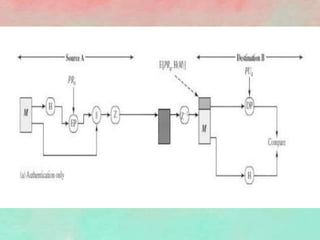
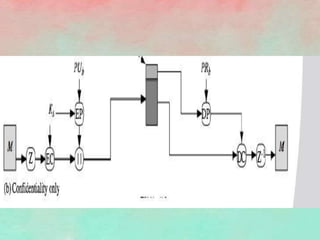
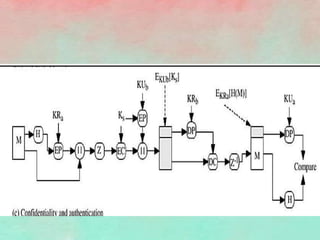
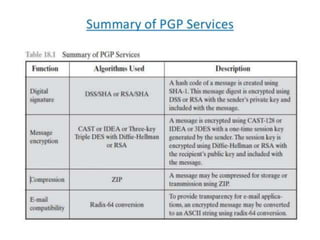
PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) is an open source encryption software that provides security mechanisms like authentication, confidentiality, compression, and email compatibility. It uses strong cryptographic algorithms like IDEA, RSA, and SHA-1. PGP protects messages by signing them with the sender's private key, encrypting them with a random symmetric key, and encrypting that key with the recipient's public key. This ensures message integrity and confidentiality. Compression is applied before encryption to save space. Radix-64 encoding allows encrypted messages to be transmitted over email. PGP's features help secure email communications and stored files from unauthorized access.