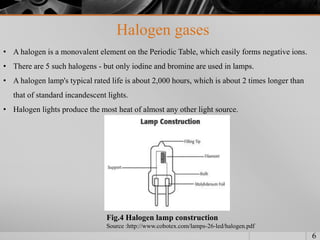
The document discusses different types of headlights used in vehicles. It describes standard incandescent headlights, sealed-beam halogen headlights, high-intensity discharge (HID) headlights using xenon gas, and LED headlights. For each type, it provides details on the light source technology, brightness levels, lifespan, advantages and disadvantages compared to other types. Halogen headlights are cheaper but less bright than HID xenon headlights. LED headlights have very high efficiency and lifespan though they are not as bright as HID currently. The document compares the key differences between the headlight types through diagrams and images.