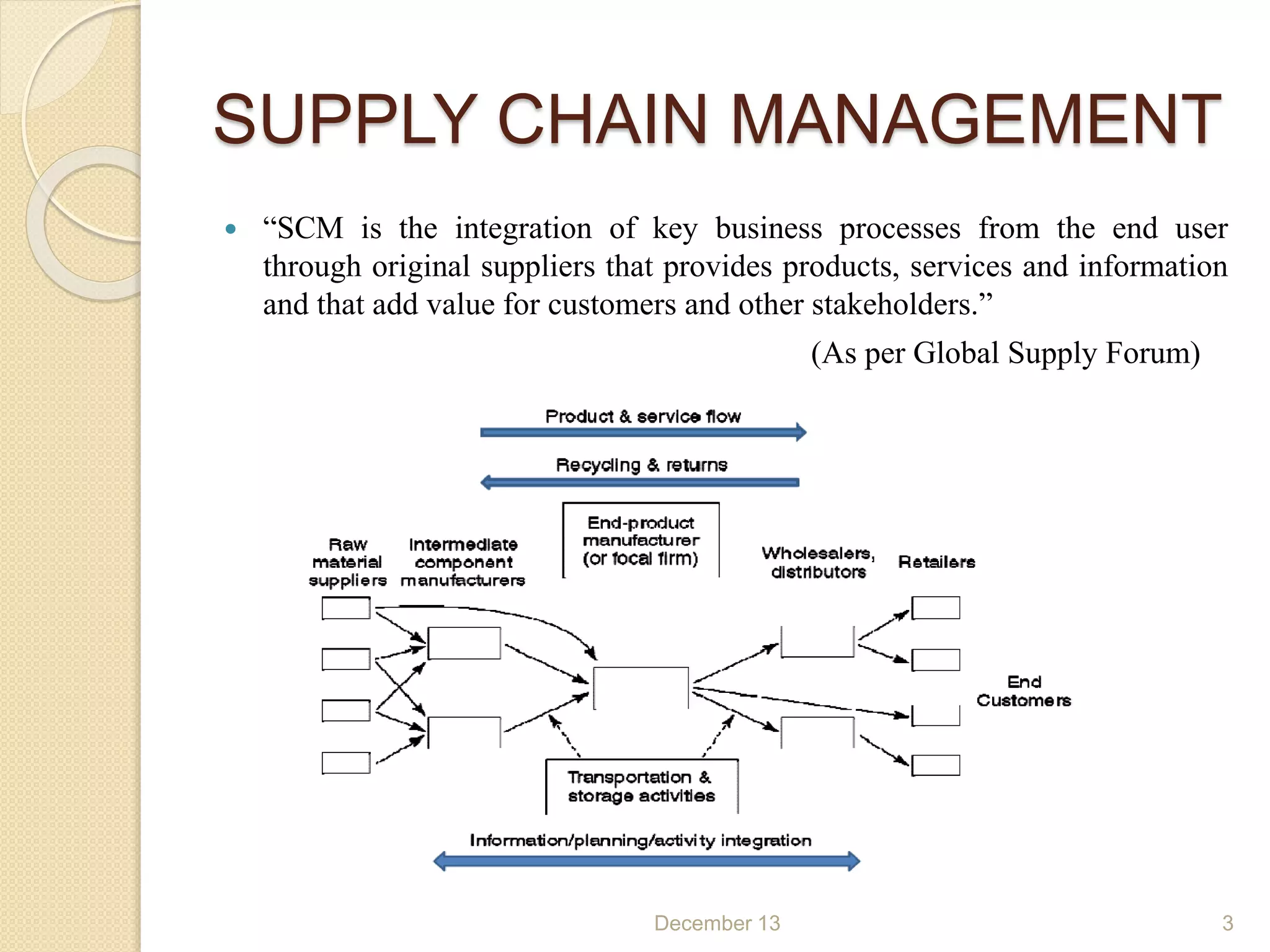
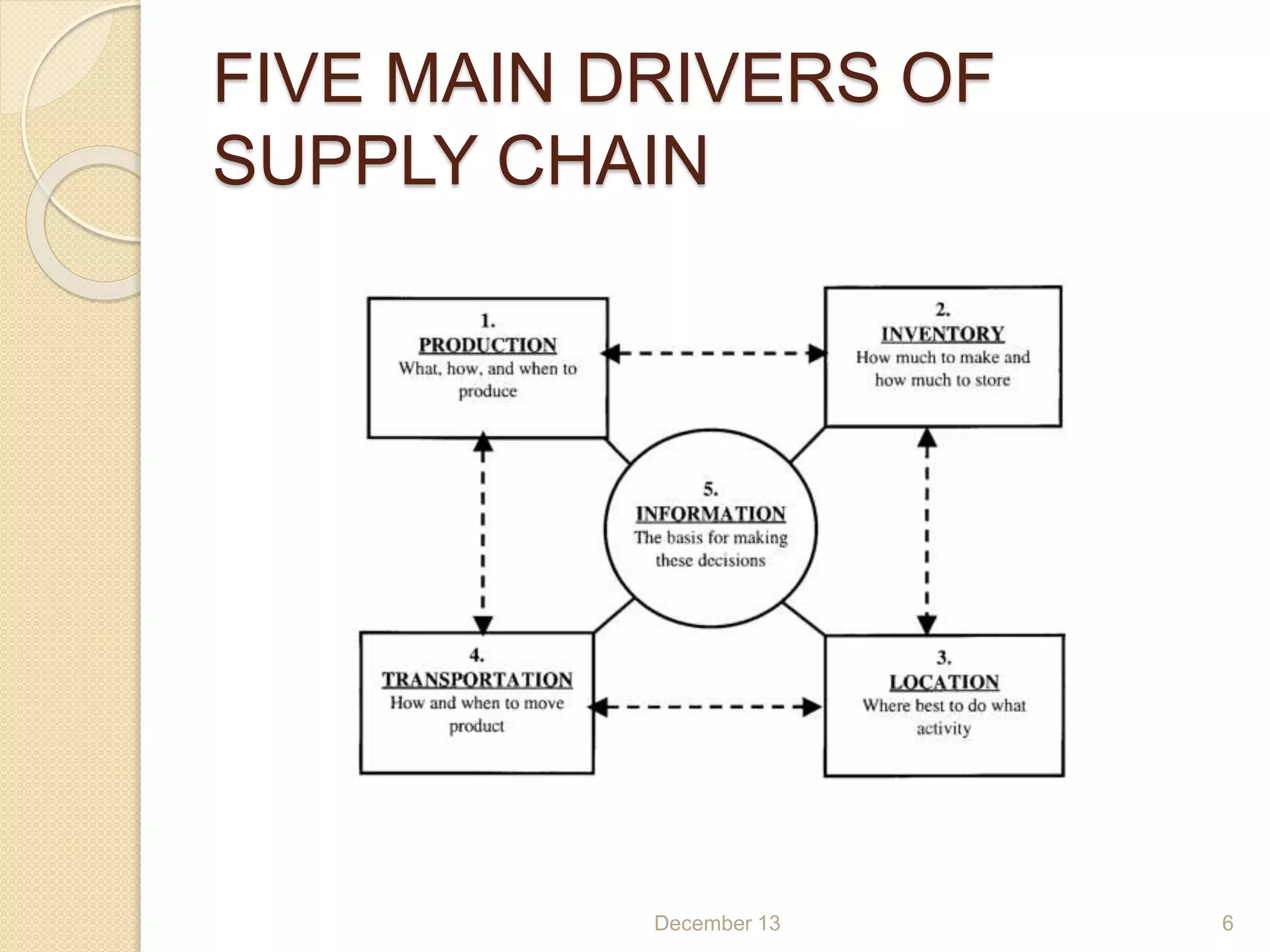
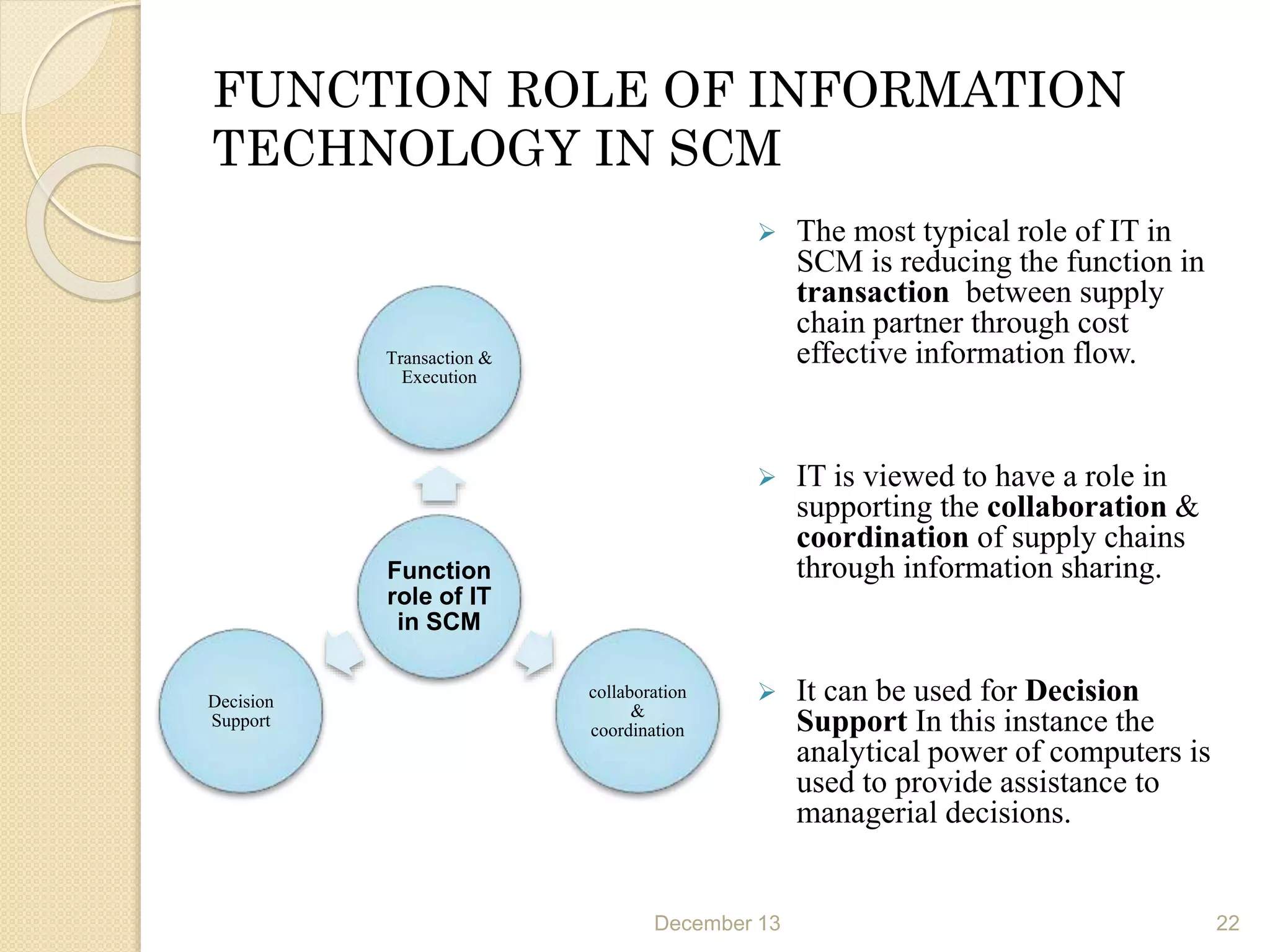
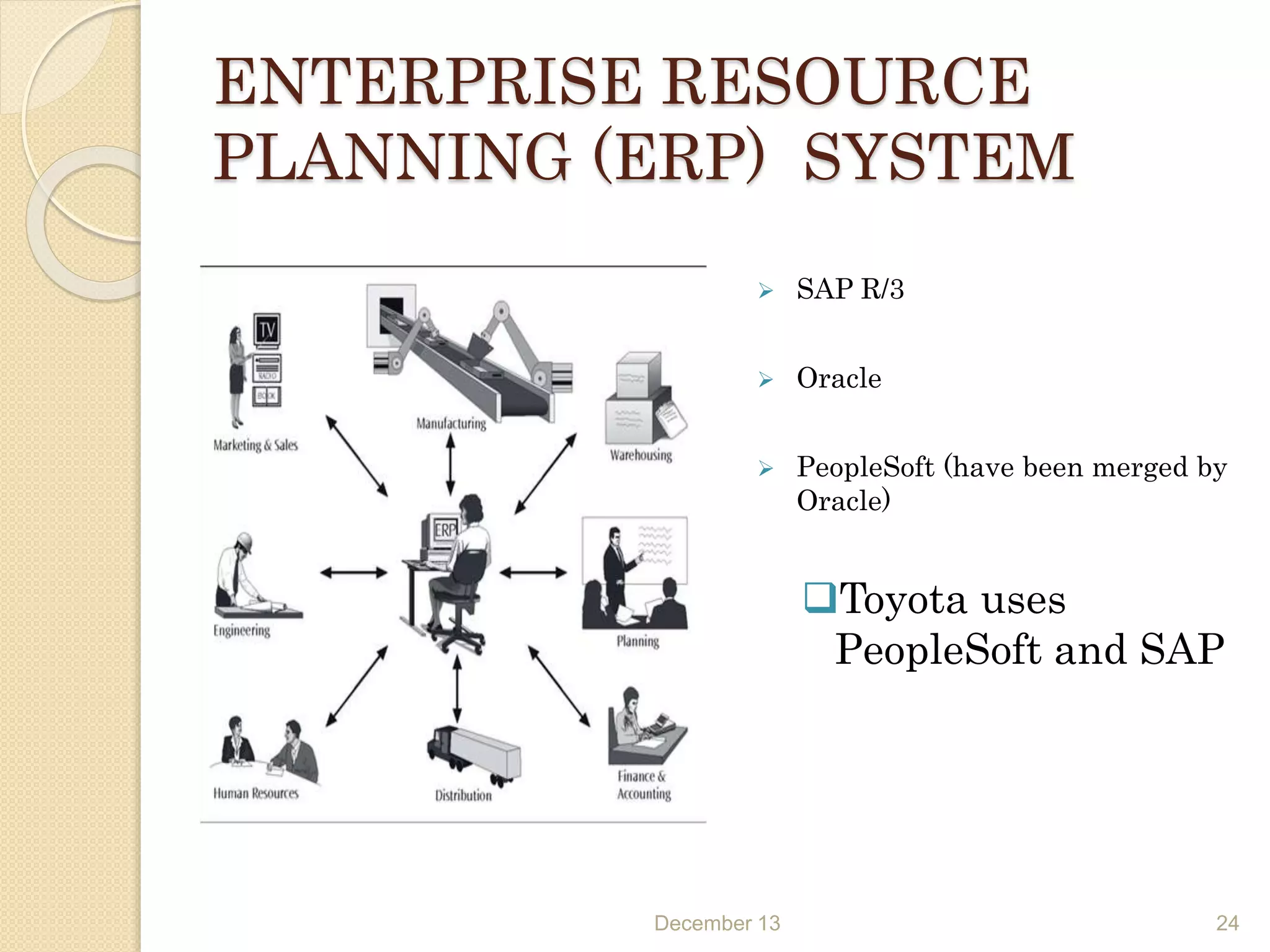
This document provides an outline for a seminar on supply chain management. It covers topics such as the definition of supply chain management, logistics, dynamics of the supply chain including the bullwhip effect, vendor managed inventory, third party logistics, outsourcing, and the role of information technology in supply chain management. Key points discussed include the necessity of SCM for industry, objectives of SCM, drivers of the supply chain, decision making factors, and benefits of approaches like VMI.