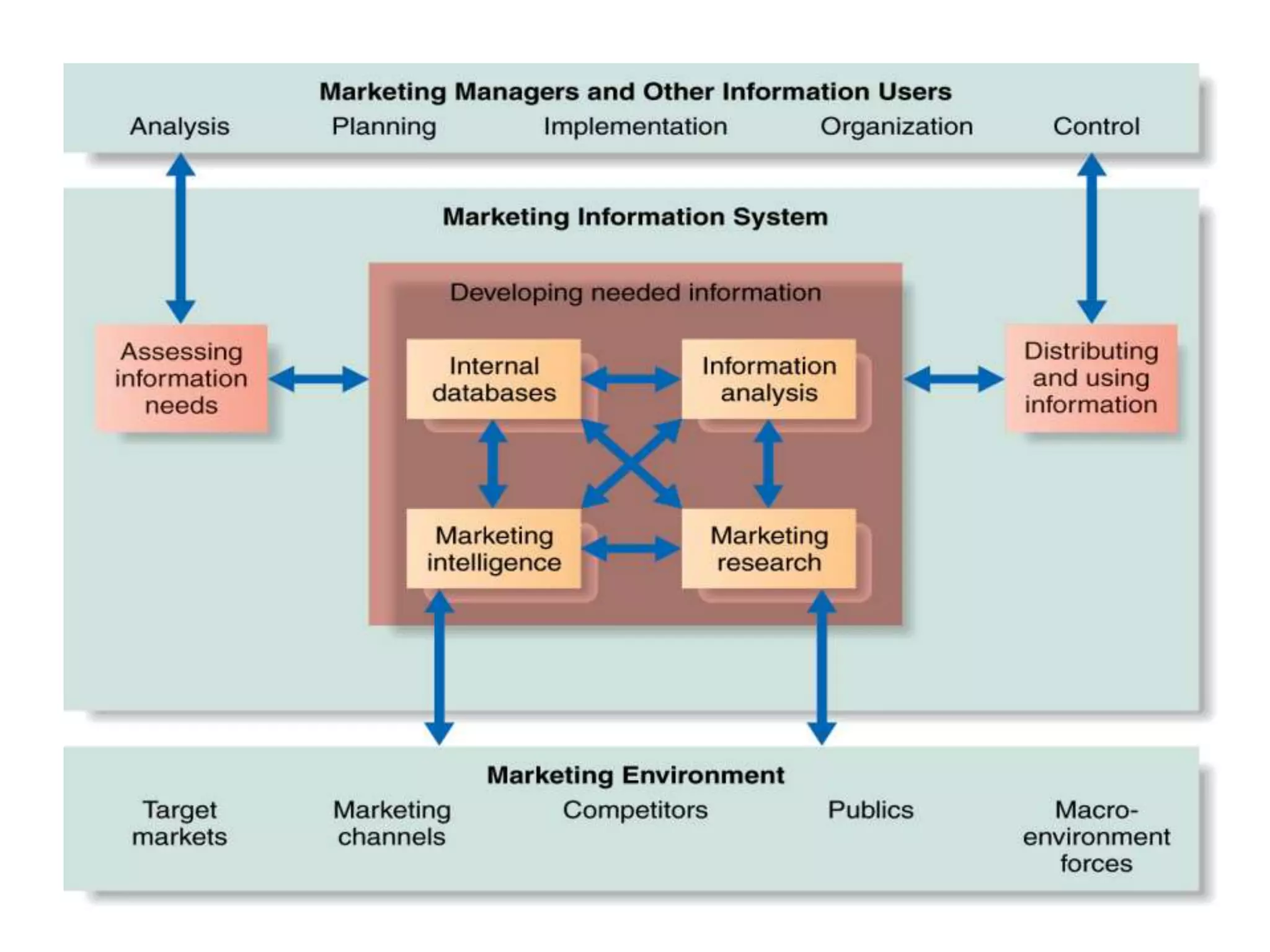
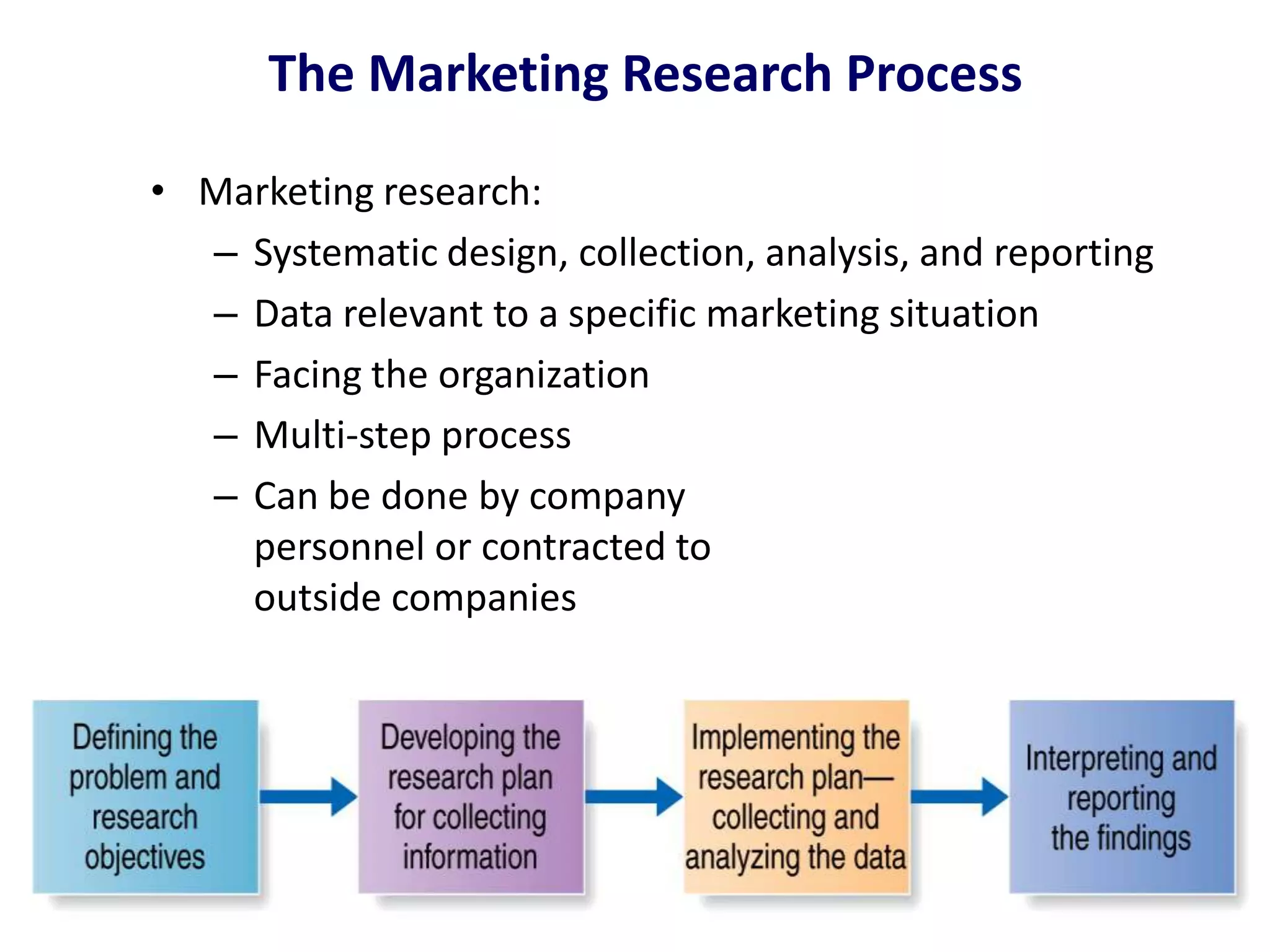
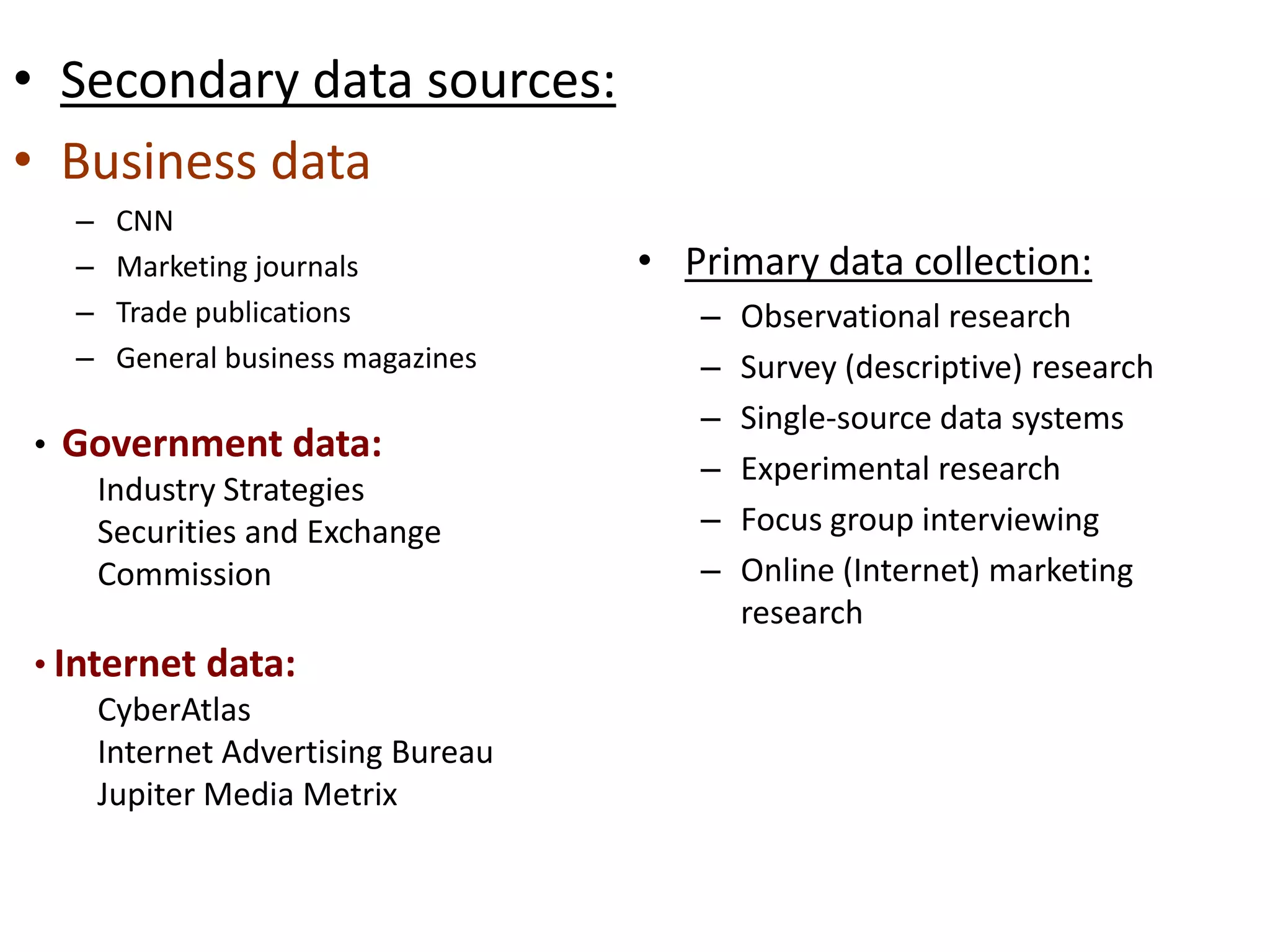
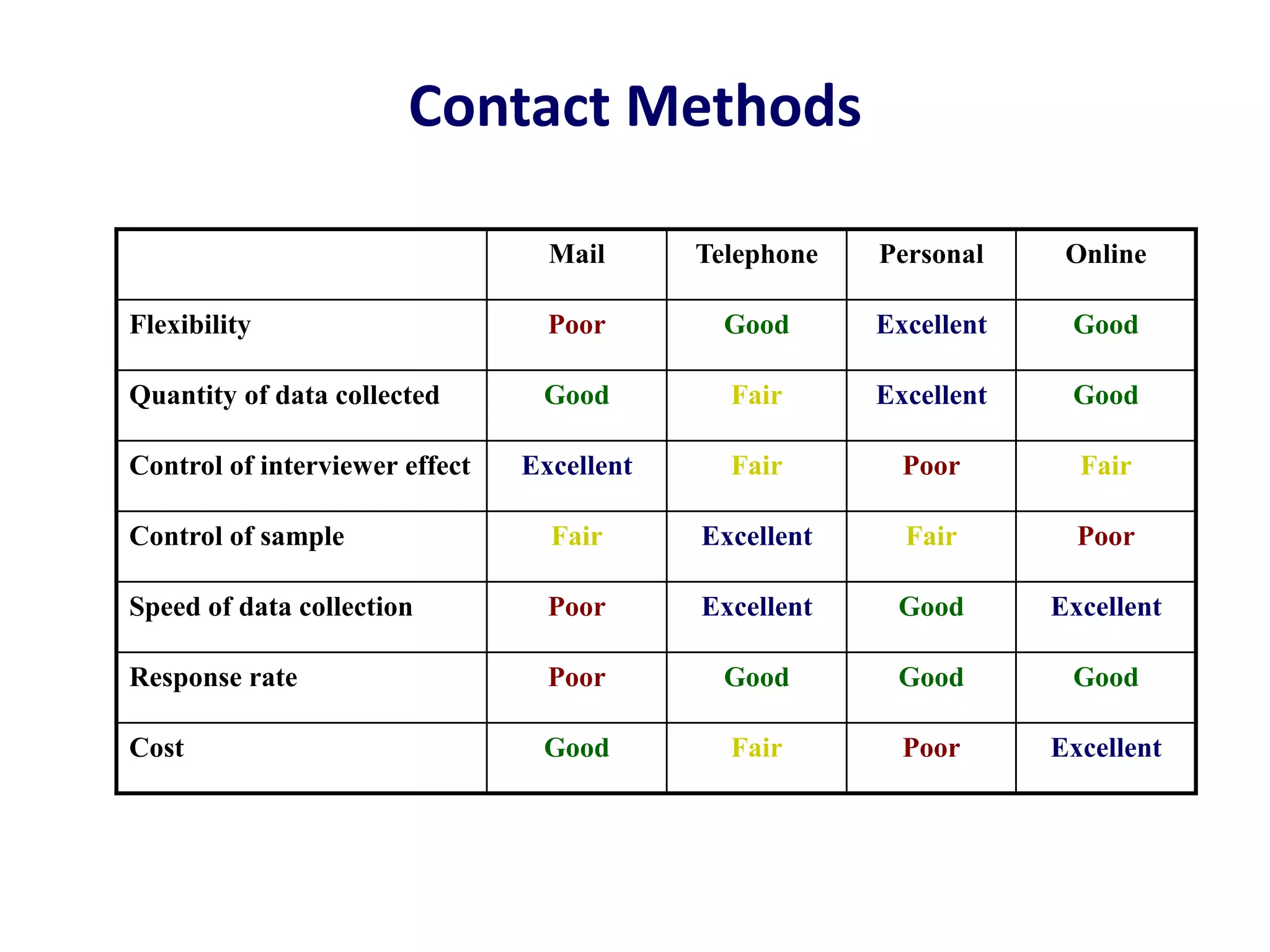
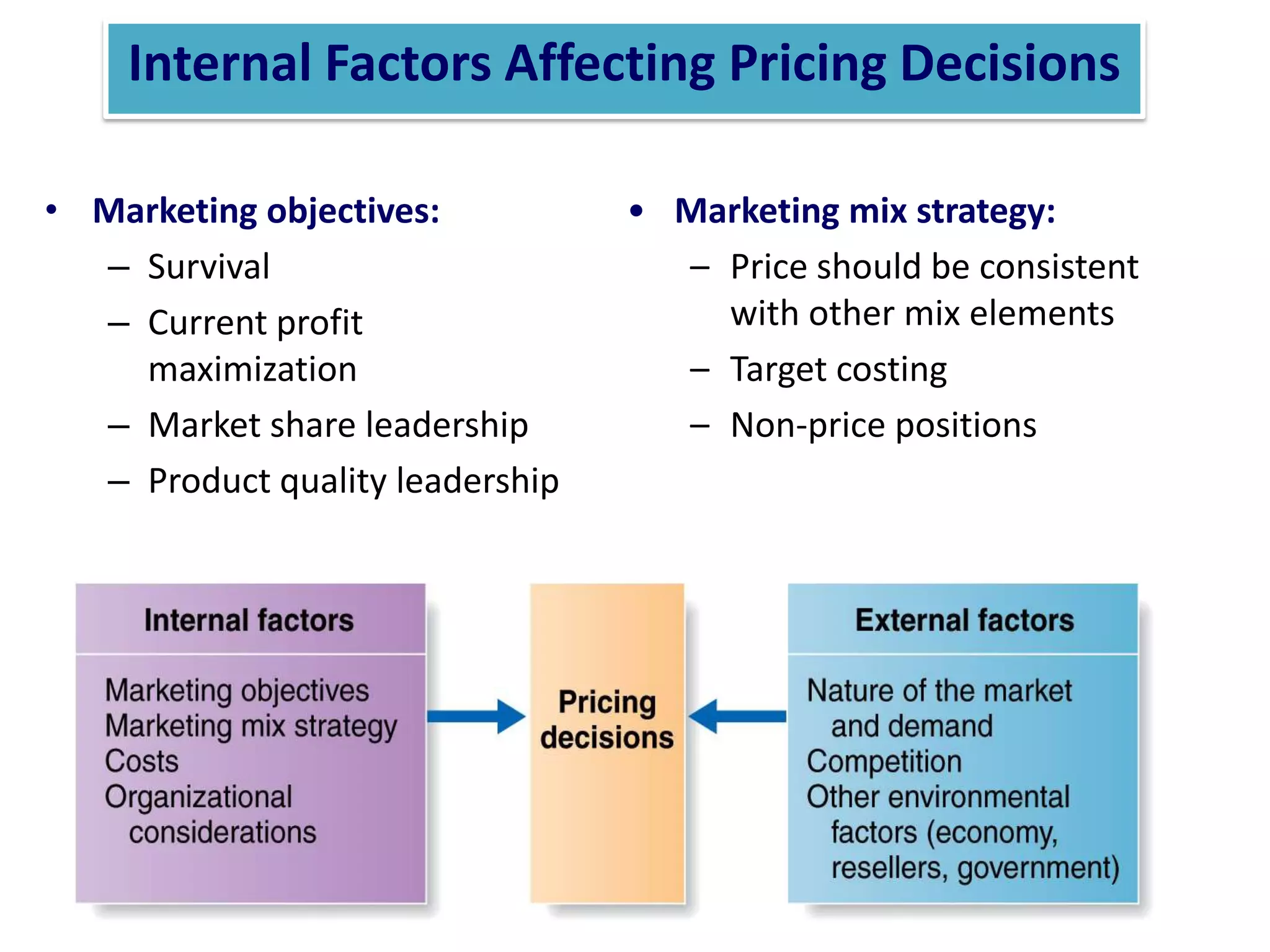
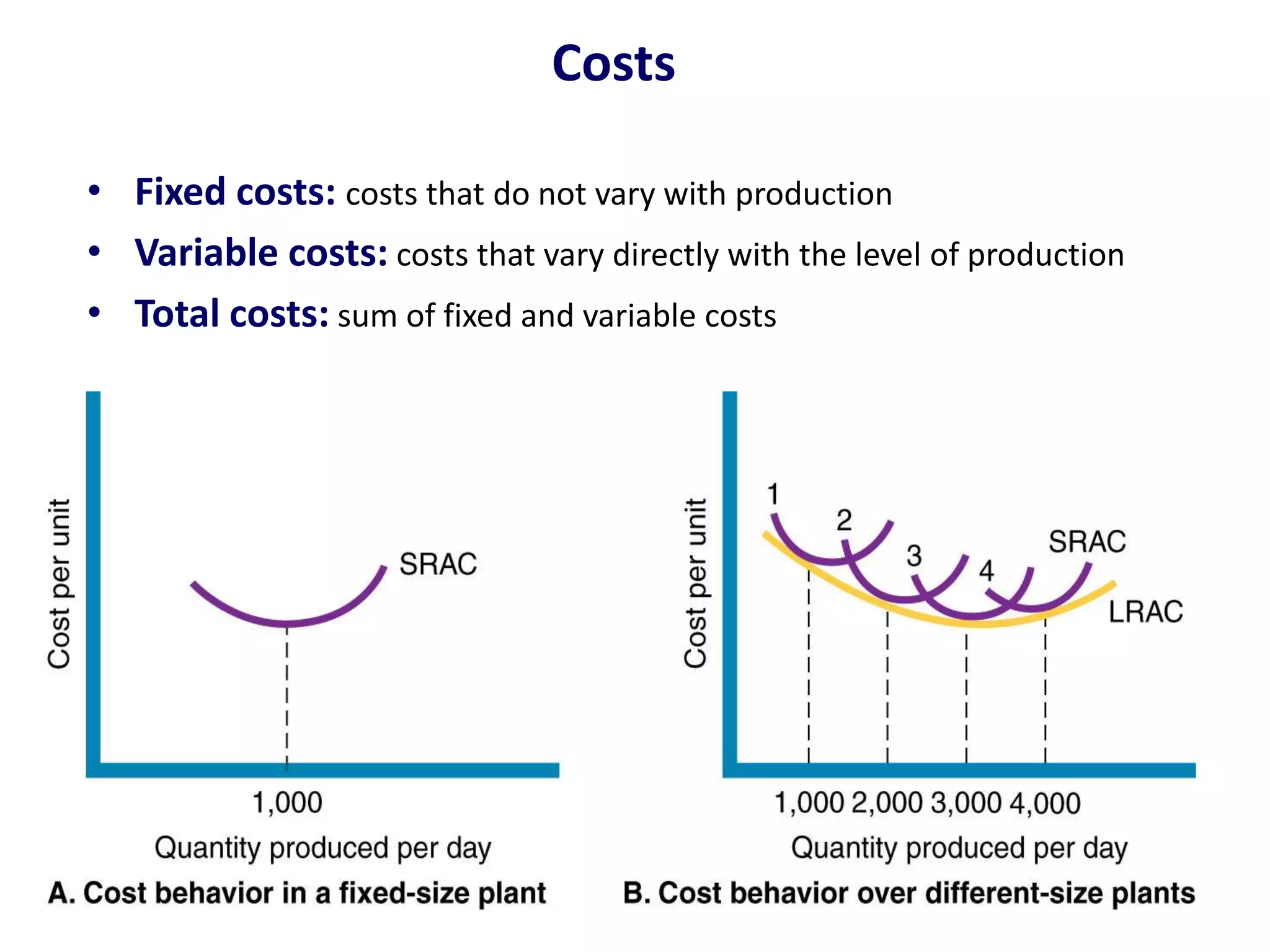
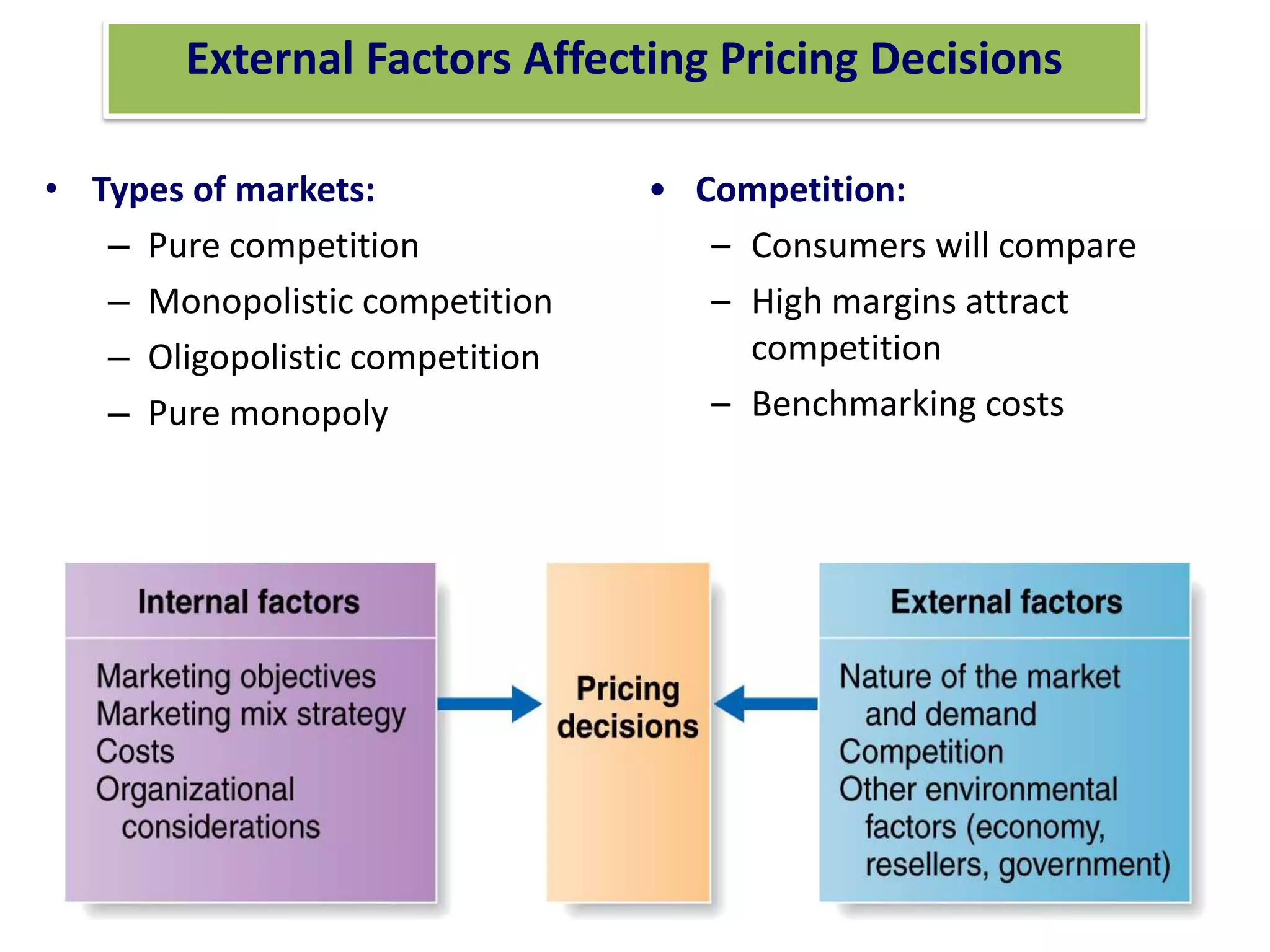
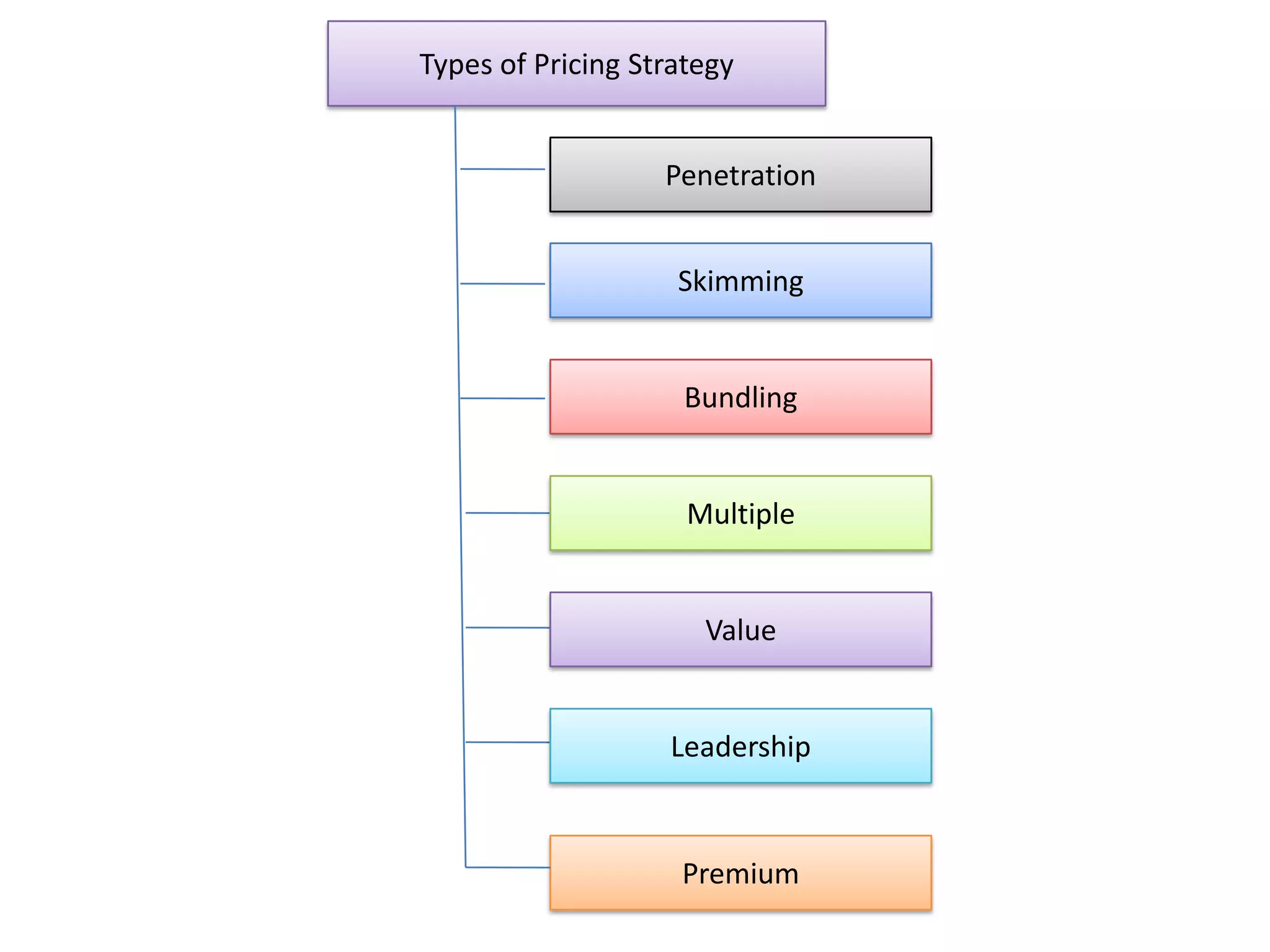
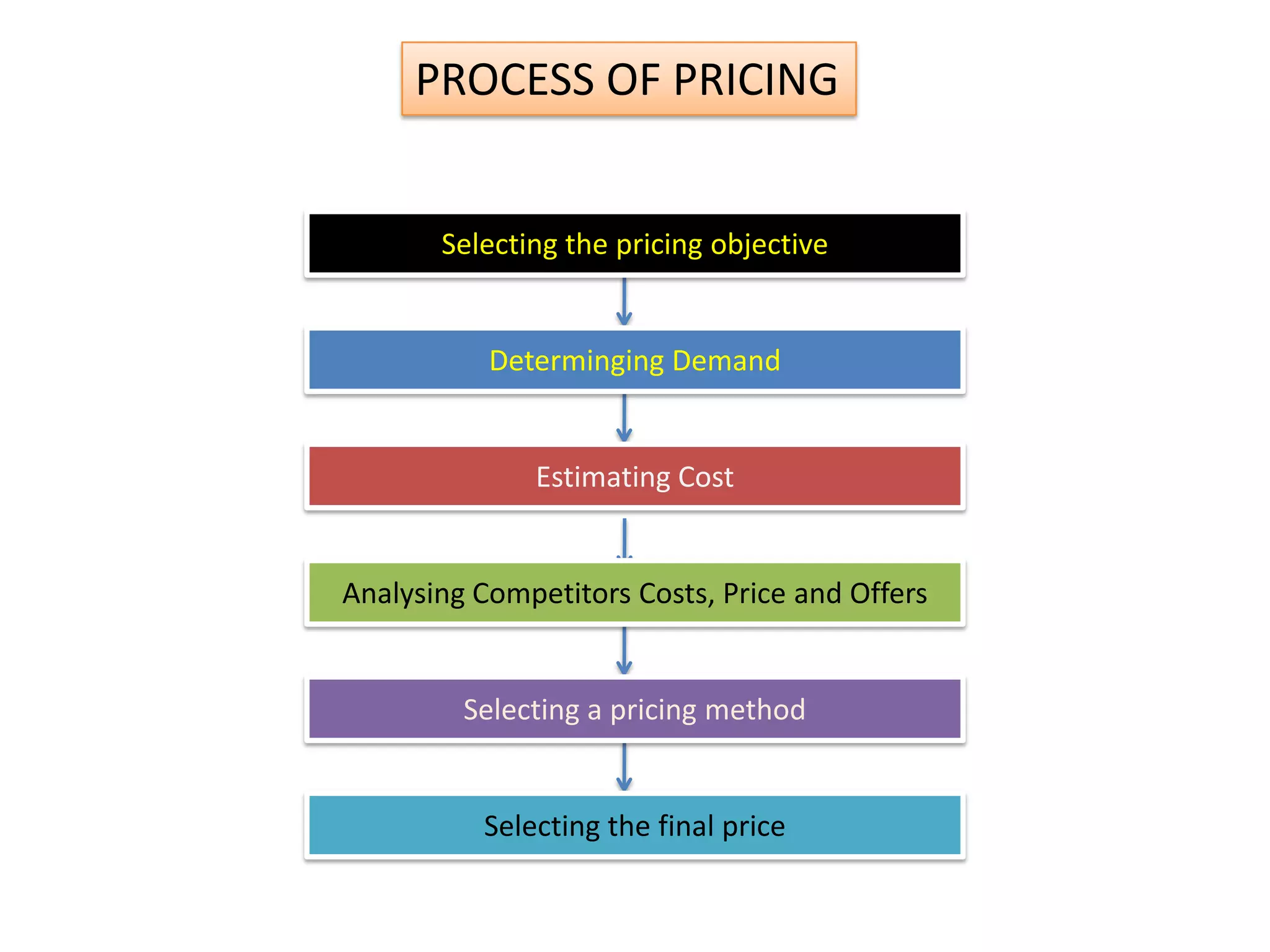
This presentation discusses market research and pricing methods. It begins by defining market research as a systematic process of problem analysis, model building, and fact-finding to aid important decision-making regarding goods and services. The key aspects covered include the marketing information system, marketing research process, methods of pricing, and the pricing process. The marketing research process involves defining the problem, developing a research plan, collecting primary and secondary data, analyzing the data, and reporting the findings. Different pricing strategies like penetration pricing, skimming pricing, and premium pricing are explained. The pricing process involves selecting objectives, estimating demand and costs, analyzing competitors, choosing a pricing method, and determining the final price.