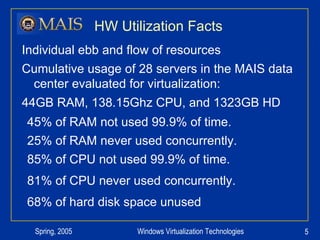
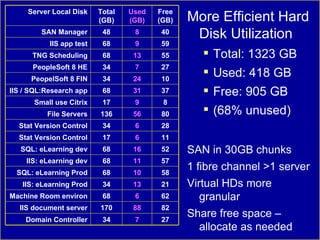
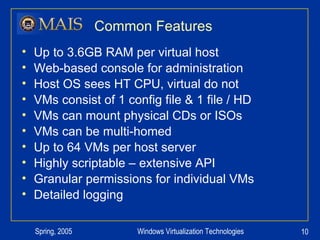
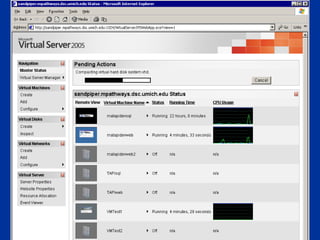
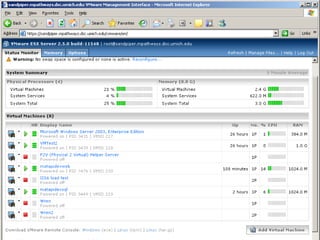
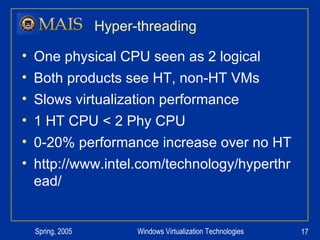
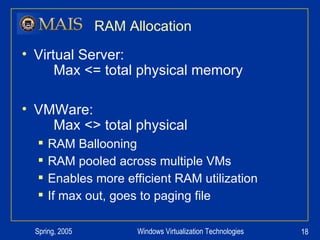
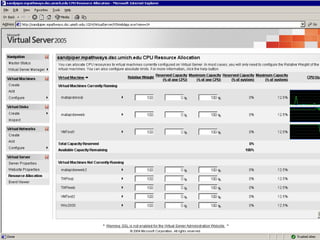
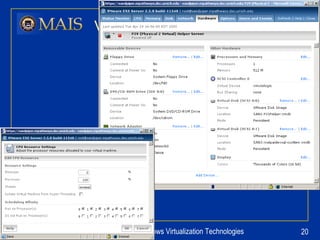
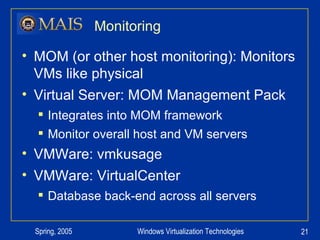
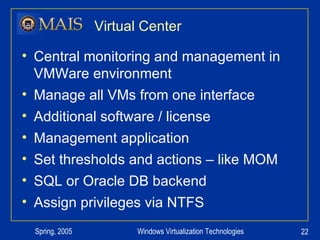
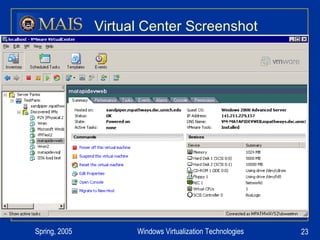
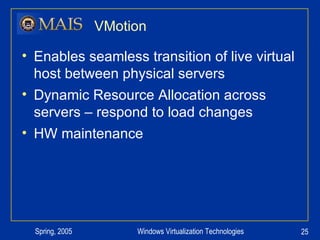
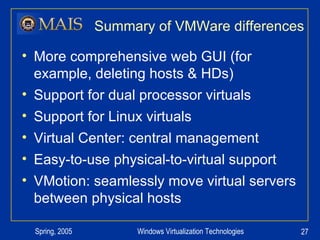
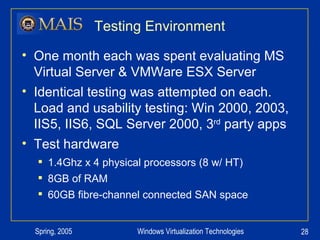
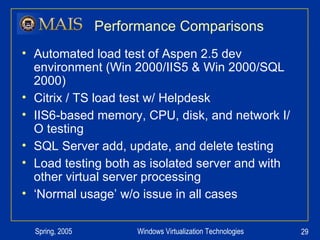
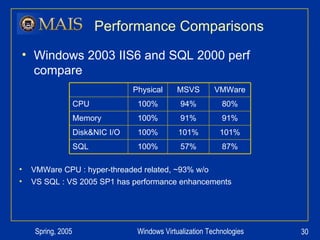
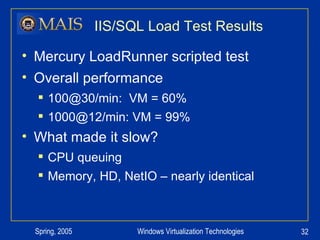
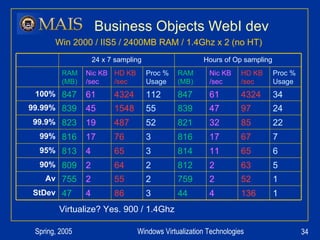
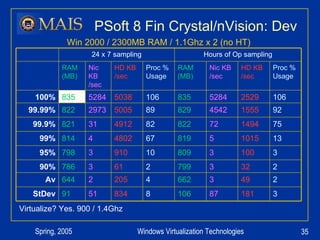
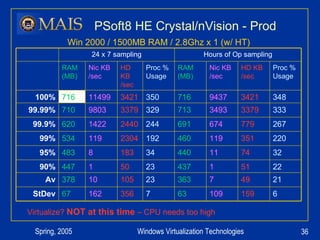
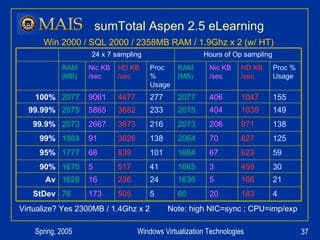
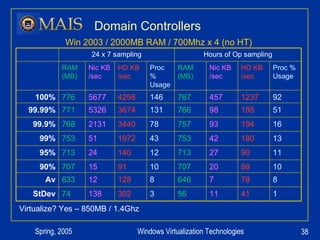
The document compares server virtualization technologies Microsoft Virtual Server 2005 and VMWare ESX Server. It finds that both products provide comparable performance, with VMWare offering more isolation between virtual machines and features like VMotion. While VMWare costs more initially, it may provide better long-term cost savings through increased hardware utilization and flexibility in allocating resources. Testing at various universities found virtualization improved reliability, response to changing needs, and reduced costs.
![Server Virtualization Technologies: Uses, Comparisons, and Implications David Sweetman Windows Enterprise Systems Admin Administrative Information Services University of Michigan [email_address] University of Michigan Administrative Information Services](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prezentcit1901/75/prezentaciot-1-2048.jpg)



















![David Sweetman University of Michigan [email_address] Questions?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prezentcit1901/85/prezentaciot-46-320.jpg)