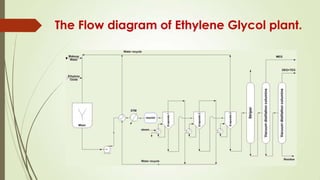
This document describes a study for the production of ethylene glycol through the hydrolysis of ethylene oxide with water. It discusses the significance of ethylene glycol and its uses in various industries such as antifreeze and polyester fibers. The most common manufacturing method is described as the hydrolysis of ethylene oxide through a ring-opening reaction. A flow diagram shows the process which involves hydrating ethylene oxide in a reactor, evaporating the water-glycol mixture in multiple stages, stripping remaining water and purifying through distillation. The study aims to design a process capable of producing 100,000 tons per year of ethylene glycol.