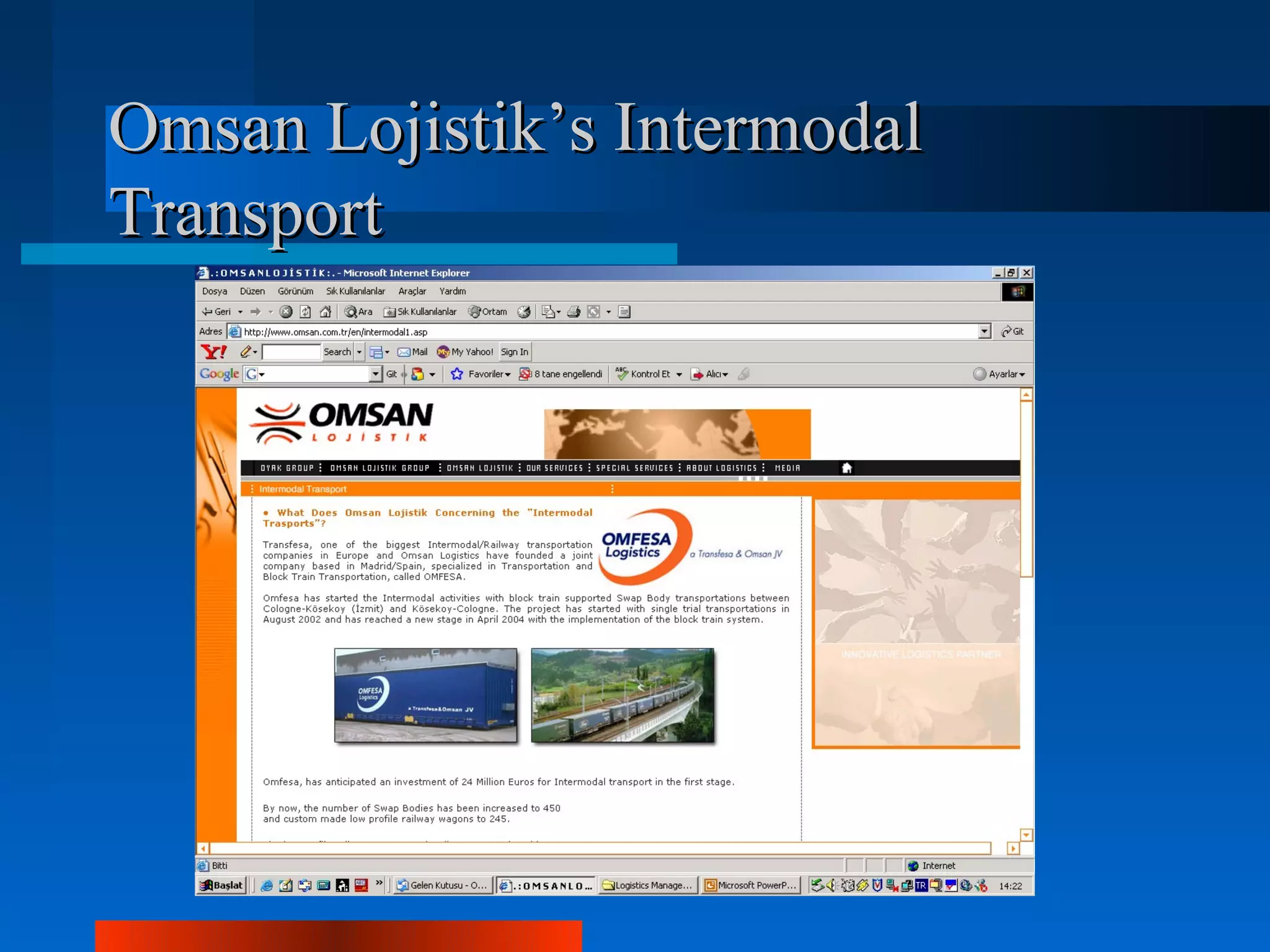
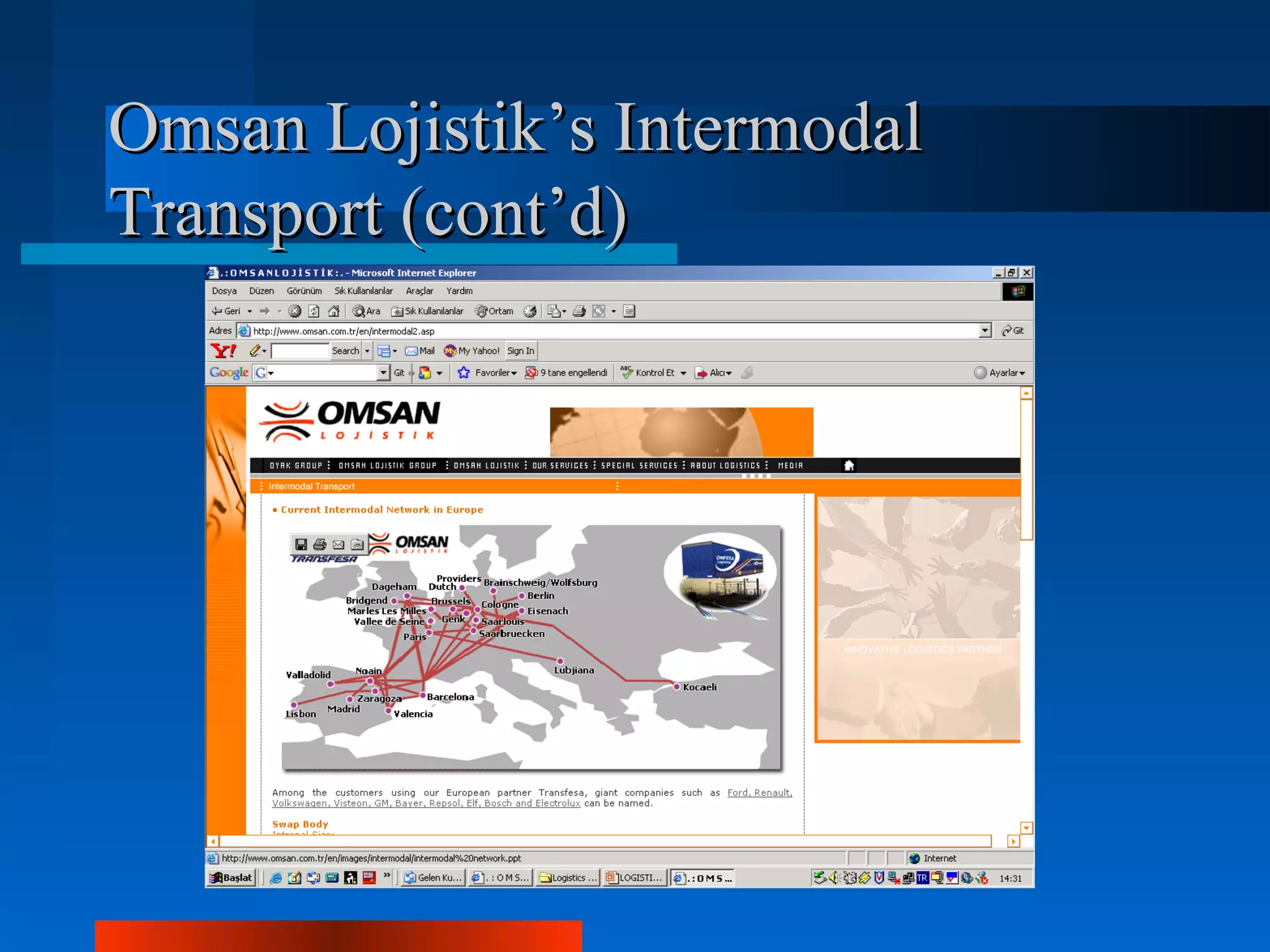
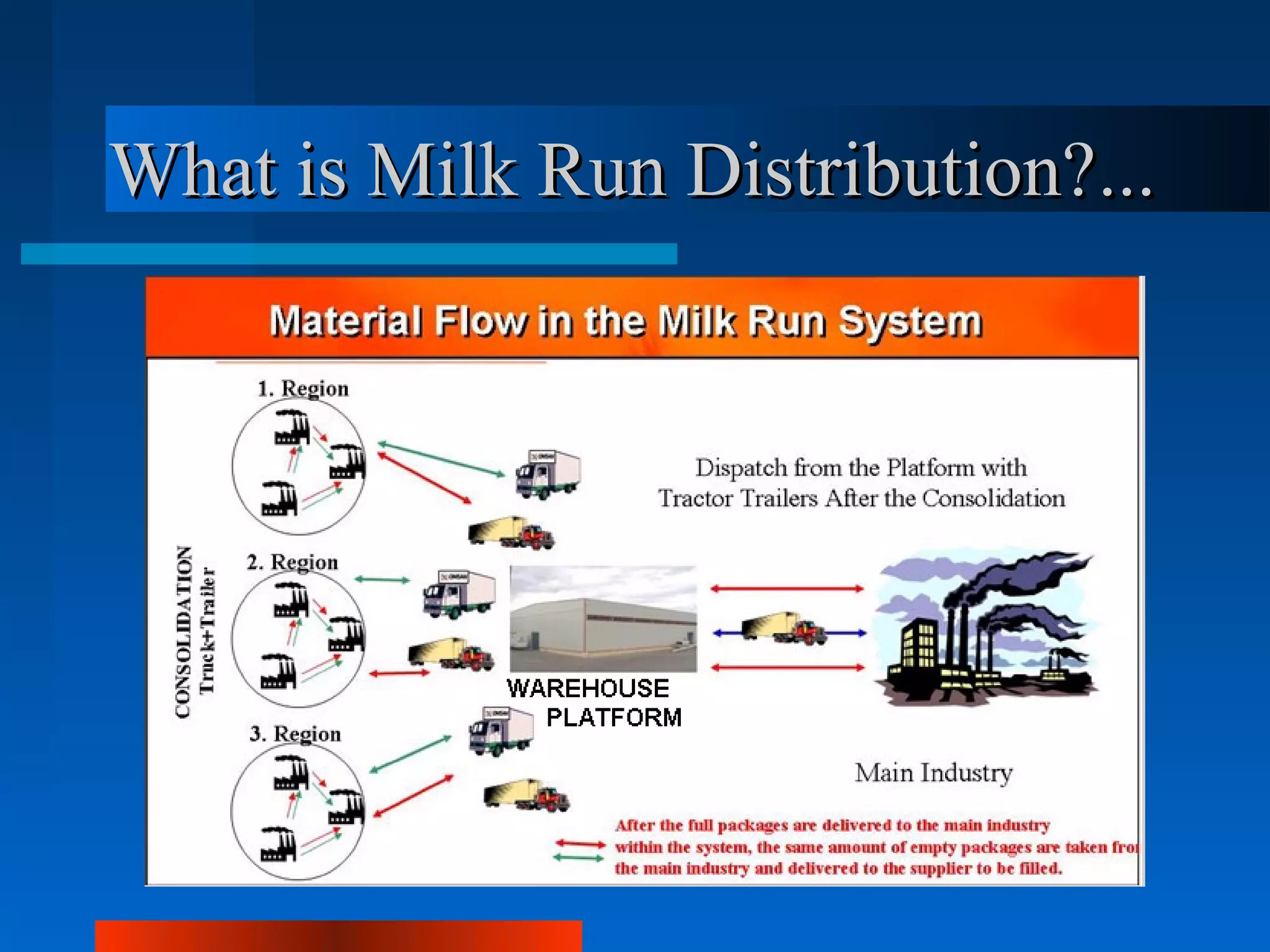
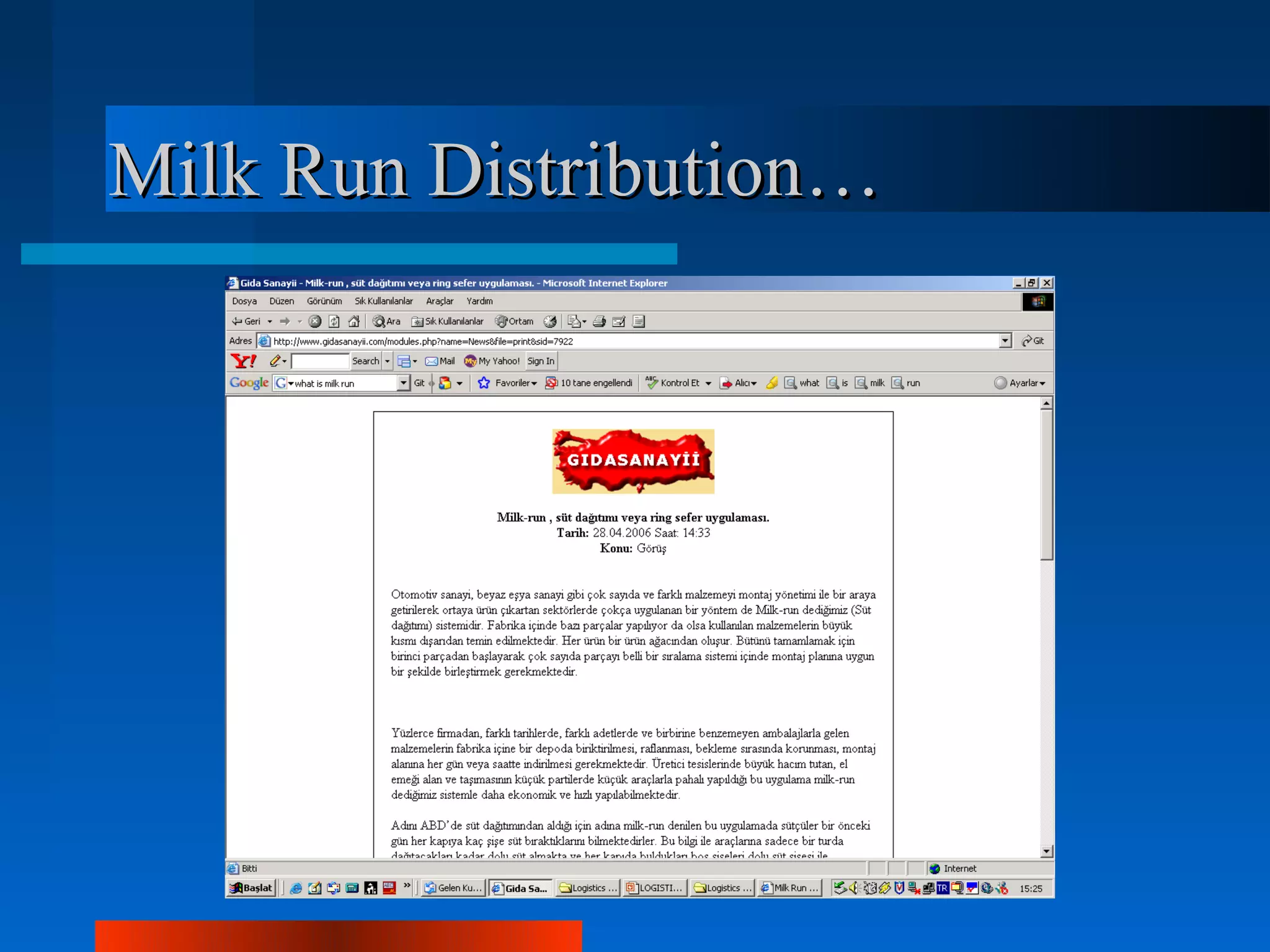
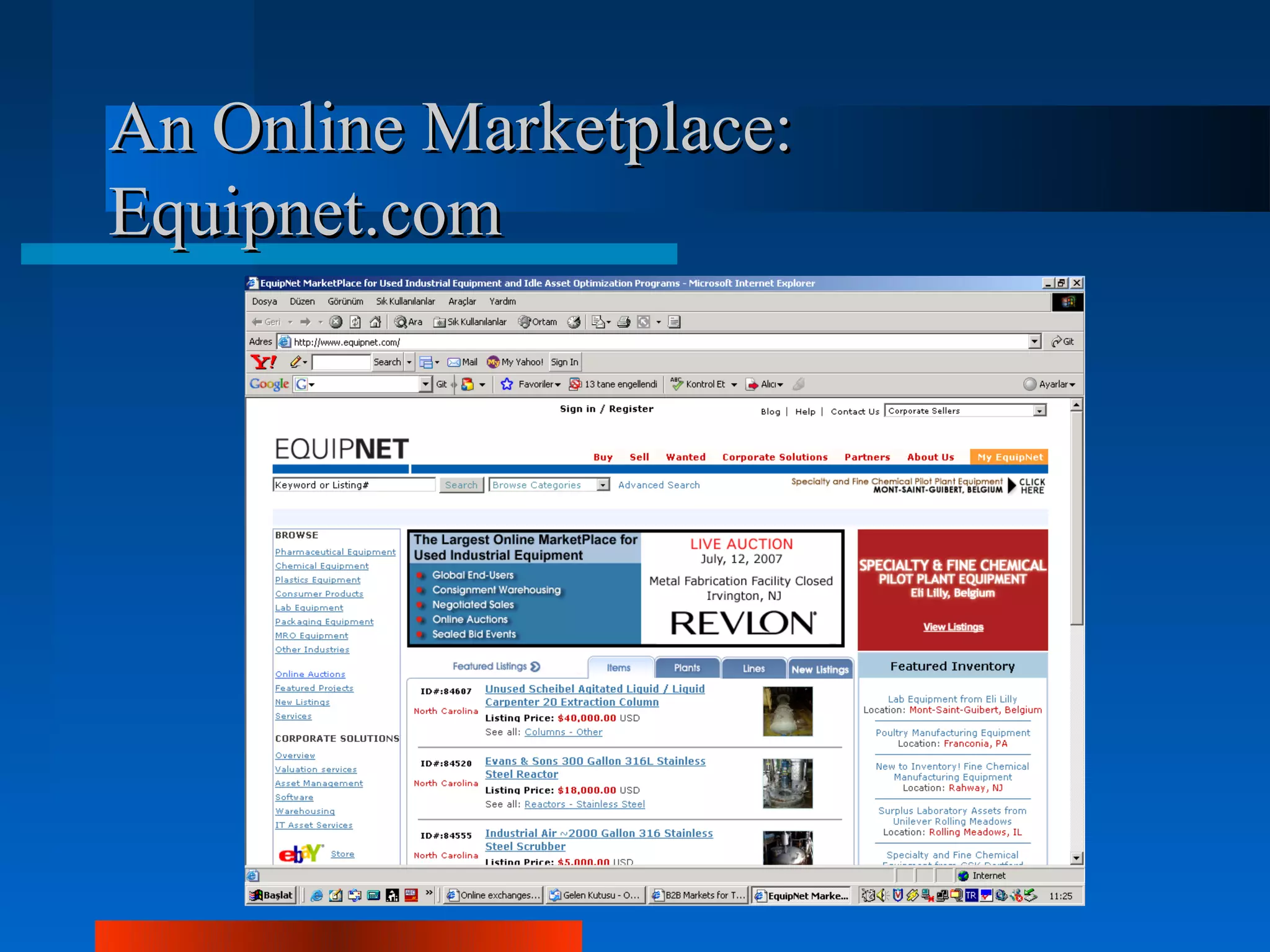
Logistics is the process of planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient flow of goods, services and information from origin to consumption. Logistics and supply chain management are equivalent terms. Key logistics functions include purchasing, inventory control, transportation, warehousing and customer service. Approaches in logistics management include just-in-time, vendor managed inventory, and collaborative transportation management. Logistics operations differ across sectors like textiles, retailing, health and automotive due to factors like seasonality, inventory risks and delivery requirements. Outsourcing logistics to experts can help streamline operations and integrate information systems as seen in the case studies of Intra Medikal and Carşı working with Ekol Logistics.