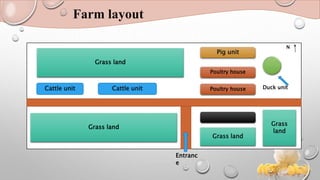
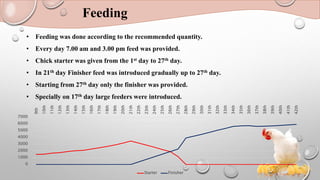
The document outlines the practical knowledge gained in poultry management, focusing on broiler management practices such as housing, feeding, and disease prevention. It details various methodologies employed, including daily observations, litter management, and special care like debeaking and nutrition supplements. The conclusion highlights the importance of maintaining records and improving facilities for better poultry management outcomes.