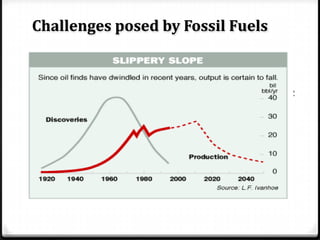
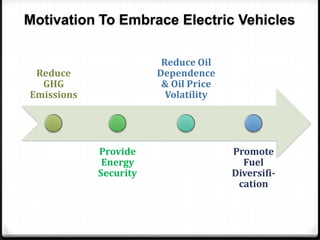
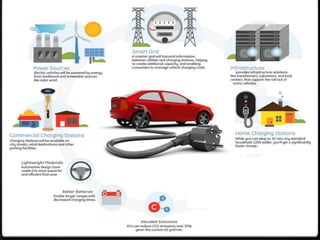
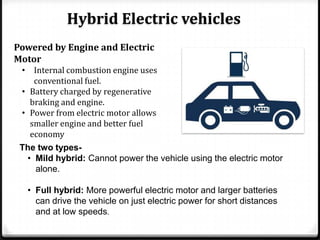
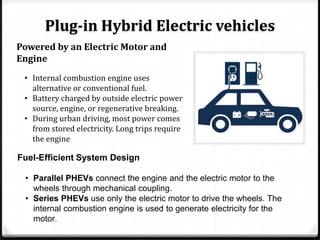
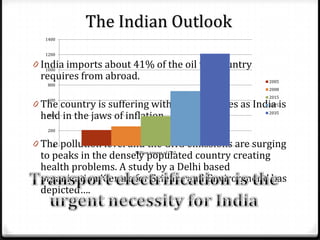
The document discusses the challenges associated with fossil fuels, including environmental degradation, rising oil prices, and the need for electric vehicles (EVs) to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and oil dependence. It outlines various types of electric and hybrid vehicles, their advantages, and the infrastructure required for electric transport systems in India. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of electrification for energy security, emission reductions, and the need for ongoing research to address the associated challenges.