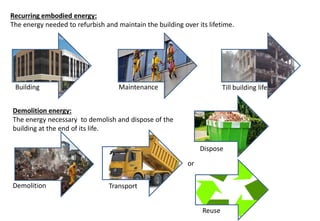
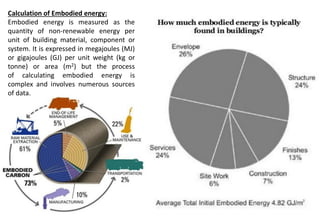
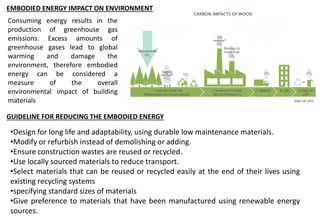
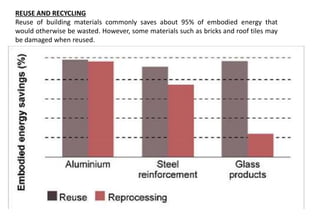
Embodied energy refers to the total energy required for the entire lifecycle of a building, from extracting and processing raw materials to manufacturing, transportation, construction, maintenance, replacement, and eventual disposal or recycling. There are three main types of embodied energy: initial embodied energy for the initial construction; recurring embodied energy for maintenance and refurbishment over the lifetime of the building; and demolition energy for dismantling and disposal at the end of the building's life. Calculating embodied energy involves determining the amount of non-renewable energy used per unit of building material or component. Reducing embodied energy helps lower the overall environmental impact of buildings through reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Strategies for lowering embodied energy include designing for longevity, reusing and