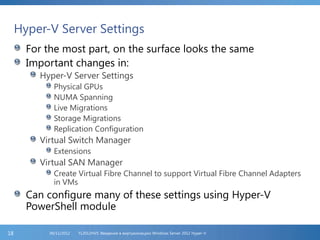
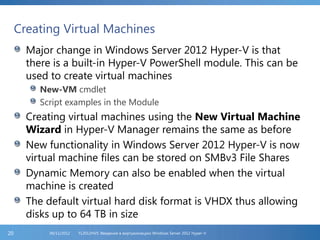
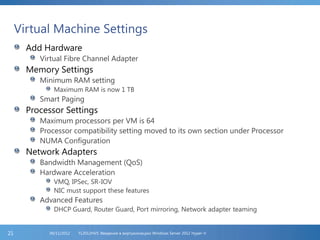
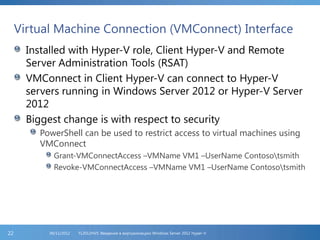
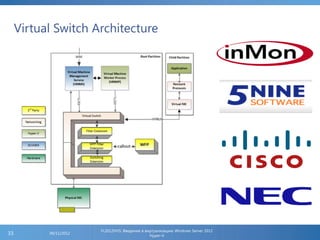
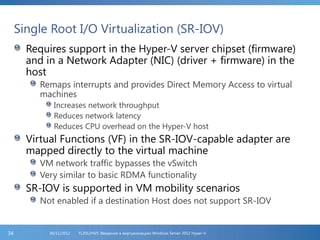
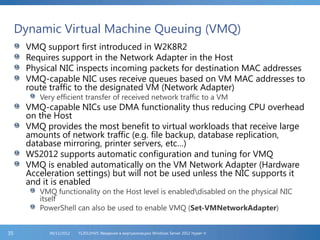
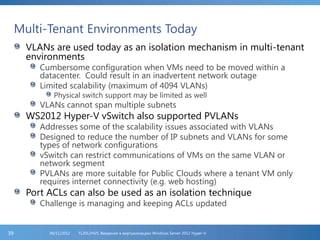
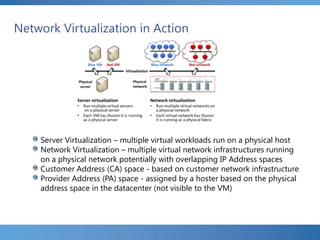
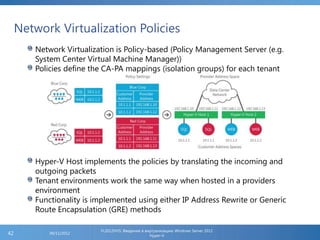
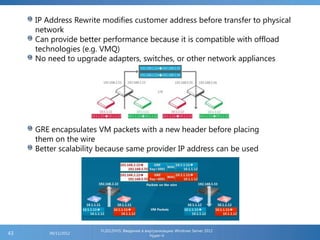
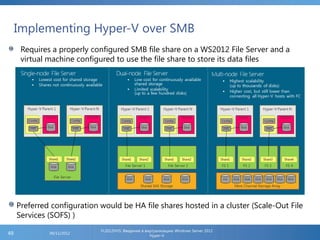
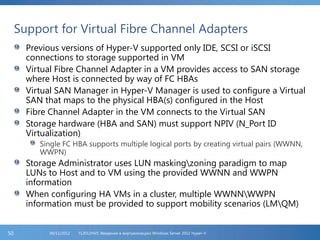
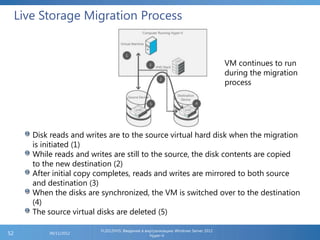
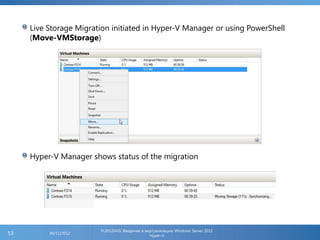
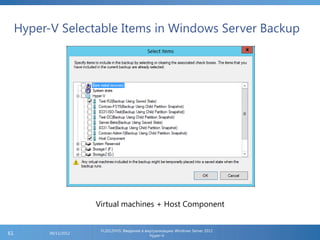
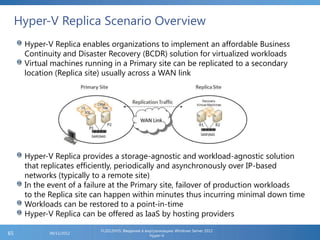
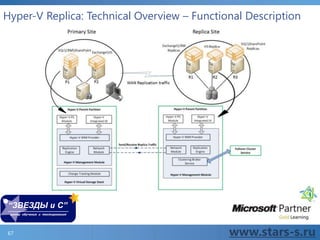
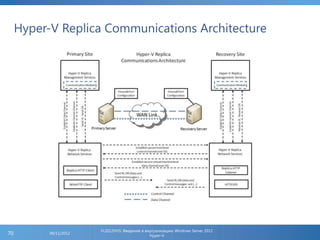
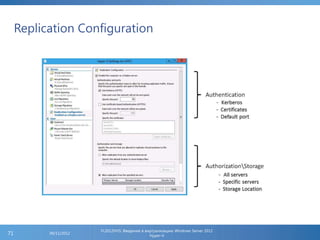
The document provides an extensive overview of Hyper-V virtualization technology in Windows Server 2012, detailing its capabilities for virtualizing hardware to run multiple operating systems simultaneously. Key features covered include dynamic memory management, enhanced networking capabilities, storage options with the new VHDX format, and improved migration methods. Additionally, it emphasizes management tools, automation through PowerShell, and security measures essential for effectively utilizing Hyper-V in enterprise environments.