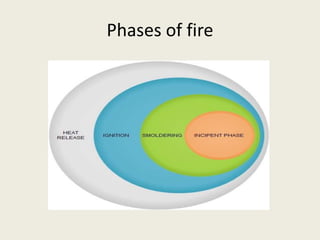
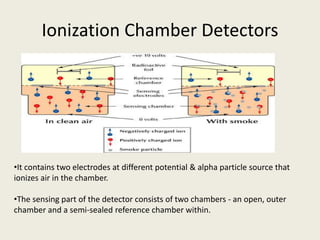
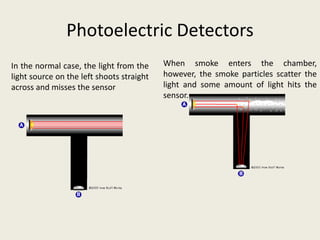
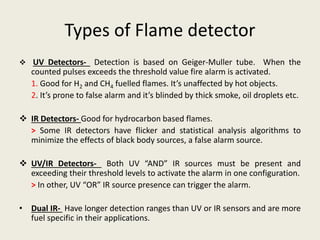
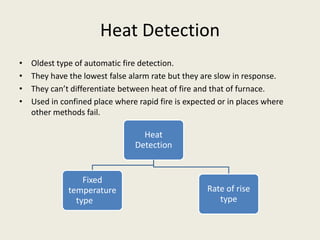
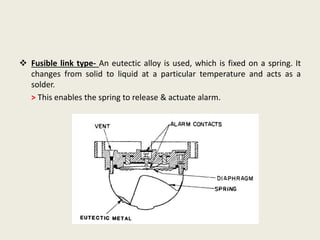
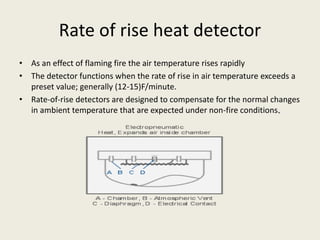
This document summarizes various methods of fire detection, including smoke, flame, and heat detection. It describes the phases of fire and how different sensor types detect fires at different phases. Smoke detectors use ionization chambers or photoelectric sensors. Flame detectors use spectral analysis to detect flickering frequencies unique to flames. Heat detectors include fixed temperature types and rate-of-rise types. Other detection methods discussed are air aspiration systems and gas sensors.