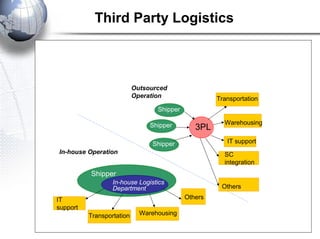
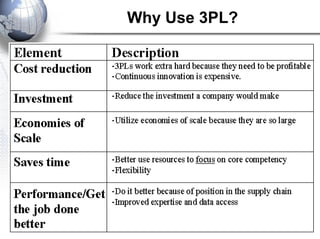
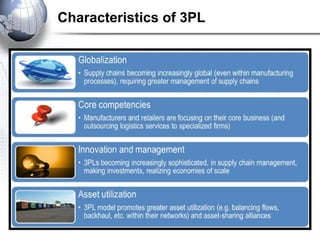
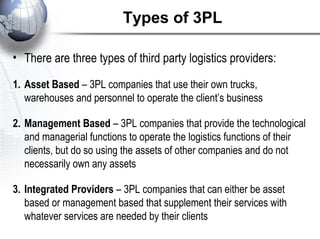
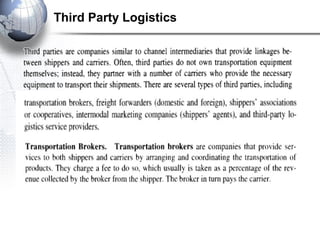
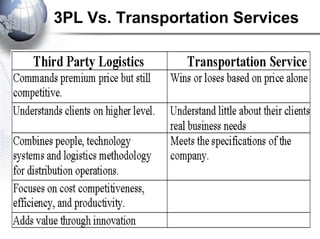
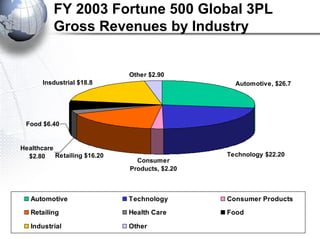
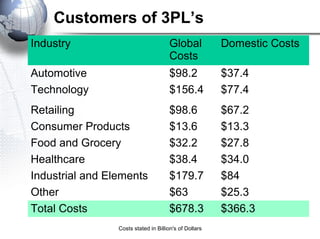
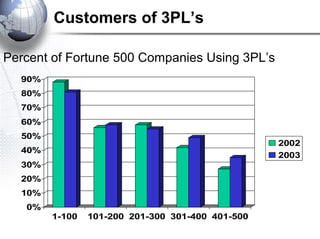
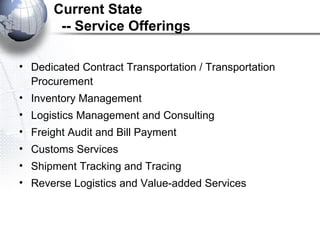
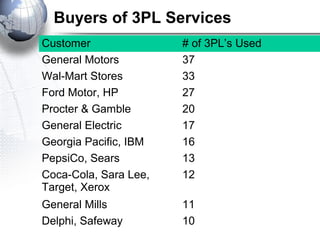
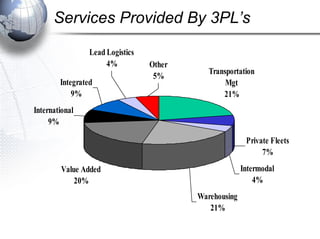
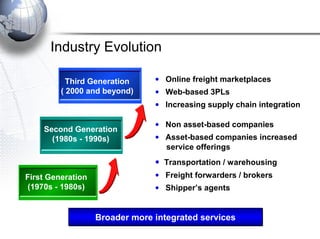
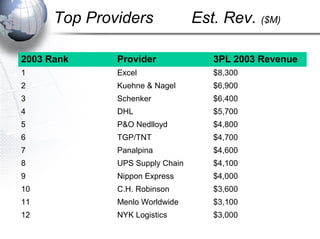
Third party logistics (3PL) involves outsourcing elements of supply chain management to a third party provider. 3PL providers can perform transportation, warehousing, distribution, and other logistics functions. Using 3PLs allows companies to focus on their core competencies while improving efficiency. There are different types of 3PL providers, including asset-based providers that use their own assets and management-based providers that coordinate using other companies' assets. Outsourcing to 3PLs has grown as companies seek to reduce costs and improve supply chain performance.