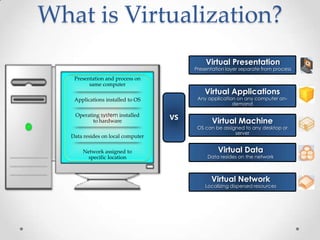
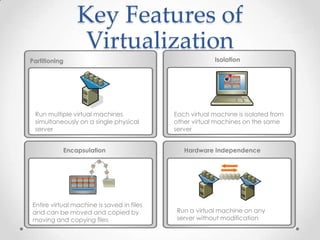
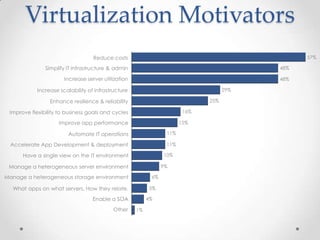
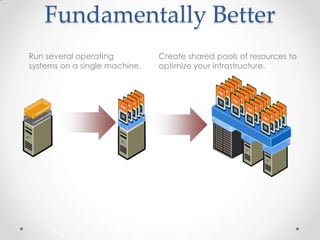
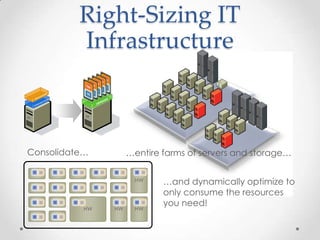
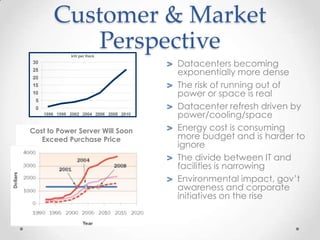
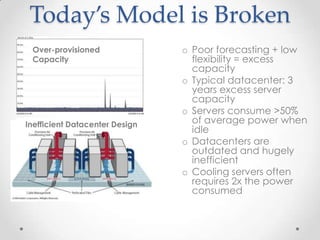
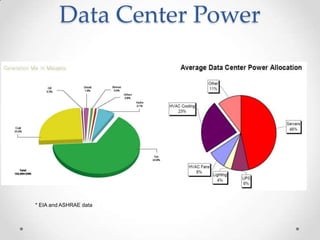
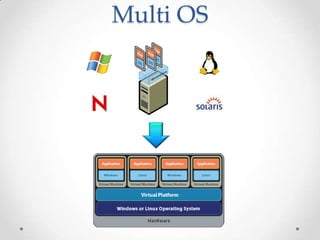
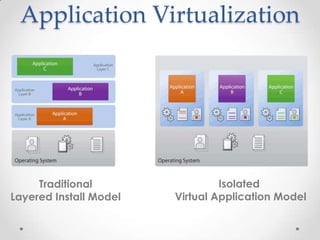
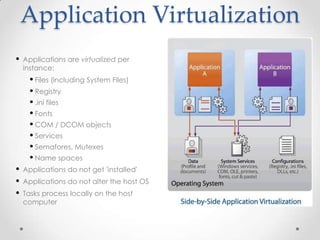
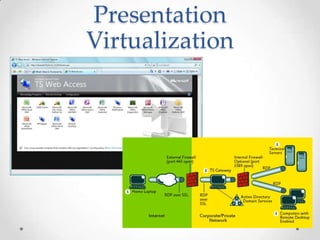
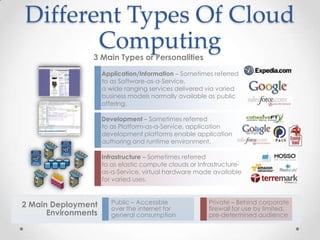
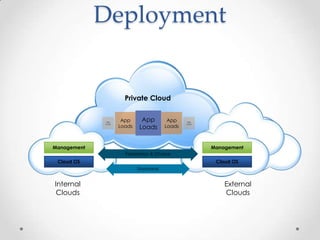
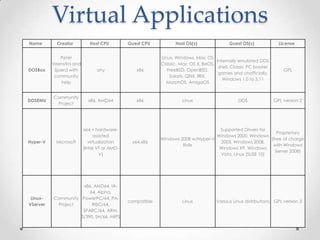
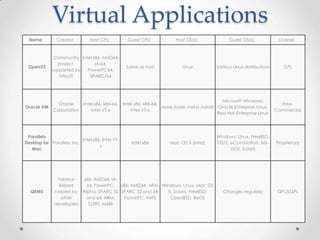
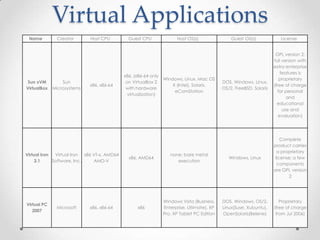
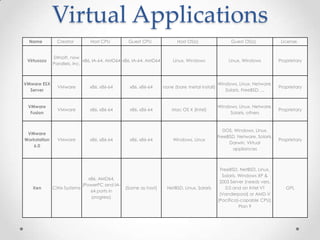
Virtualization allows multiple operating systems to run on a single physical machine by abstracting the physical hardware and presenting virtual hardware instead. This allows for greater flexibility, efficiency, and cost savings by consolidating servers. There are different types of virtualization including server, desktop, application, and presentation virtualization. Server virtualization allows multiple virtual machines to run isolated operating systems on a single physical server. Cloud computing takes virtualization further by providing on-demand access to computing resources over the internet.