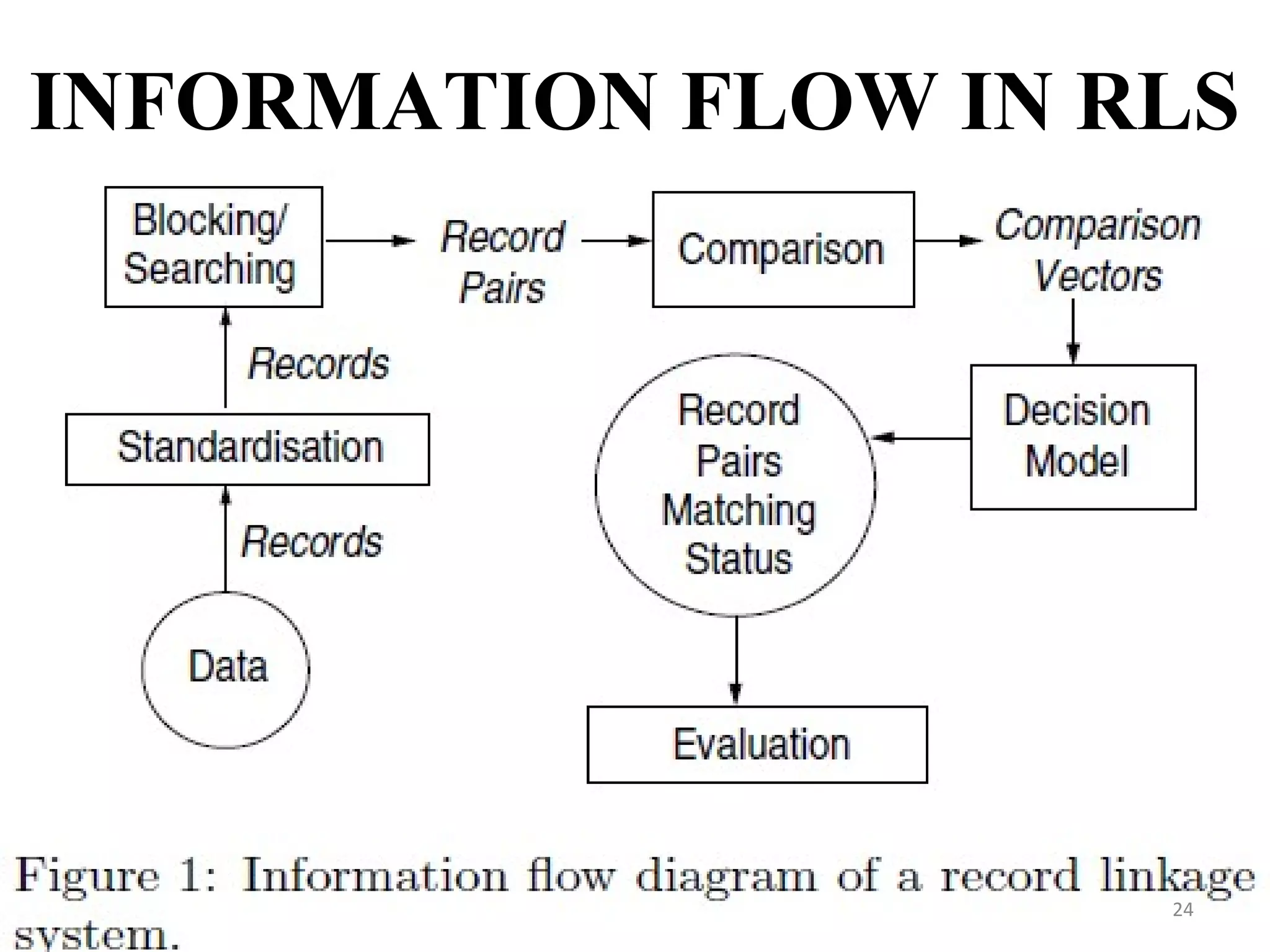
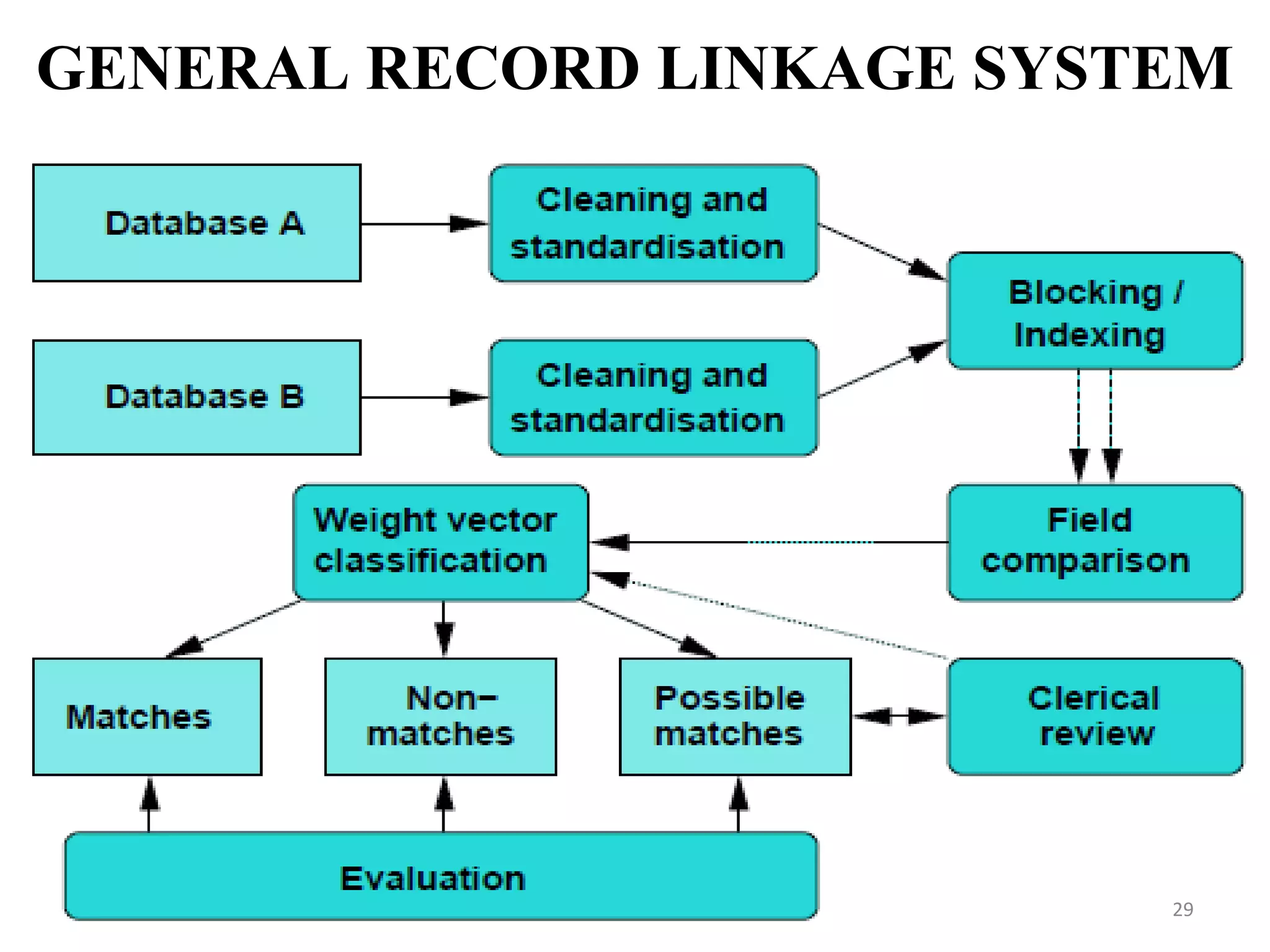
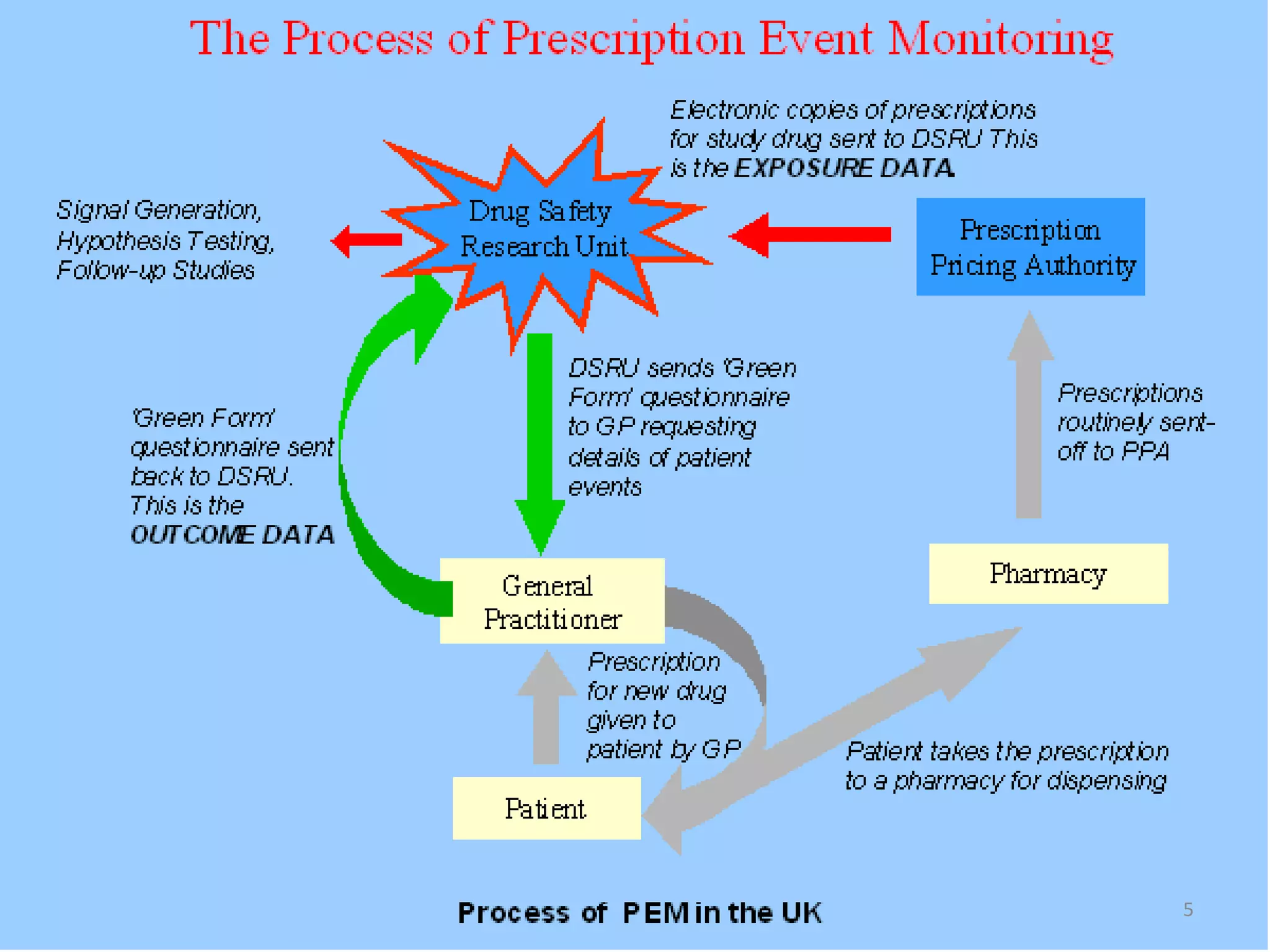
- Prescription-Event Monitoring (PEM) is a non-interventional observational cohort technique used to study the safety of new medications prescribed by general practitioners. It involves collecting data on all clinical events reported by patients after being prescribed a new drug.
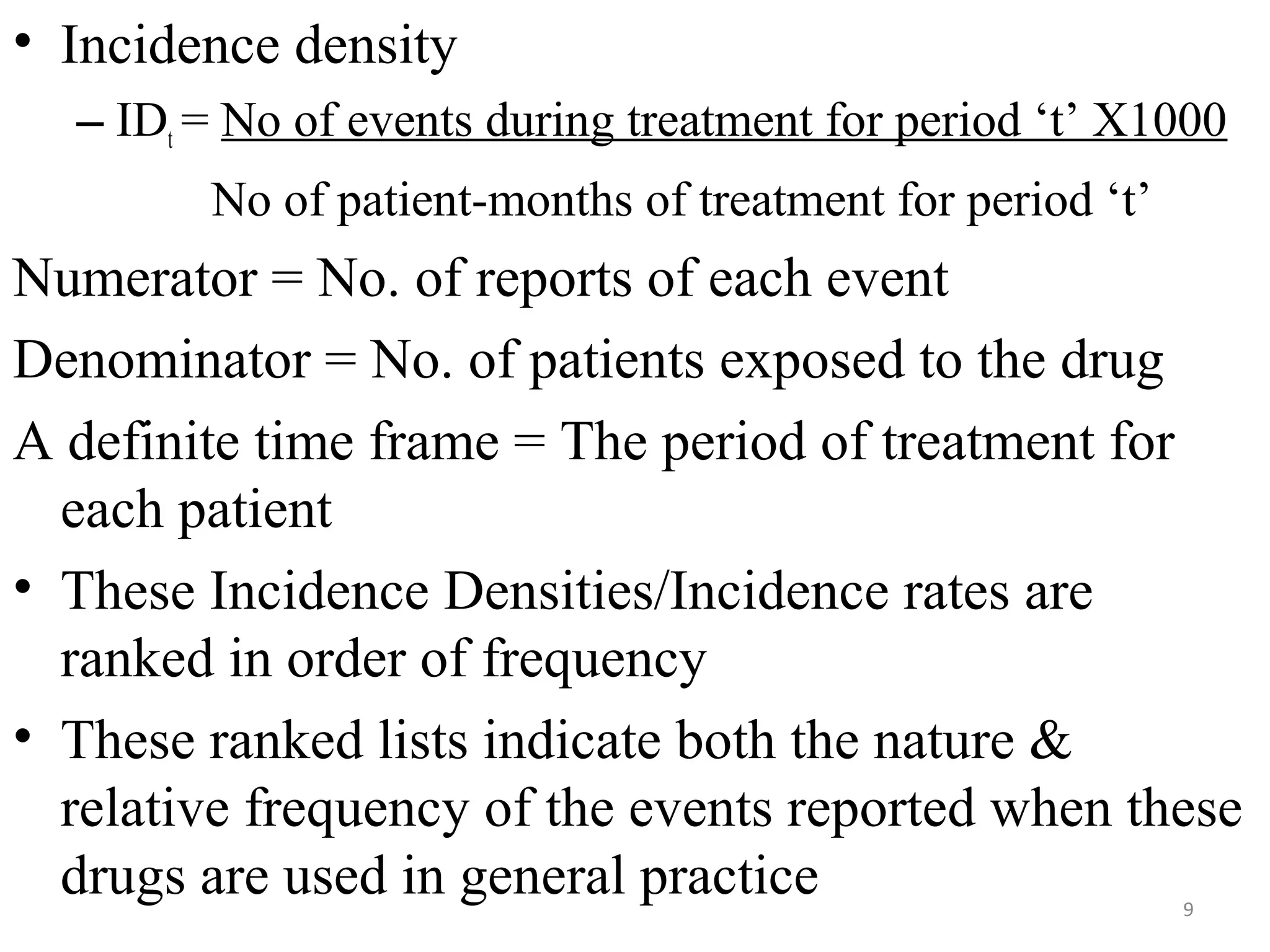
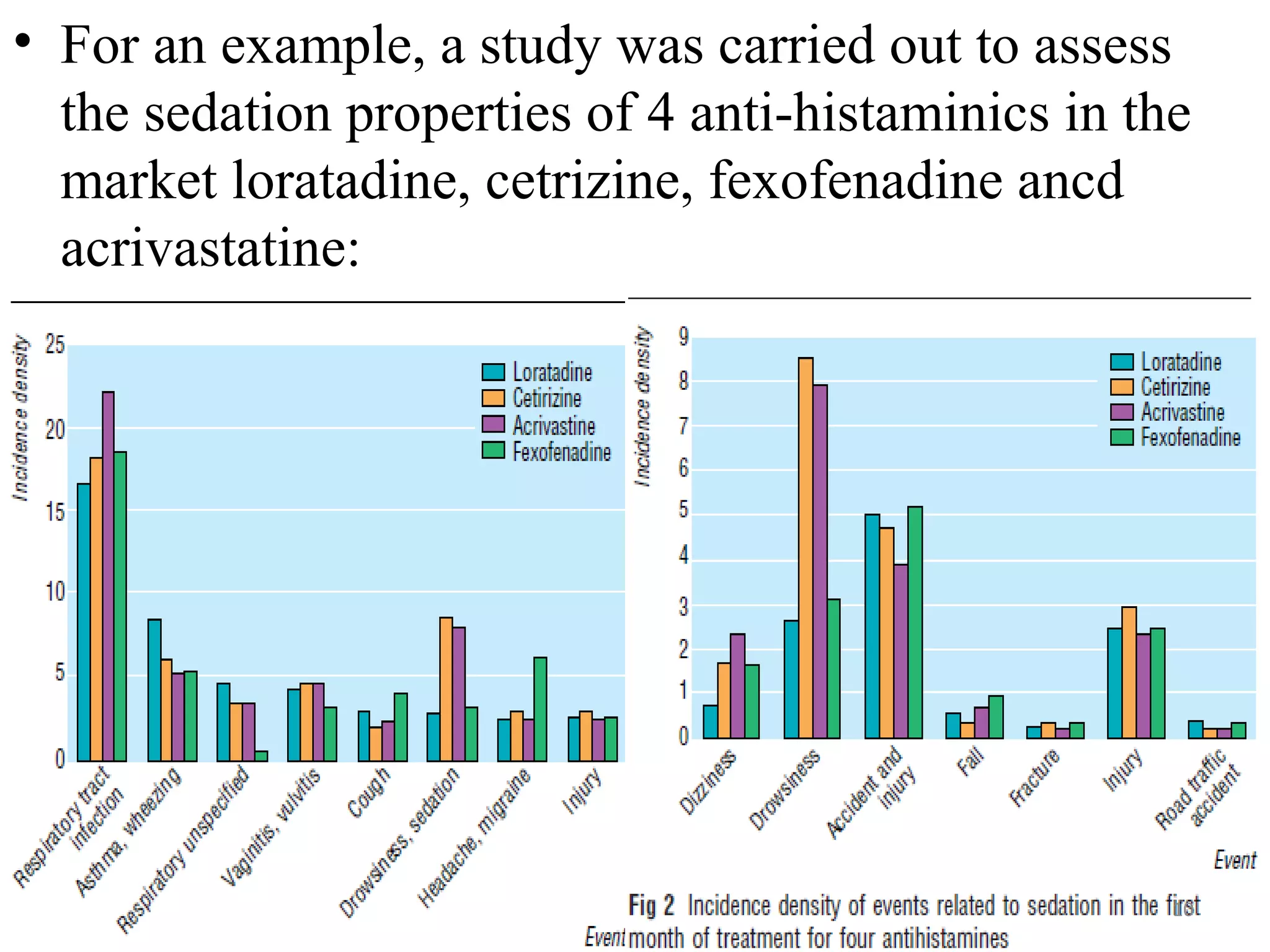
- PEM provides clinically useful safety information as it establishes incidence densities for all reported events during treatment with the monitored drug based on data collected from the first 5,000-18,000 prescriptions. This allows for comparisons of event rates before and after drug use.
- While PEM provides nationally representative data on new drugs in real-world settings, it also has disadvantages like an inability to measure compliance or determine use of non-prescription medications.















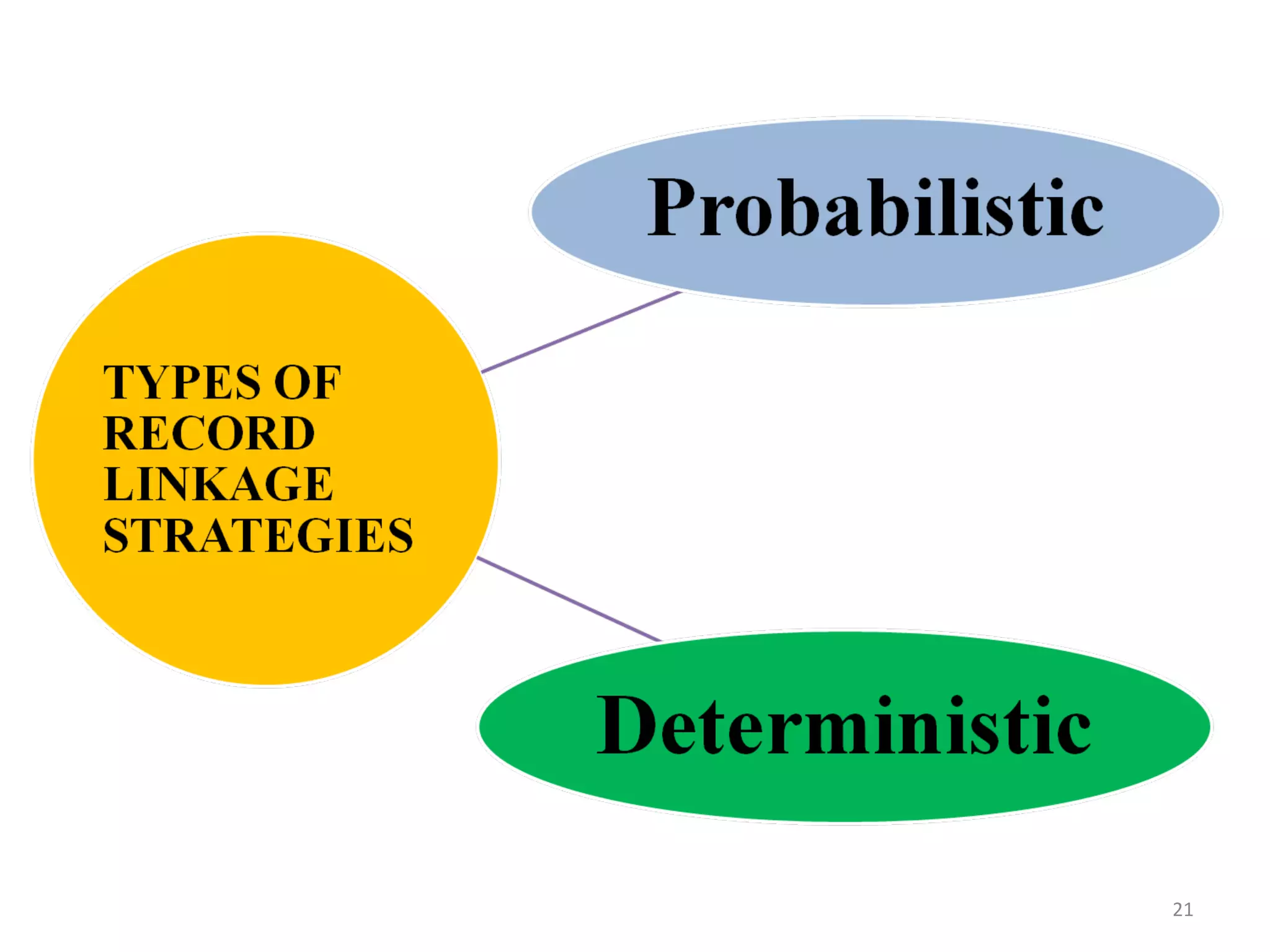

![PROBABILISTIC RECORD
LINKAGE
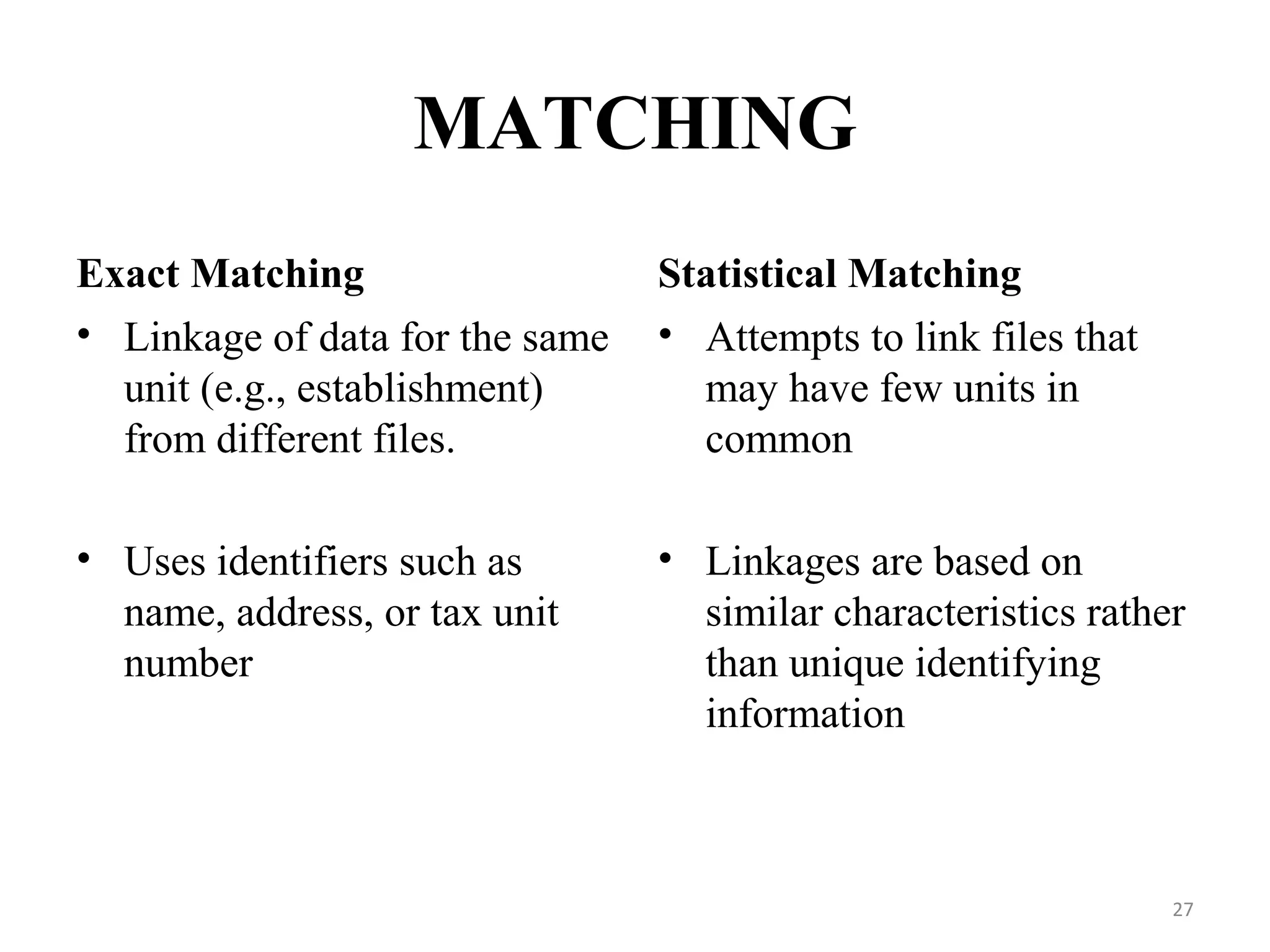
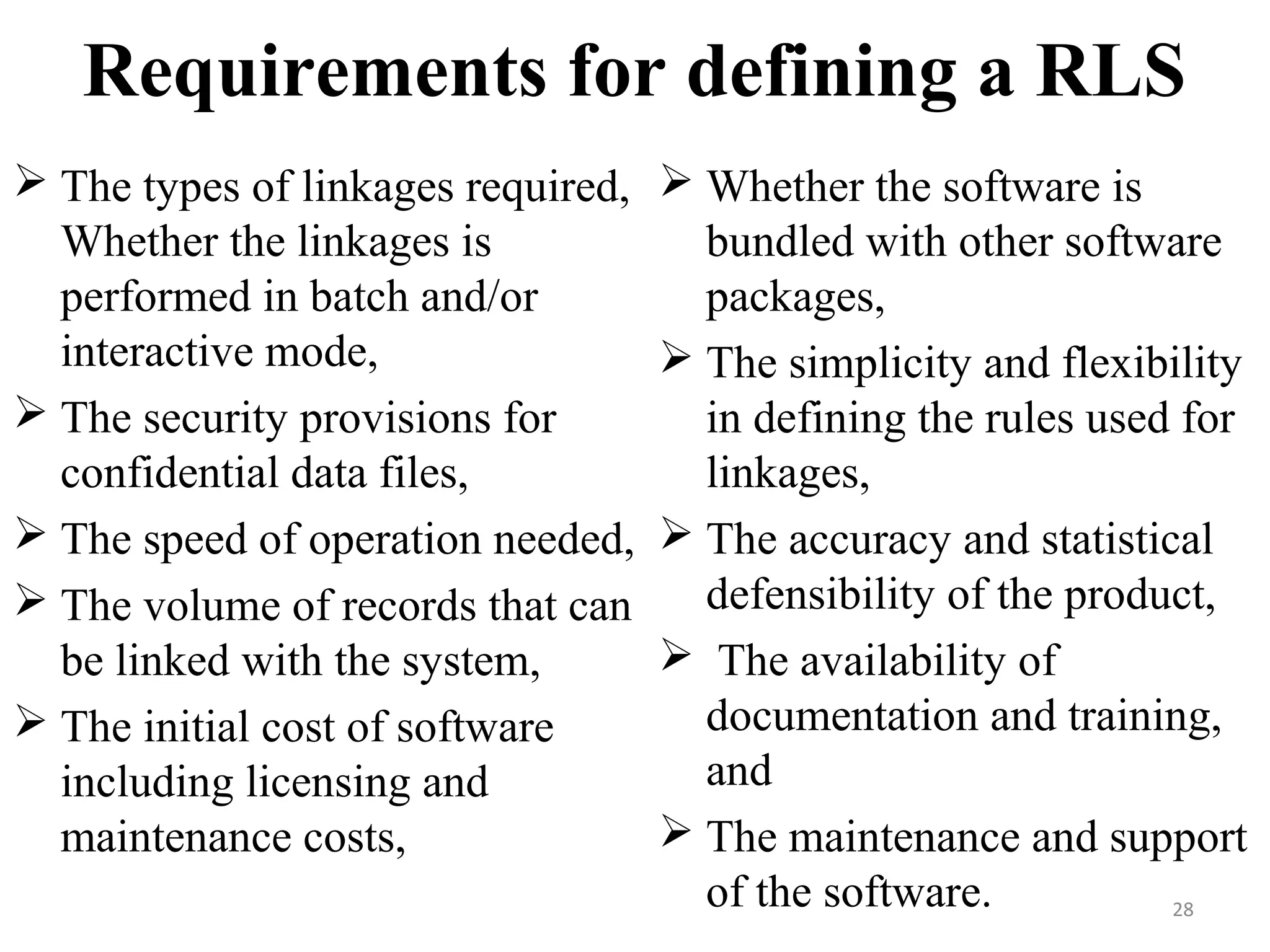
• Formalized by Fellegi and Sunter [1969].
• Pairs of records are classified as links, possible links, or
non-links.
• Here, we consider the probability of a match in the given
observed data.
• In probability matching, a threshold of likelihood is set
(which can be varied in different circumstances) above
which a pair of records is accepted as a match, relating to
the same person, and below which the match is rejected.
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pem-rls-130422205511-phpapp01/75/Prescription-Event-Monitoring-Record-Linkage-Systems-23-2048.jpg)