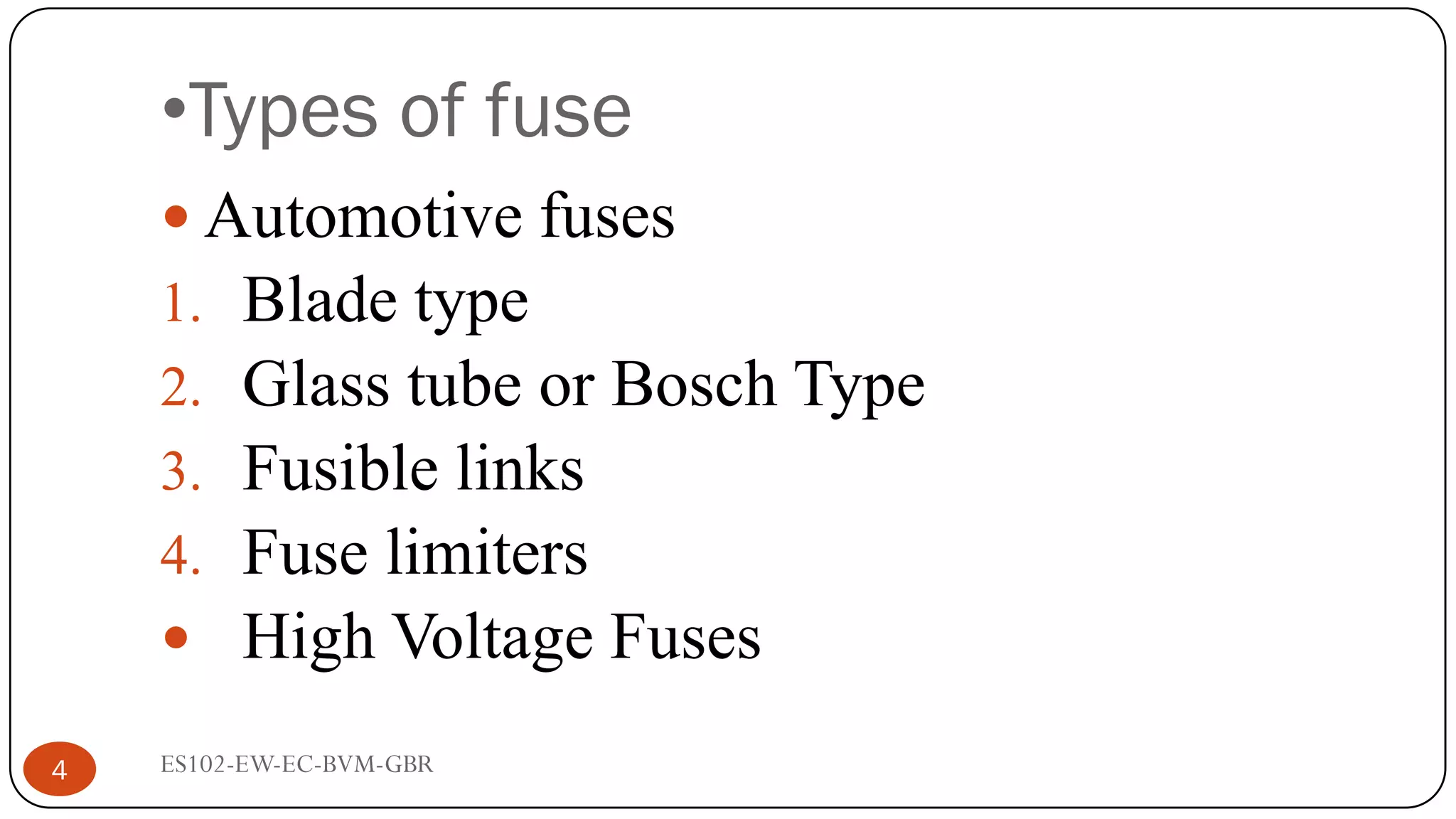
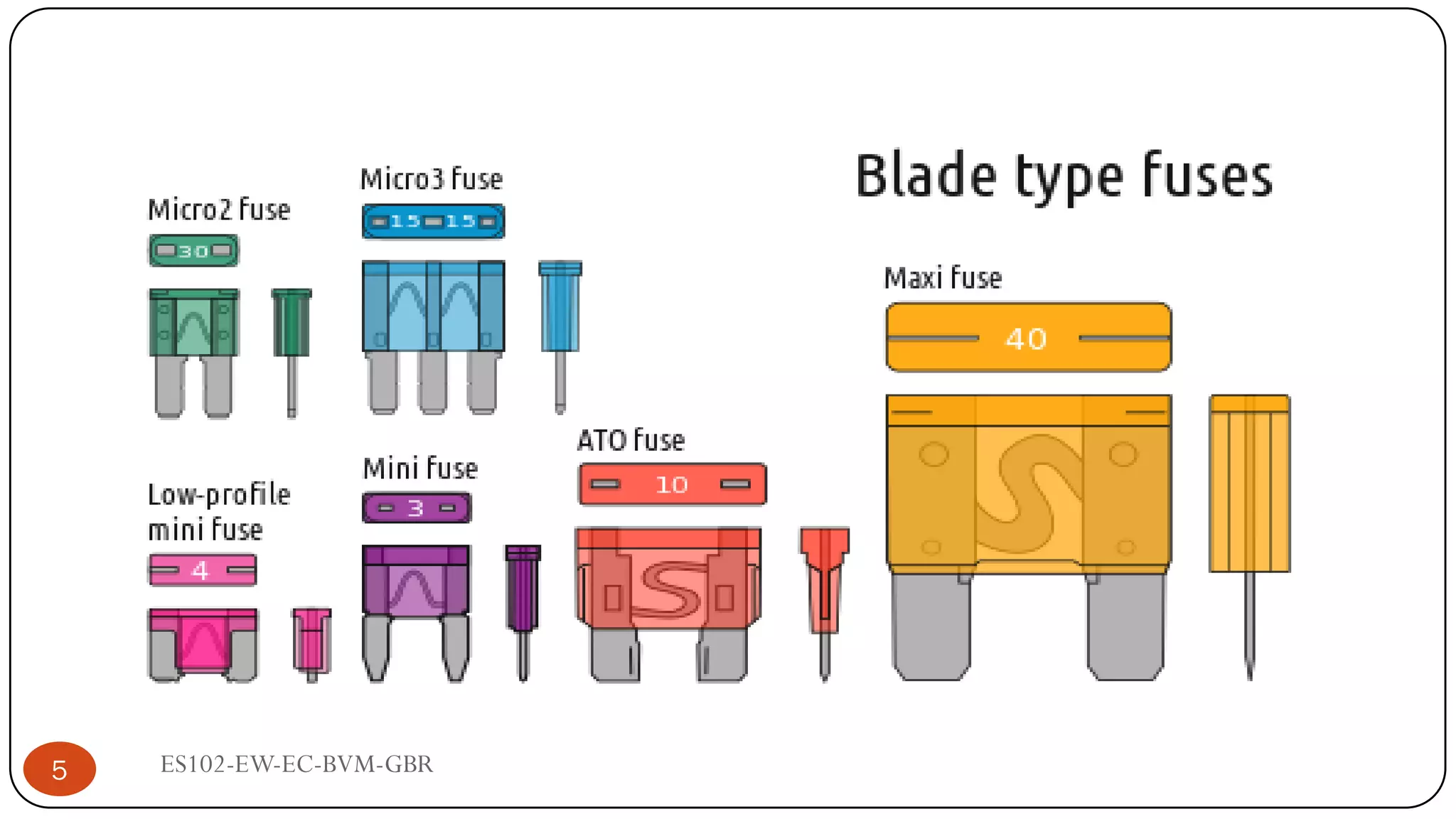
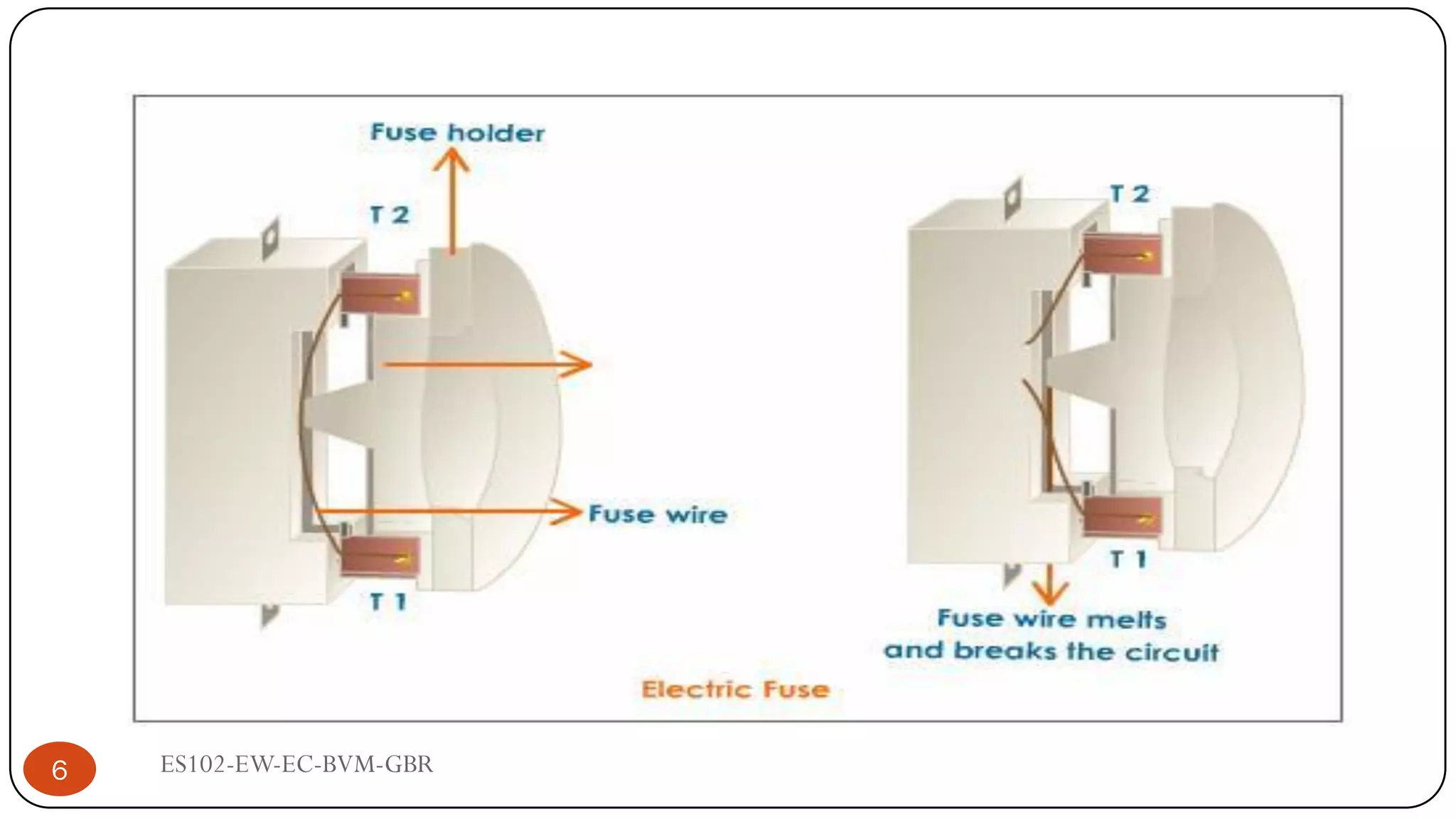
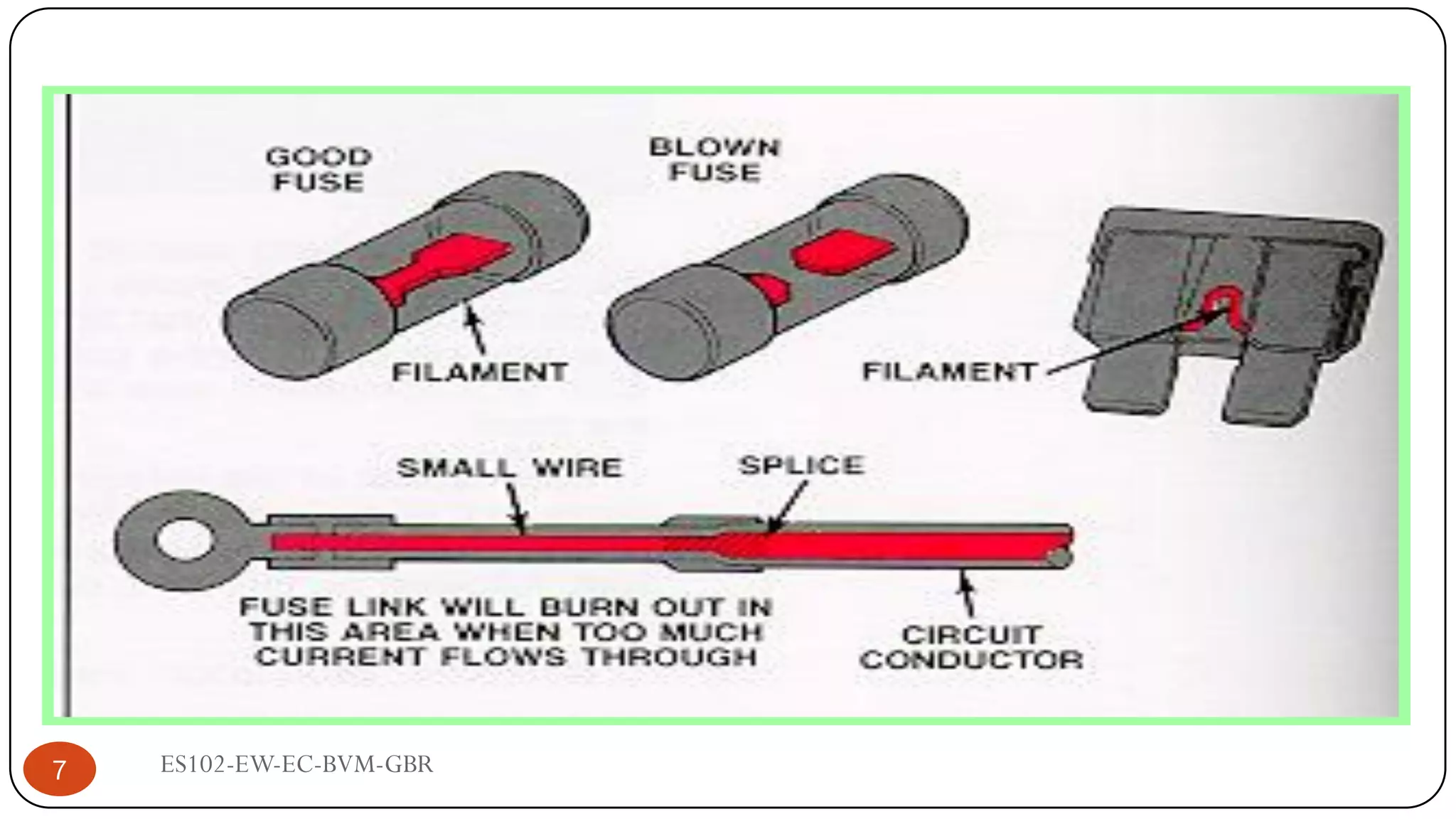
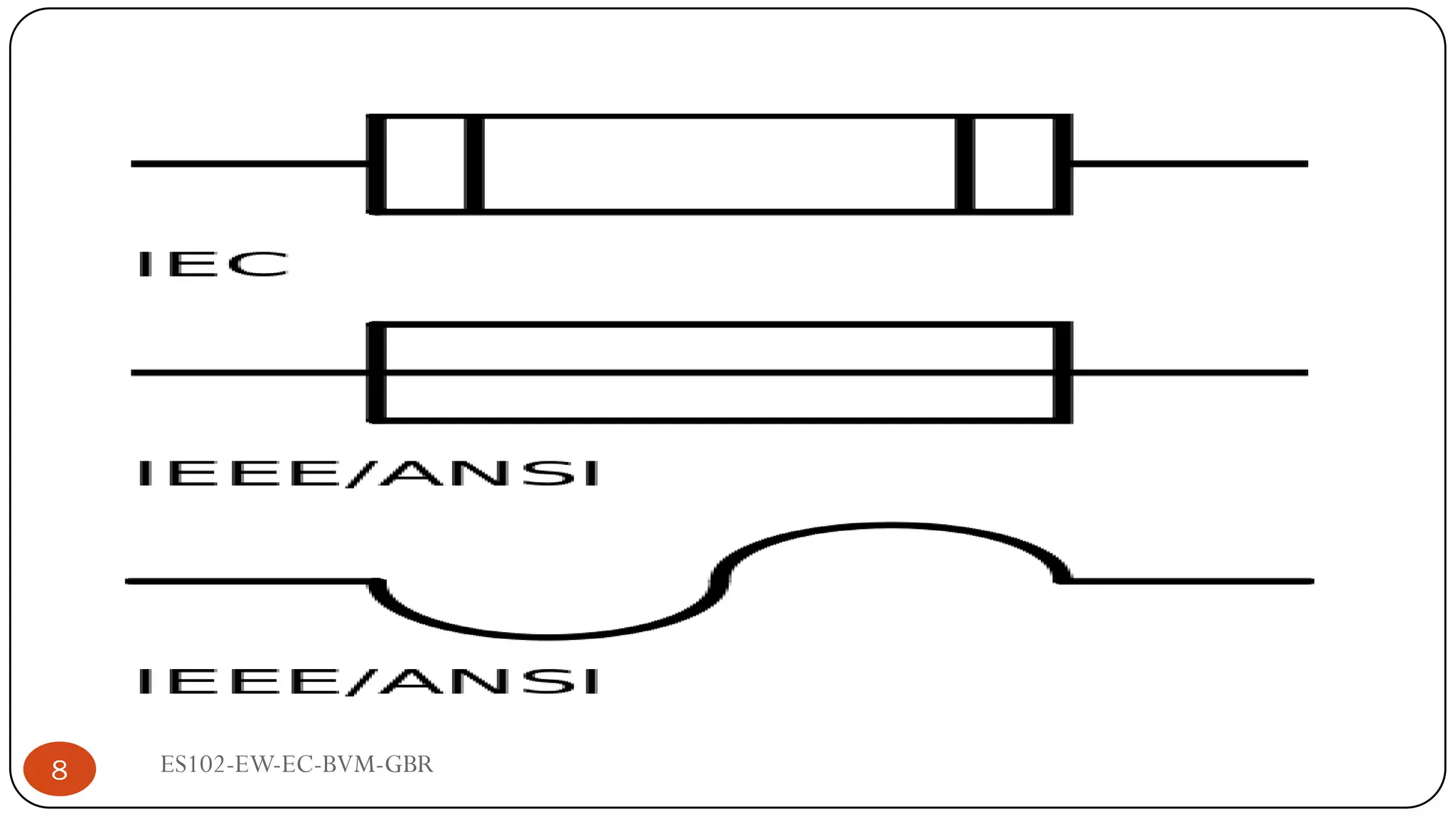
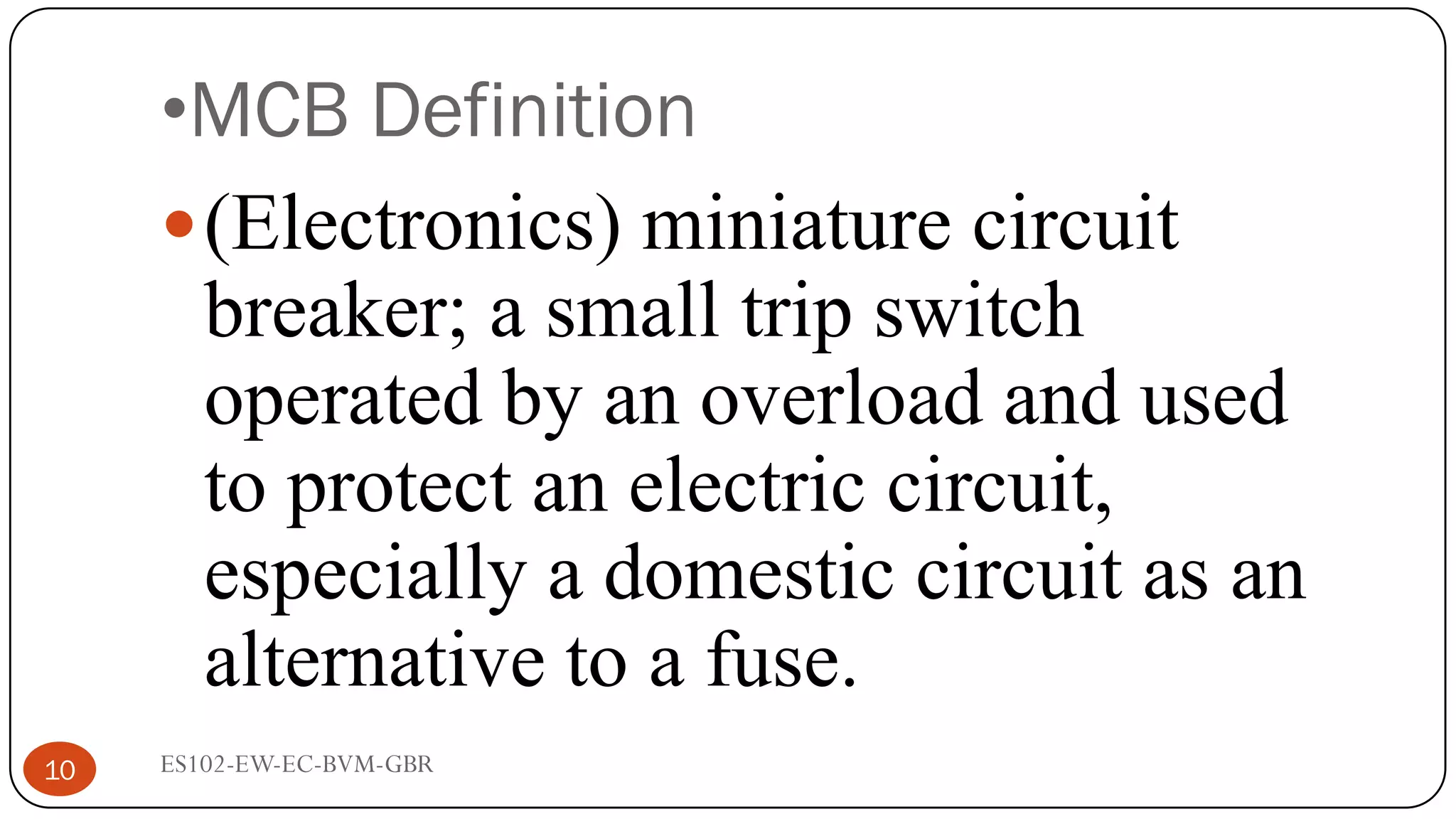
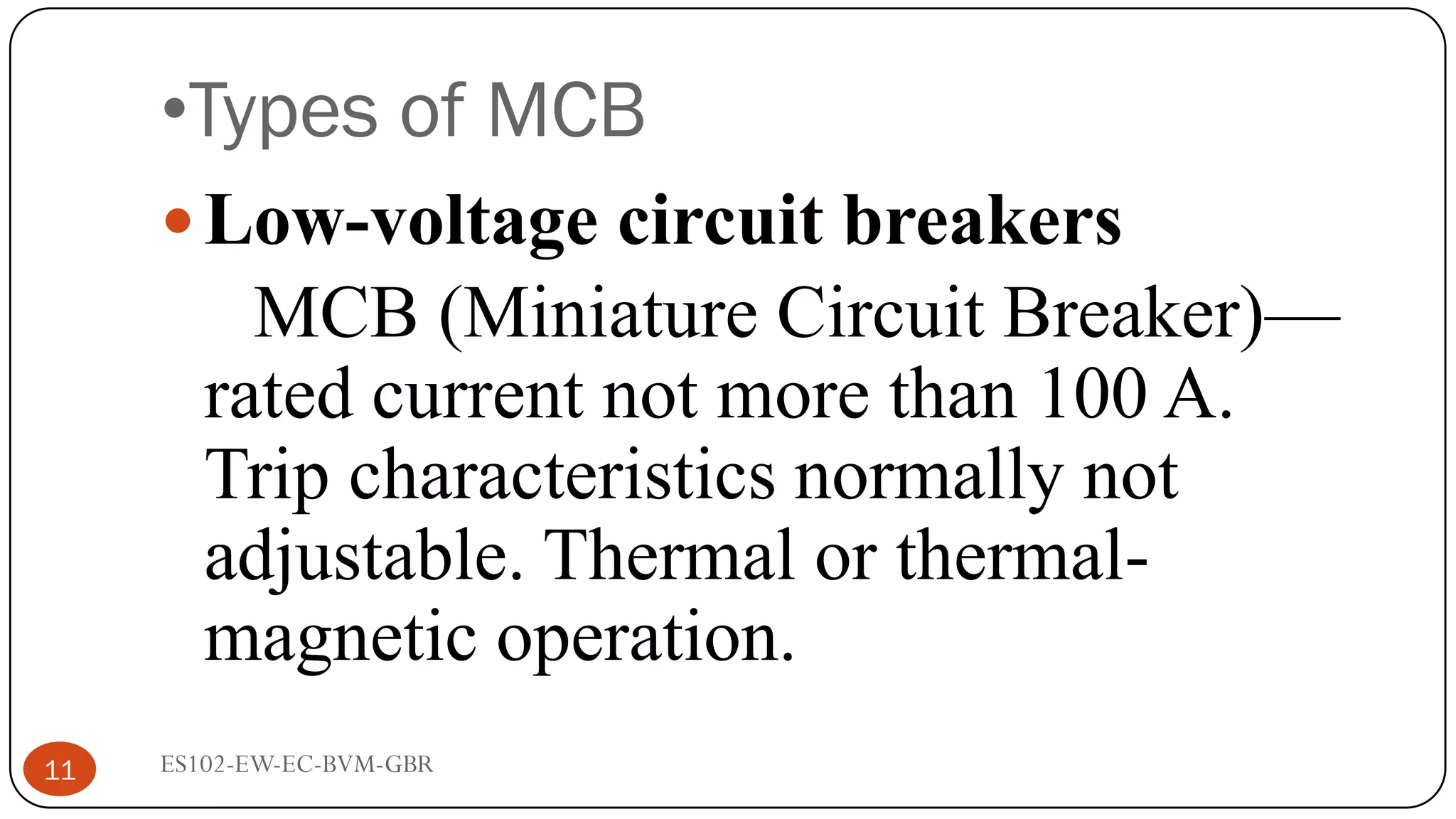
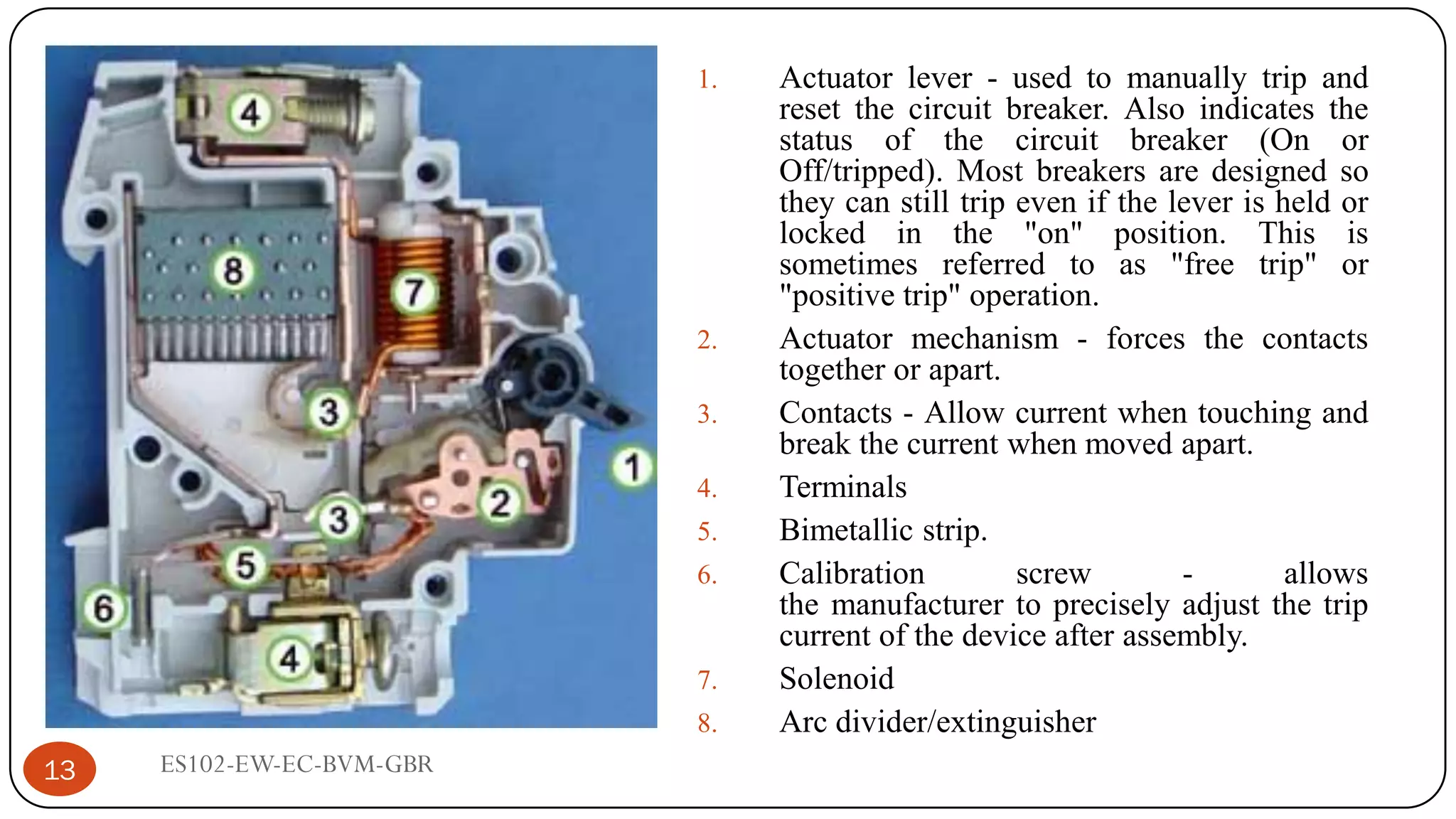
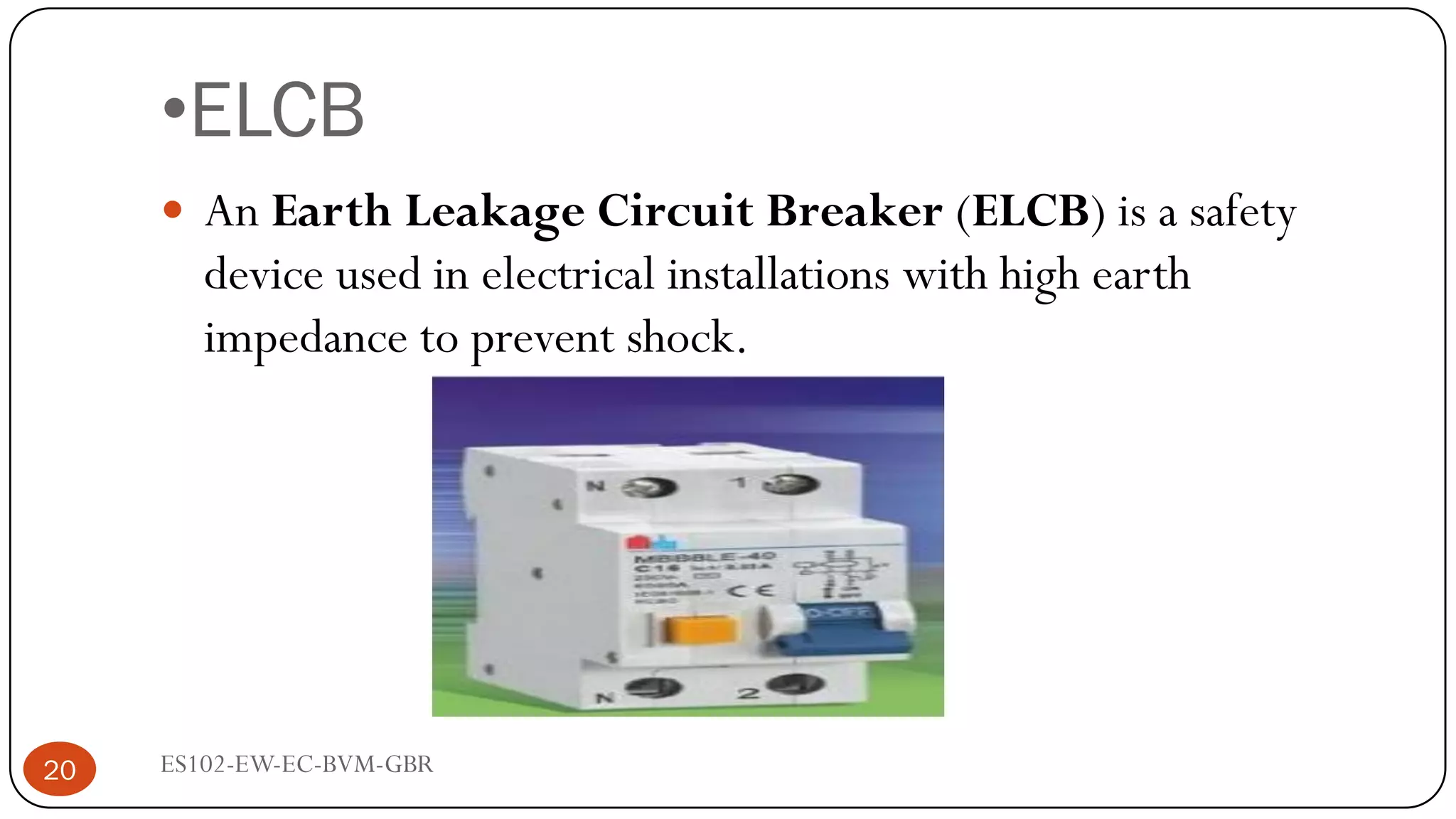
The document is a lecture on fuses, miniature circuit breakers (MCBs), and earth leakage circuit breakers (ELCBs) by Professor G. B. Rathod. It defines fuses as sacrificial devices that provide overcurrent protection, and describes common fuse types like automotive and high voltage fuses. MCBs are defined as small trip switches that protect electric circuits from overloads, and the types of MCBs like low-voltage, magnetic, and thermal-magnetic are outlined. ELCBs are safety devices that prevent electric shocks, and voltage-operated and current-sensing ELCBs are introduced.