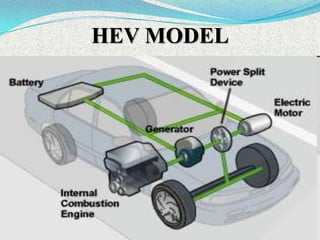
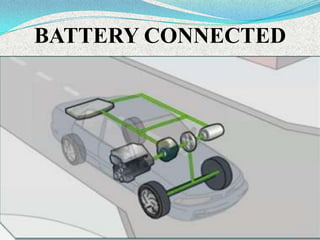
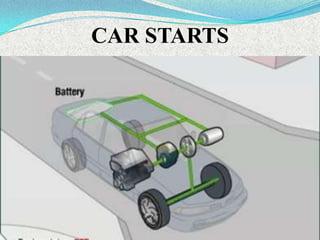
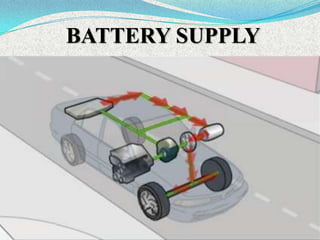
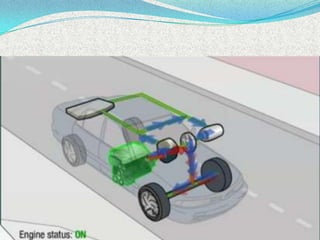
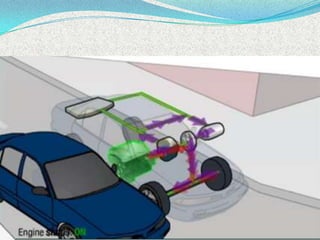
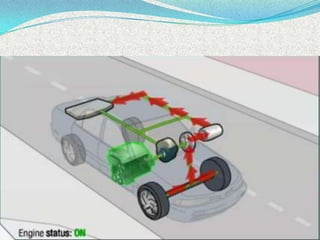
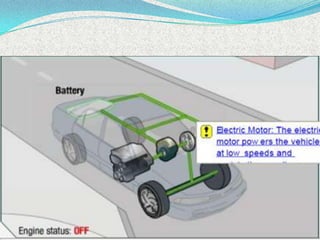
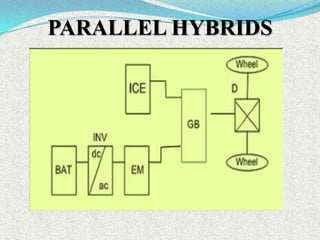
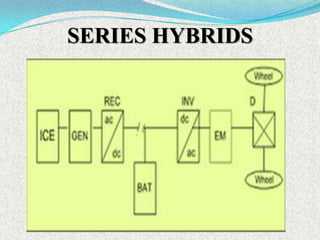
A hybrid electric vehicle combines a conventional internal combustion engine with an electric propulsion system to increase fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. HEVs can achieve twice the fuel efficiency of conventional vehicles through regenerative braking and a smaller engine size. While not zero-emissions, HEVs reduce global warming pollutants by a third to a half compared to gas-only vehicles. HEVs work by using an electric motor and batteries to supplement the gasoline engine, capturing energy through regenerative braking to recharge the batteries.