIES]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phosphoricacid-210509141123/85/Phosphoric-acid-CHEMICAL-PROCESSS-INDUSTRIES-15-320.jpg)