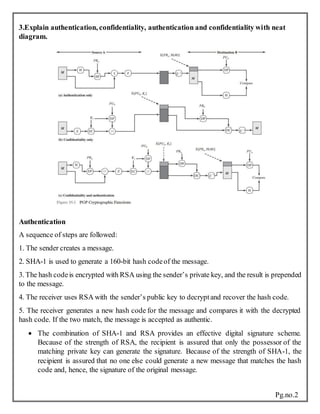
PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) provides confidentiality and authentication services for email and file storage. It uses algorithms like RSA, IDEA, and SHA-1. PGP grew due to being free, secure, widely applicable, and not controlled by any organization. It provides services like encryption, digital signatures, compression, and encoding messages into a format compatible with email. When sending a PGP message, it is signed, compressed, encrypted if needed, and encoded. The recipient decodes, decrypts if needed, decompresses, and verifies the signature. S/MIME is similar to PGP and provides encryption and digital signatures for email. [/SUMMARY]