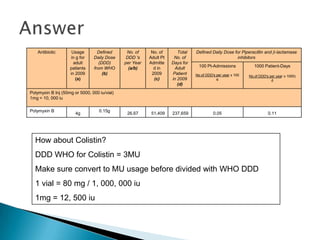
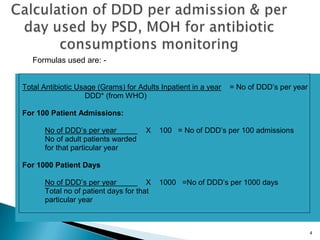
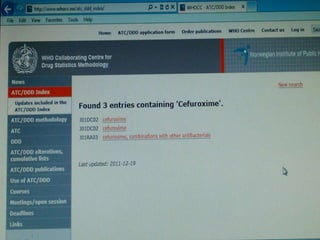
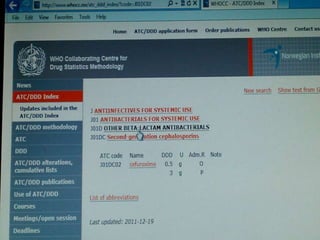
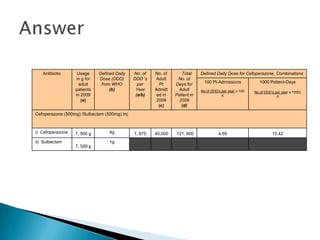
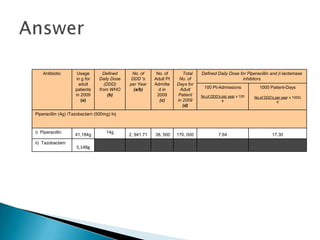
This document discusses defined daily doses (DDDs) and provides formulas and examples to calculate antibiotic usage in DDDs per 100 patient admissions and per 1000 patient days. It defines a DDD as the assumed average maintenance dose per day for a drug's main indications. Examples are given to demonstrate calculating DDDs for cefoperazone/sulbactam, piperacillin/tazobactam, and polymyxin B based on antibiotic usage data, patient admission numbers, and patient days for three hospitals. Guidance is provided that 10 DDDs per 100 admissions or 10 DDDs per 1000 patient days generally indicates the drug was received by 10% or 1% of patients respectively.




![1. Hosp. Q used 15,000 vials of Inj.
Cefoperazone/Sulbactam in 2009. No. of
patients admitted in 2009 was 40,000 and
average length of stay of adult patients
warded was 3.04 days.
Calculate the DDD per 100 patient-
admissions and DDD per 1000 patient-
days.
[DDD WHO for Cefoperazone, combination
= 4g]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dddtalk-130531010203-phpapp02/85/Ddd-talk-10-320.jpg)
![2. Hosp. R used 10, 296 vials of Inj.
Piperacillin/Tazobactam in 2009. No. of
patients admitted in 2009 was 38, 500
patients and total no. of days adult
patients were warded was 170 000 days.
Calculate the DDD per 100 patient-
admissions and DDD per 1000 patient-
days.
[DDD WHO for Piperacillin & B-lactamase
Inhibitors, combination = 14g]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dddtalk-130531010203-phpapp02/85/Ddd-talk-12-320.jpg)
![3. Hosp. S used 80 vials of Inj. Polymyxin B
in 2009. No. of patients admitted in 2009
was 51, 409 patients and total no. of
days adult patients were warded was 237,
659 days.
Calculate the DDD per 100 patient-
admissions and DDD per 1000 patient-
days.
[DDD WHO for Poly B = 0.15g]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dddtalk-130531010203-phpapp02/85/Ddd-talk-14-320.jpg)