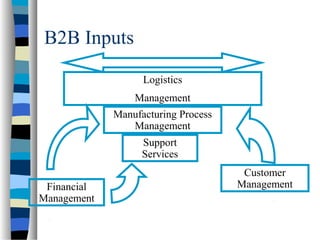
This document discusses logistics management and supply chain management. It begins with an overview of key topics like global value models, logistics management, customer relations management, and financial management. It then discusses supply chain management in more detail, explaining that SCM extends management functions outside the organization to suppliers and distribution channels. SCM can increase revenues by 4-6% and has become an industry expectation. The document also covers components of SCM like purchasing, distribution, and warehouse management. It discusses approaches to SCM, integrating functions, and software used for interfaces. The ultimate goals of SCM are customer-driven manufacturing and customization.