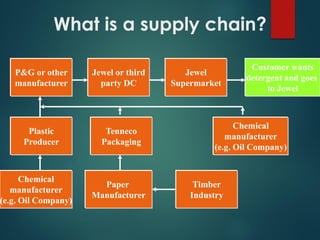
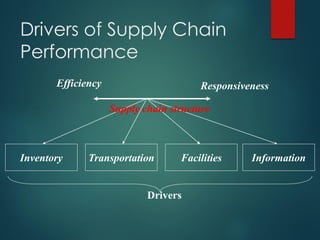
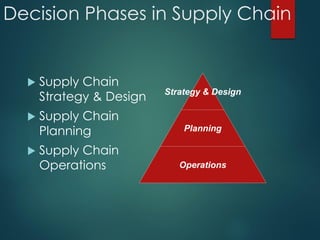
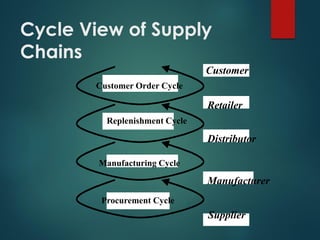
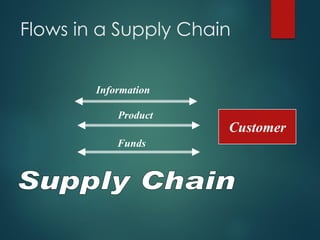
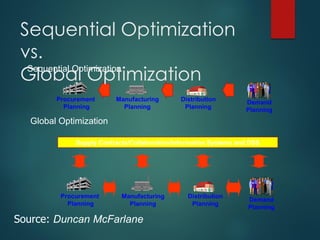
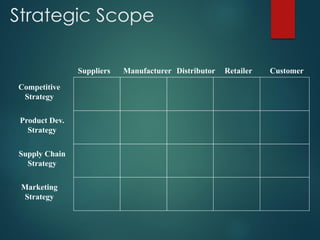
Supply chain management involves the integration of suppliers, manufacturers, warehouses, and stores to minimize costs while meeting customer demand. It aims to produce and distribute goods in the right quantities, locations, and times. Key aspects of supply chain management include supply chain planning, procurement, manufacturing, and distribution. Effective supply chain management requires cross-functional collaboration, information sharing, and managing uncertainties to achieve global optimization across the entire supply chain network.