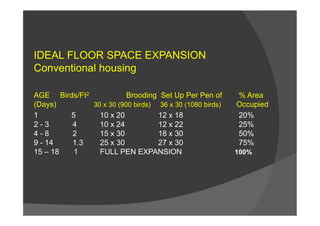
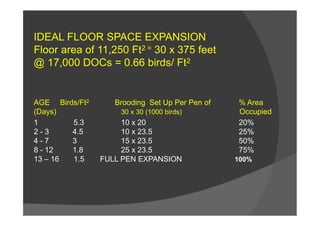
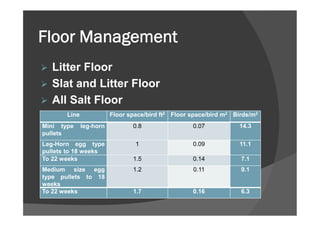
This document discusses brooding management for poultry. It begins by defining brooding as the special care and management of baby chicks until they no longer require artificial heat. It then describes the two main types of brooding systems: colony brooding which uses individual brooders, and continuous brooding which houses large numbers of chicks together. The document provides details on various brooding management factors like temperature, ventilation, feeding and sanitation that affect chick health and uniformity. It emphasizes the importance of correct brooding management practices for optimal growth and development of the chicks in the first critical weeks after hatching.