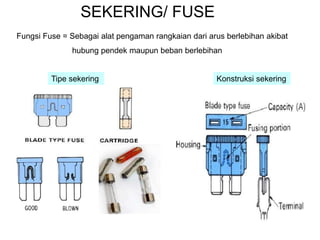
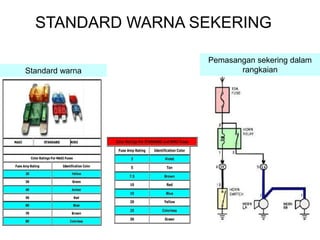
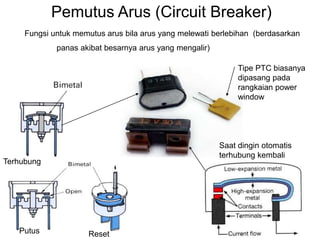
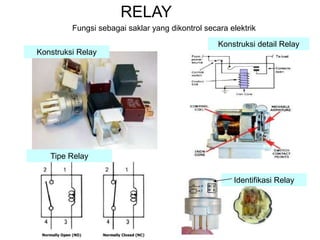
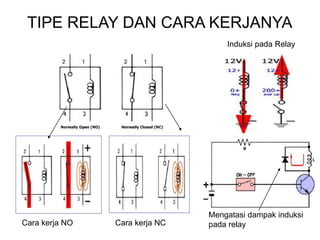
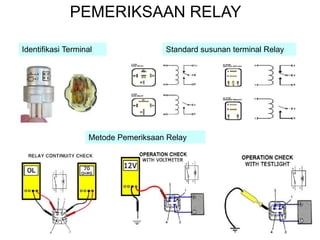
1. A circuit breaker is a manually or automatically operated switch that protects electrical circuits from damage caused by overload or short circuit.
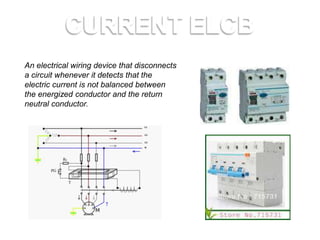
2. An ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) is a safety device used in electrical installations to prevent electric shock by detecting currents leaking to earth. There are two types of ELCBs: voltage-ELCB and current-ELCB.
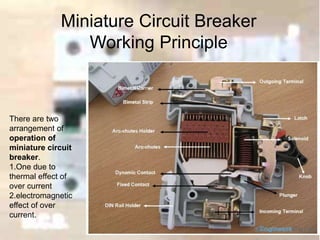
3. An MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) automatically switches off an electrical circuit during abnormal network conditions like overloads or faults. It provides overcurrent protection and is safer to handle than a fuse.