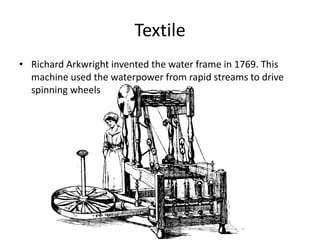
Pre-industrial society was characterized by a mixed work and social life where children learned skills on family farms. Families grew their own crops for subsistence and diets were poor, consisting mainly of bread with little meat or vegetables. Healthcare was also poor, with beliefs that illness was divine and the reliance on practices like bloodletting. Mortality rates were very high, with over 50% of children dying before age 10, and epidemics regularly killed around a third of the population. Wealth was concentrated among the few, with most living in poverty. The cottage industry allowed some agricultural families to earn extra income by spinning and weaving at home. However, this system was slow and inefficient. The beginnings of industrialization in