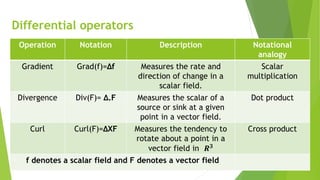
This presentation covers practical applications of vector differentiation. It introduces vector calculus concepts such as differentiation and integration of vector fields in 3D space. Key vector operations are defined, including addition, scalar multiplication, dot product, and cross product. Differential operators like gradient, divergence, and curl are explained and analogous to scalar and vector multiplications. Examples of applying vector differentiation are given in domains like cricket, electromagnetism, heat transfer, mechanics, and engineering.