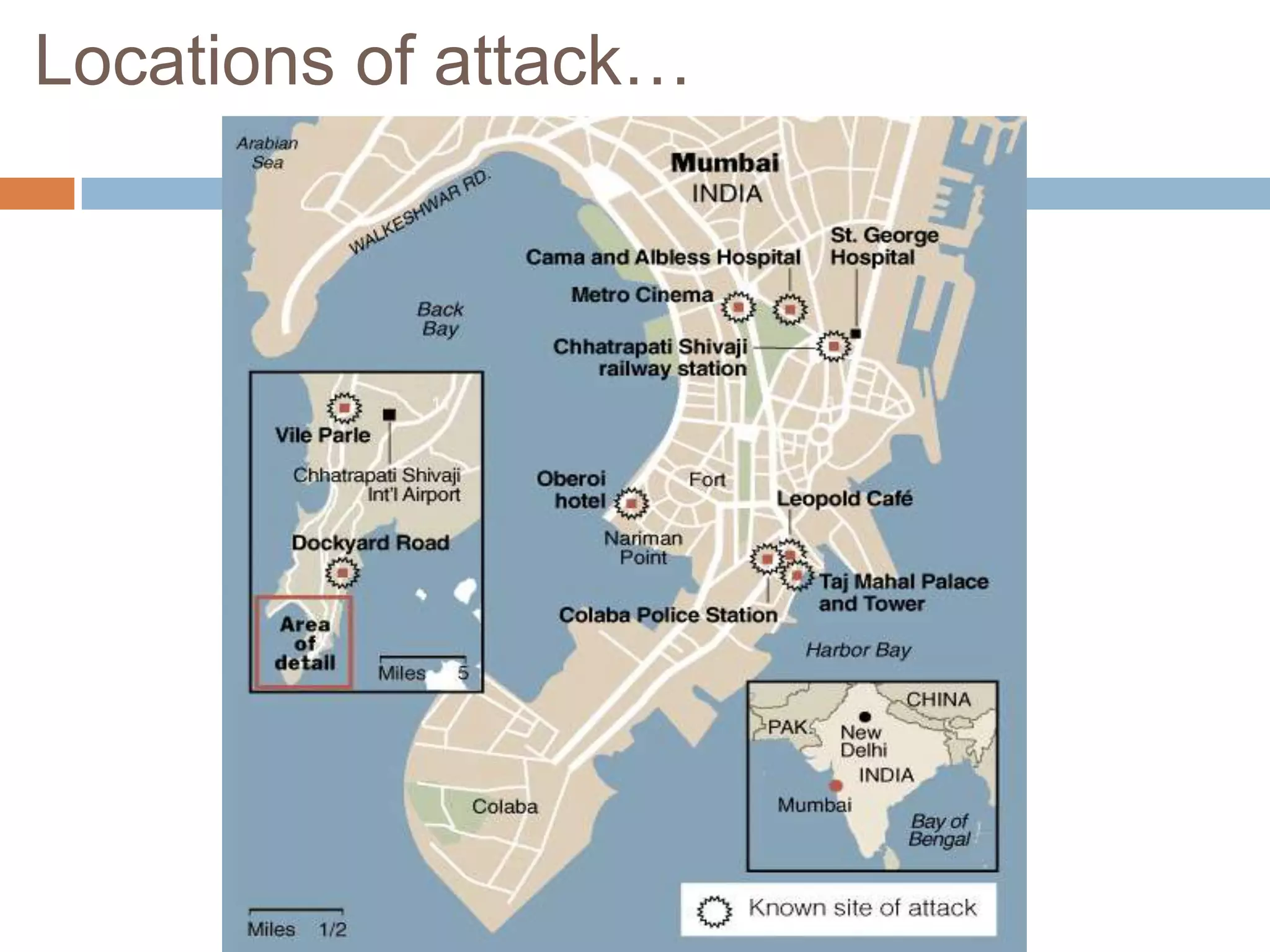
The document summarizes the 2008 Mumbai terrorist attacks where militants carried out coordinated attacks across Mumbai killing 174 people. It discusses the locations that were attacked, including hotels and train stations. It then outlines the response from governments and improvements to security and counterterrorism efforts that were implemented in India after the attacks.