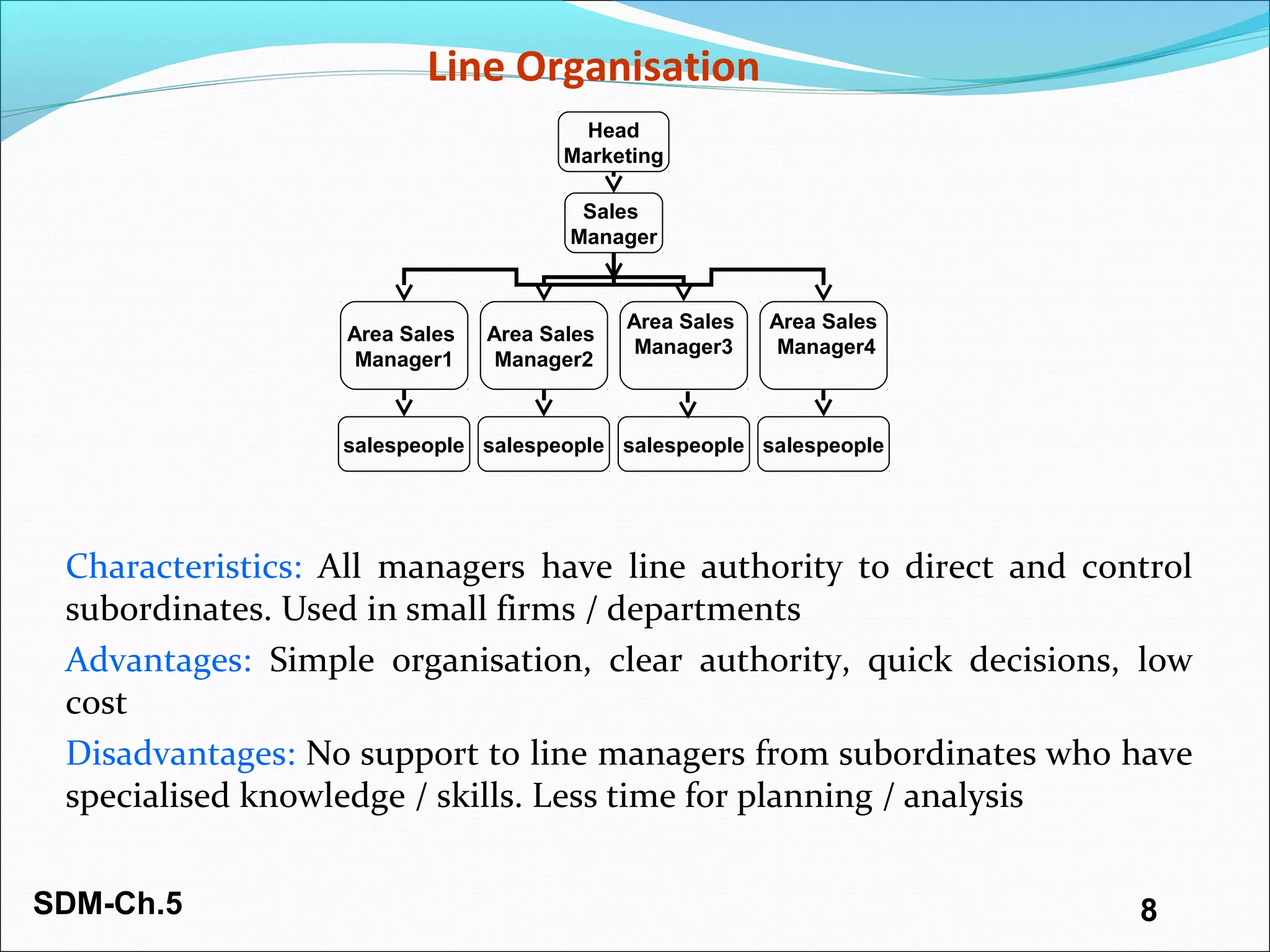
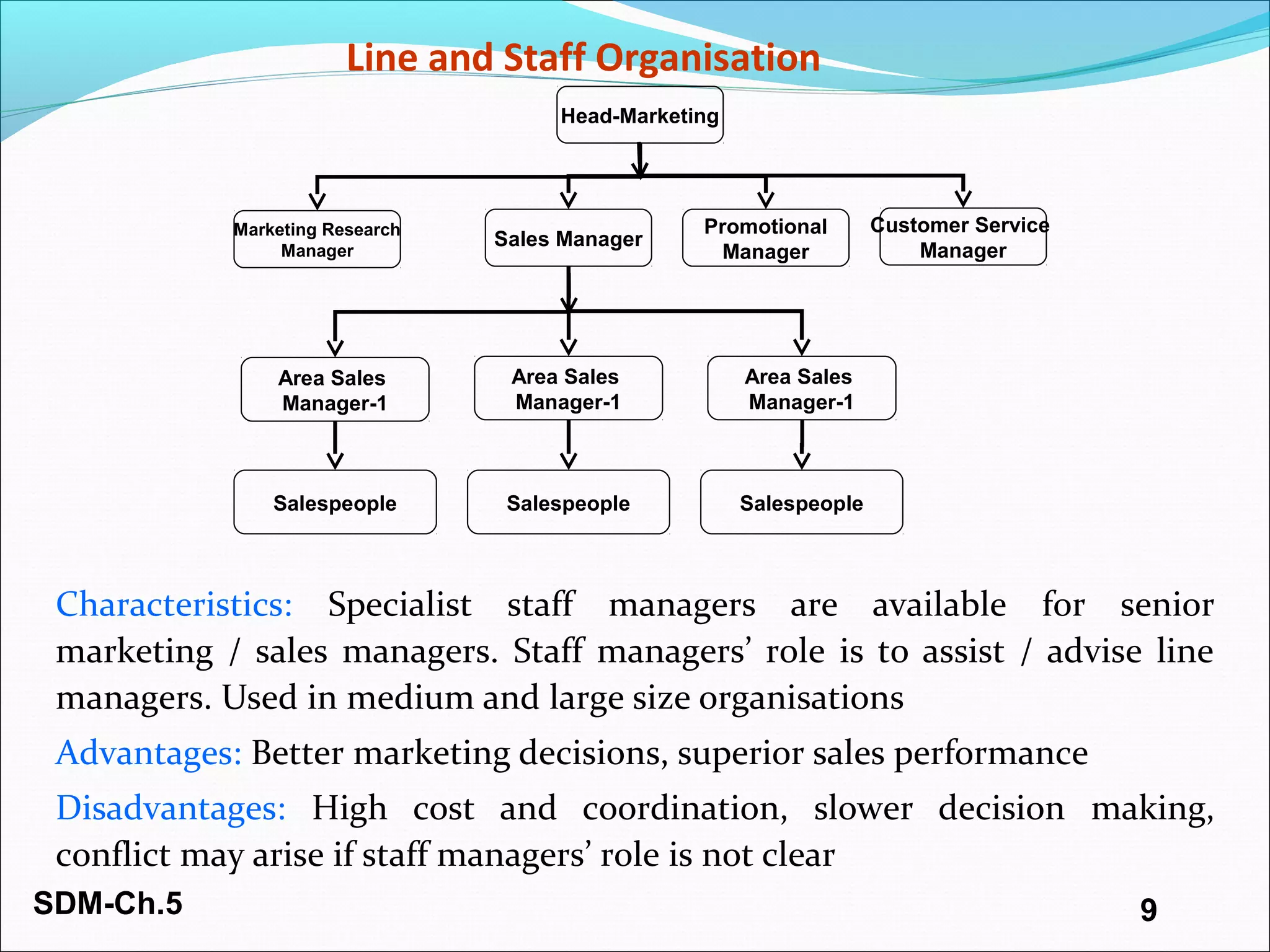
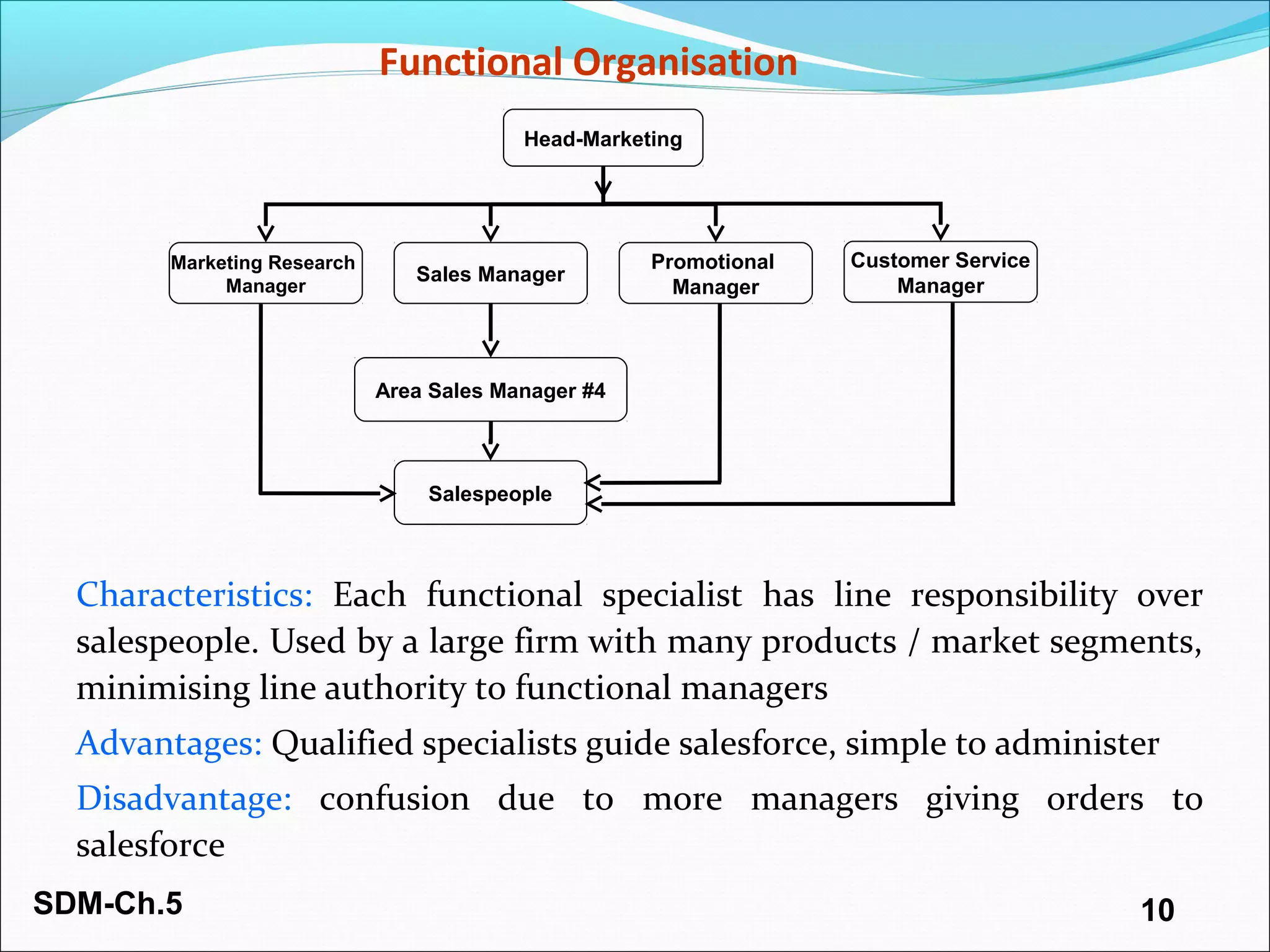
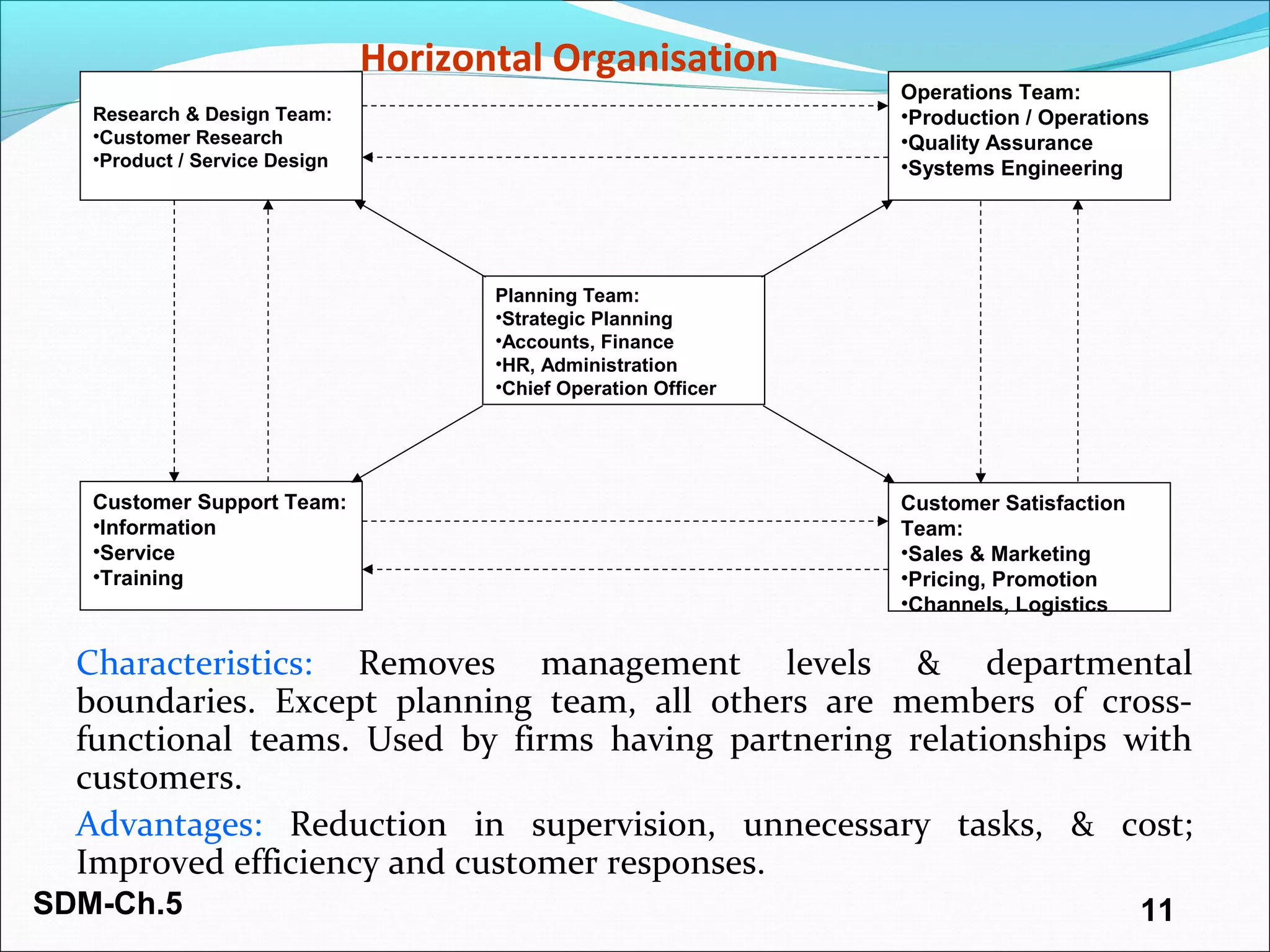
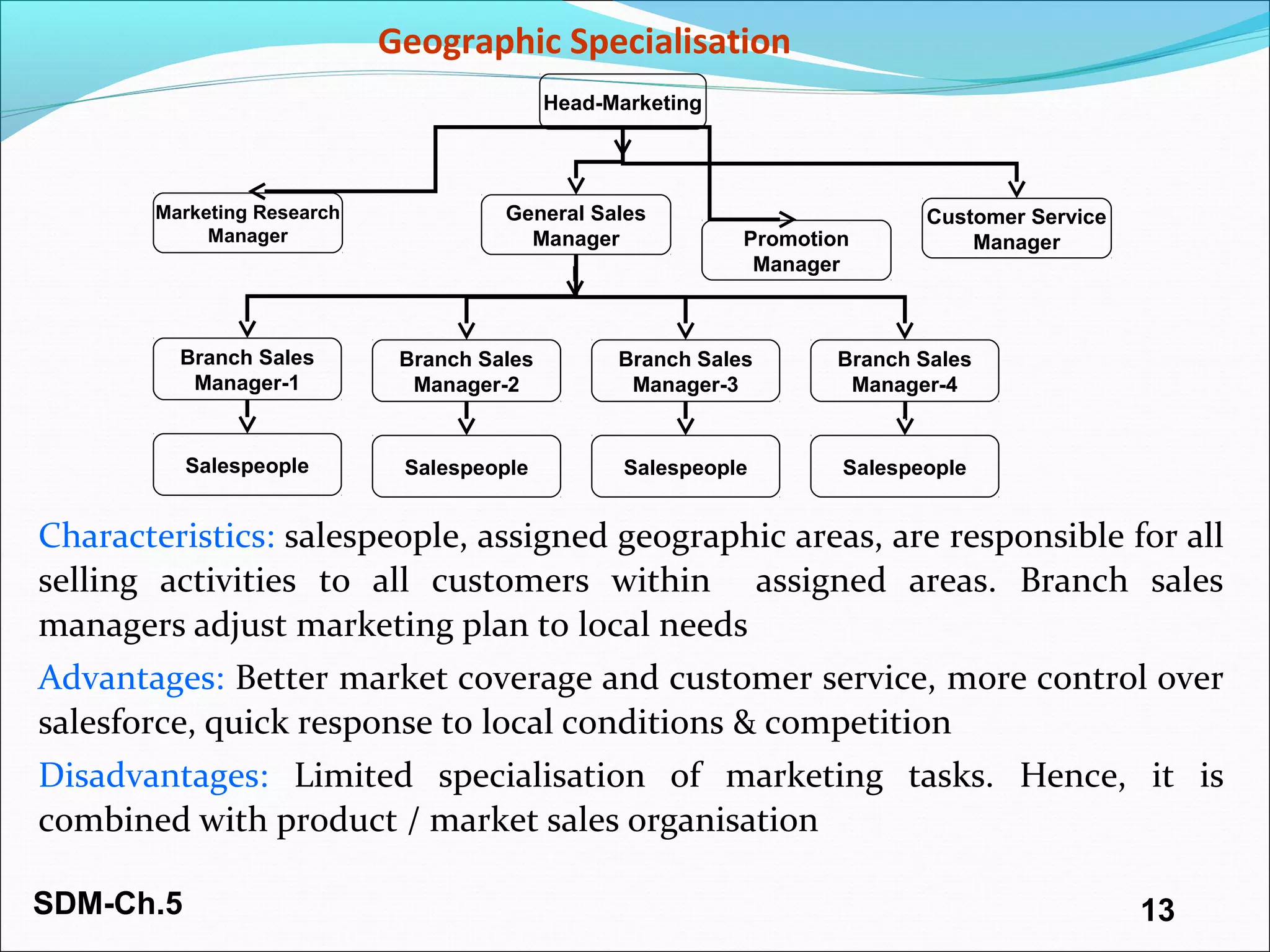
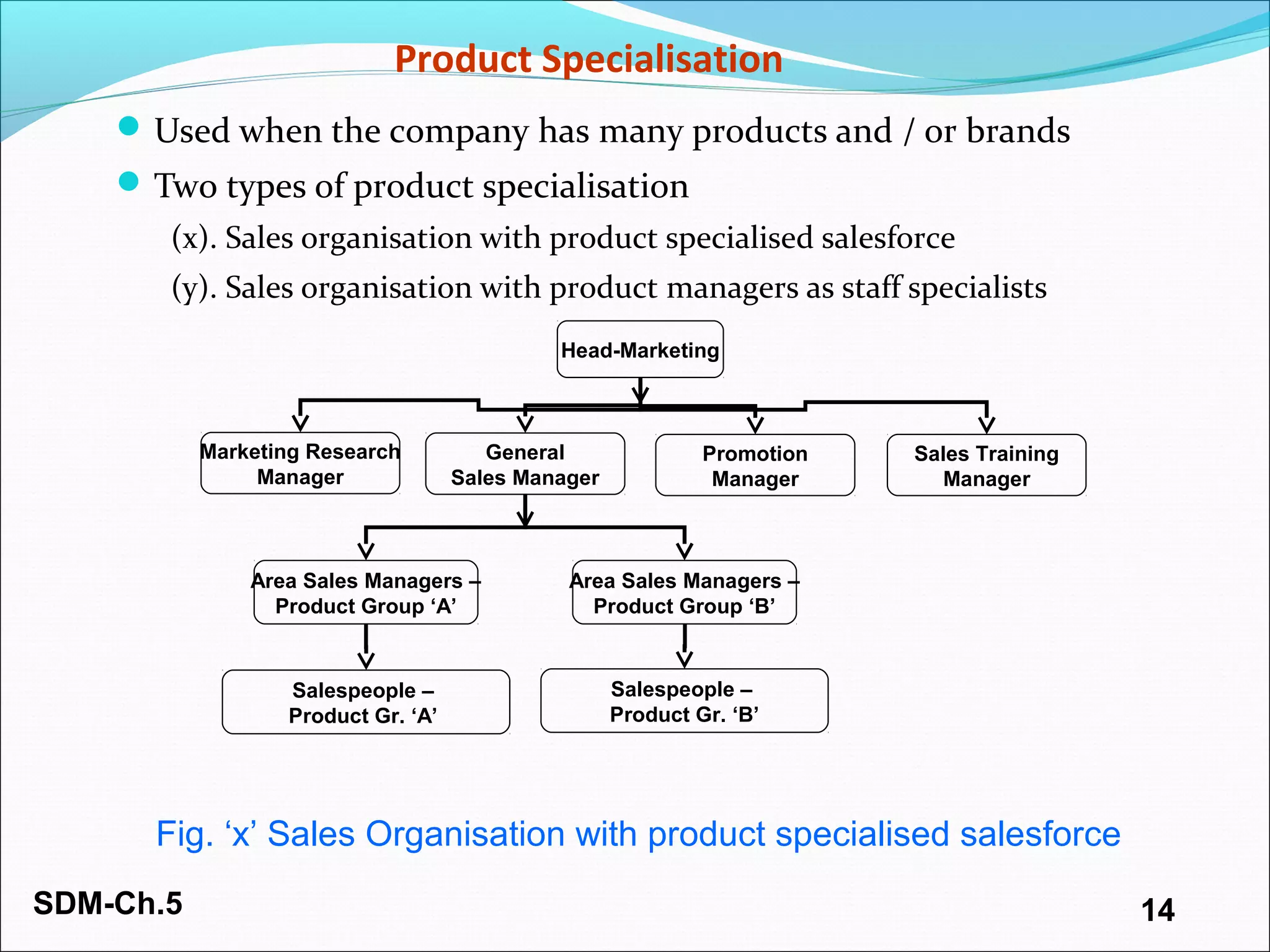
The document discusses organizing and staffing a salesforce. It covers different types of sales organizations including line, line and staff, functional, and horizontal organizations. It also discusses specialization within sales organizations based on geography, products, markets, and combinations. The size of the salesforce can be determined using workload, sales potential, and incremental methods. Staffing the salesforce is a multi-stage process involving planning, recruiting, selecting, hiring, and socializing. Planning involves determining needs, job analysis and descriptions. Recruiting sources can be internal or external. Selection tools include screening, interviews, testing, and reference checks.