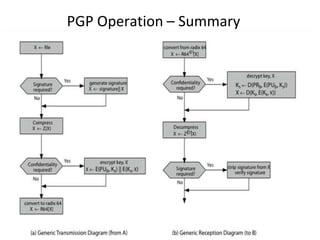
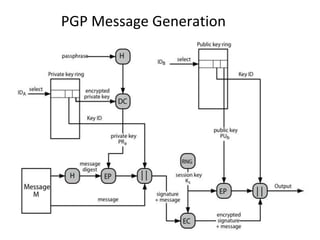
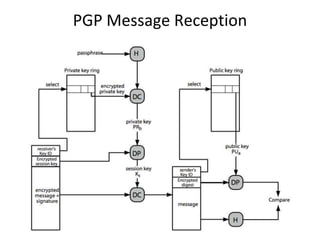
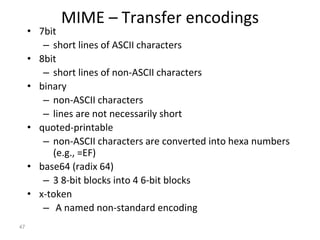
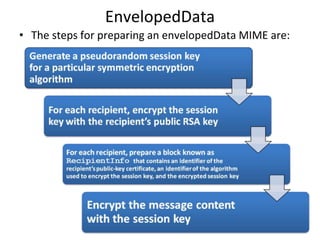
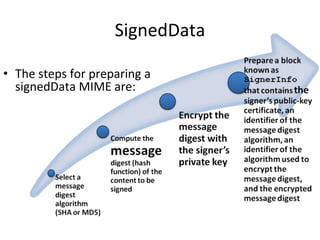
The document discusses electronic mail security and Pretty Good Privacy (PGP). PGP provides encryption, authentication, integrity, and non-repudiation for email. It uses public/private key cryptography and symmetric encryption. PGP signs messages with the sender's private key and encrypts messages using a randomly generated symmetric session key. The session key is then encrypted with the recipient's public key and attached to the encrypted message. Recipients can authenticate messages and decrypt them using their private key to recover the session key. PGP forms a "web of trust" through key signatures rather than relying on certificate authorities. The document also discusses S/MIME, which provides similar security to PGP for email using X.509 certificates and a hybrid