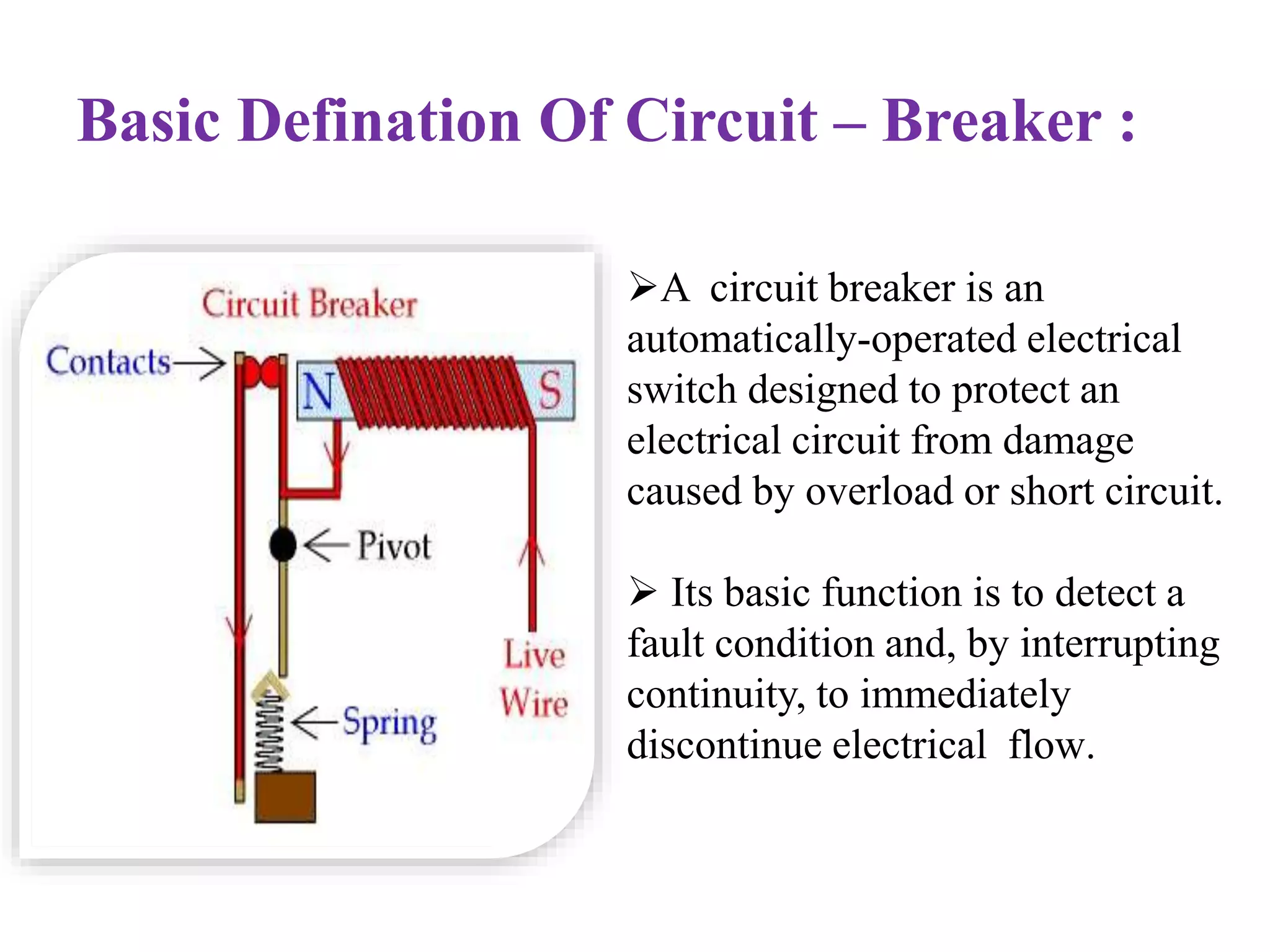
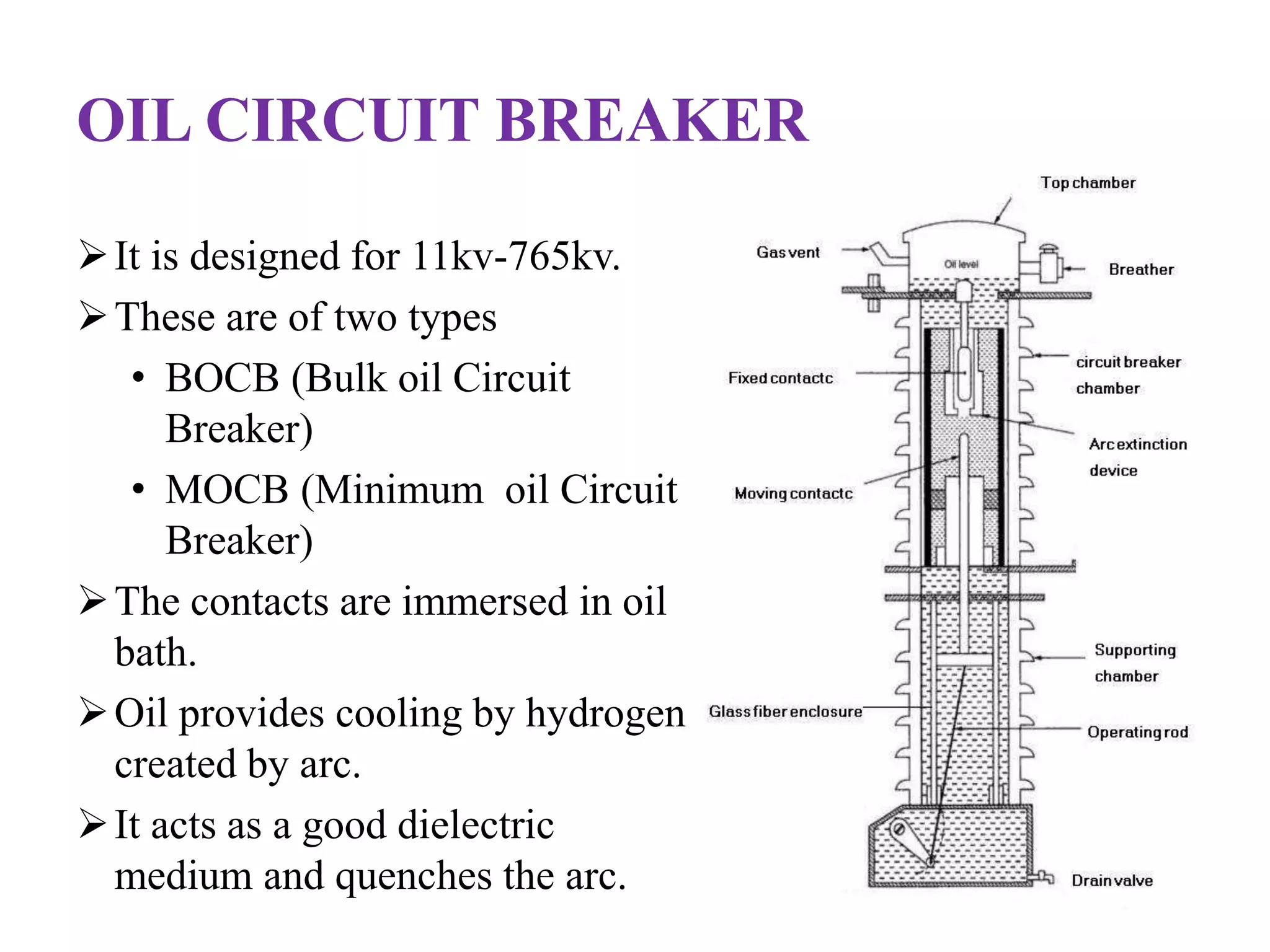
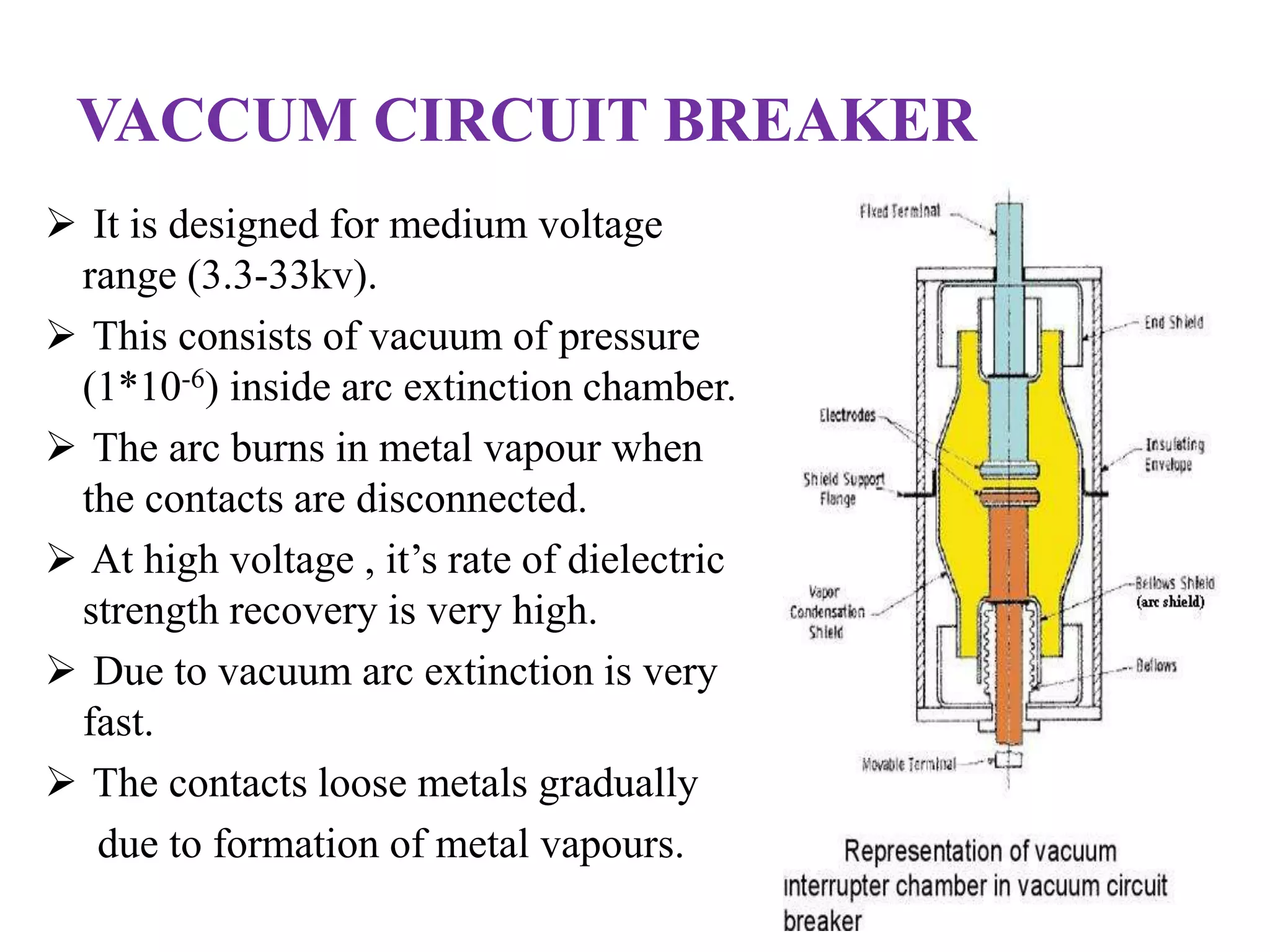
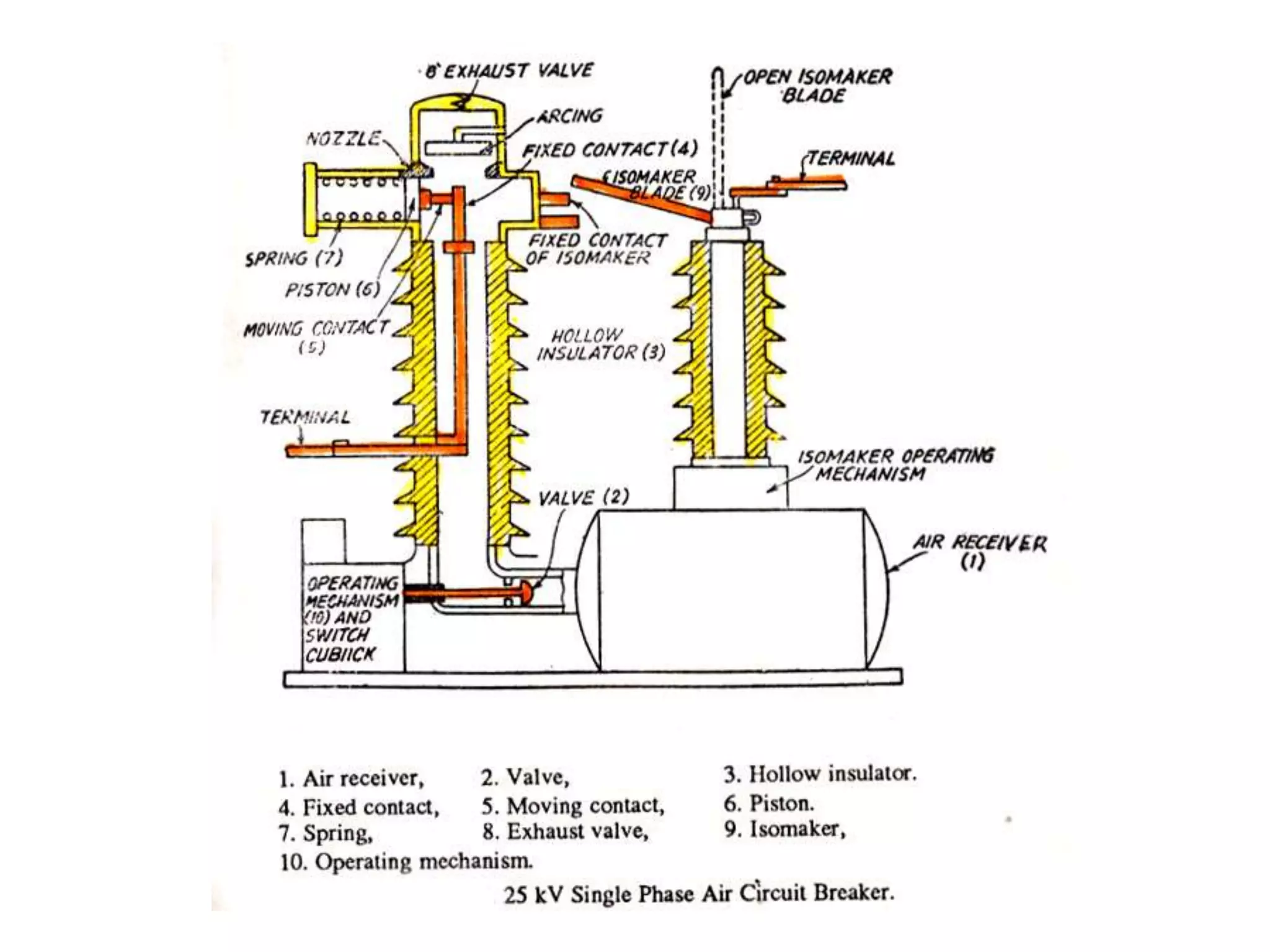
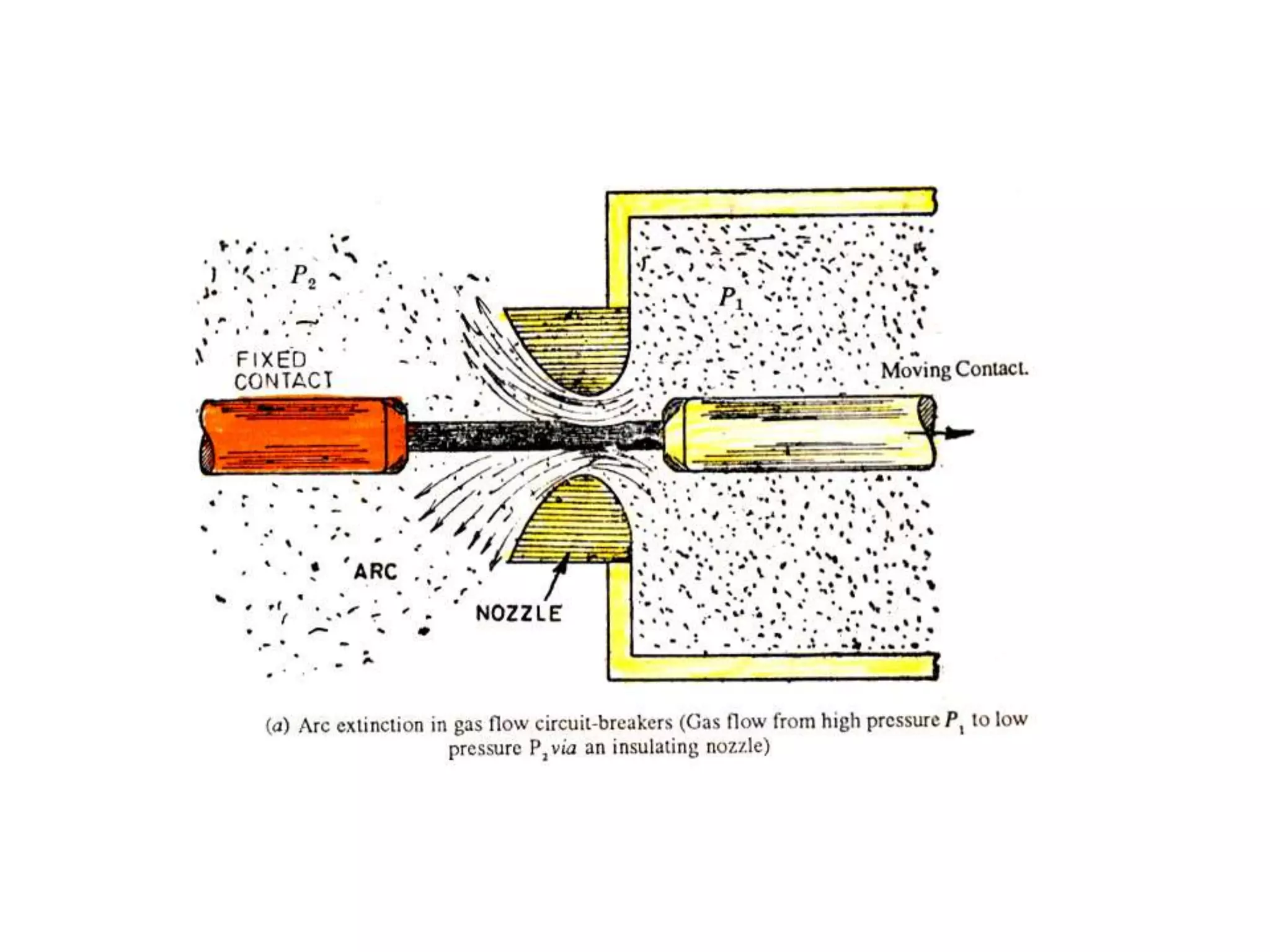
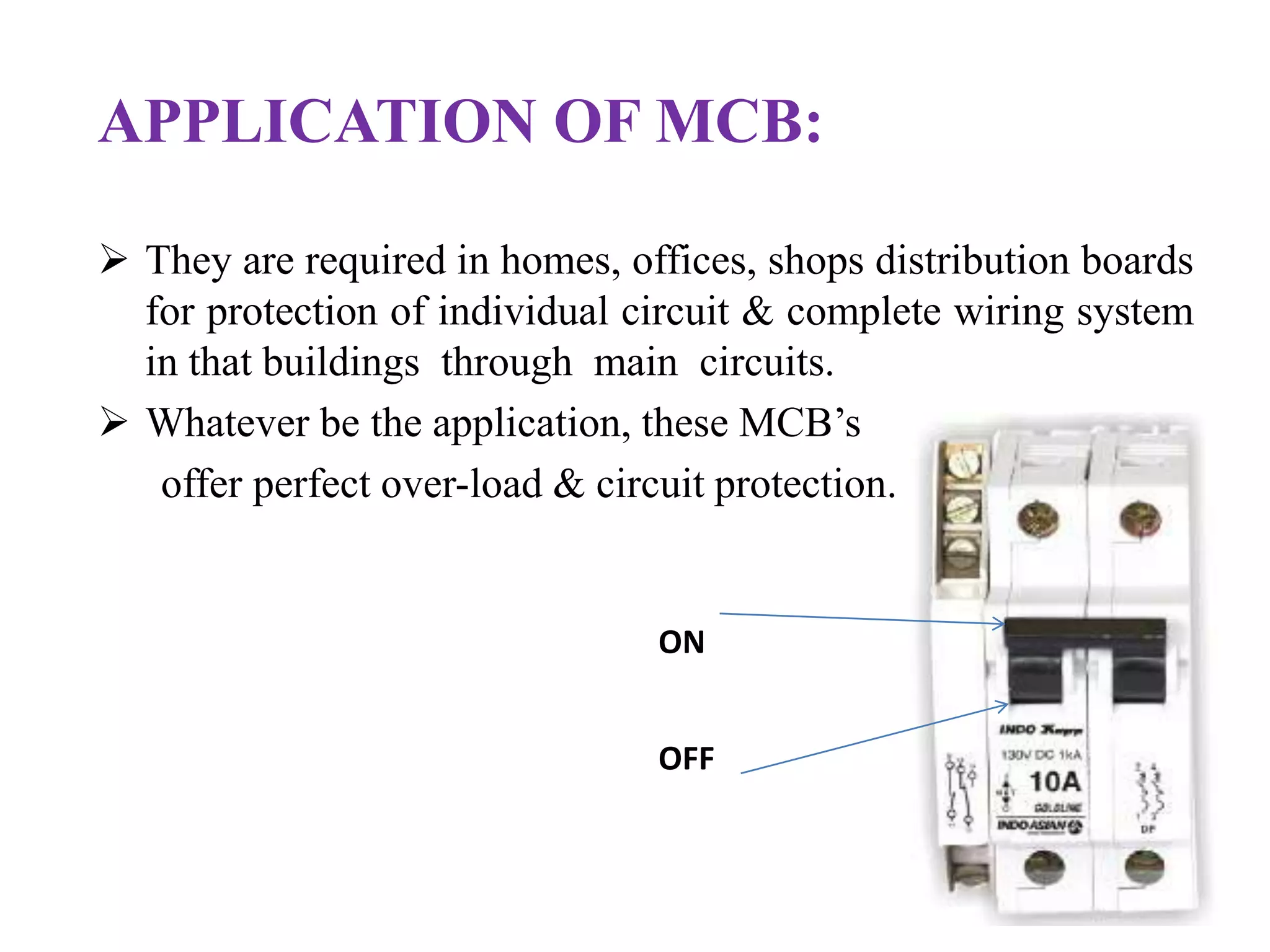
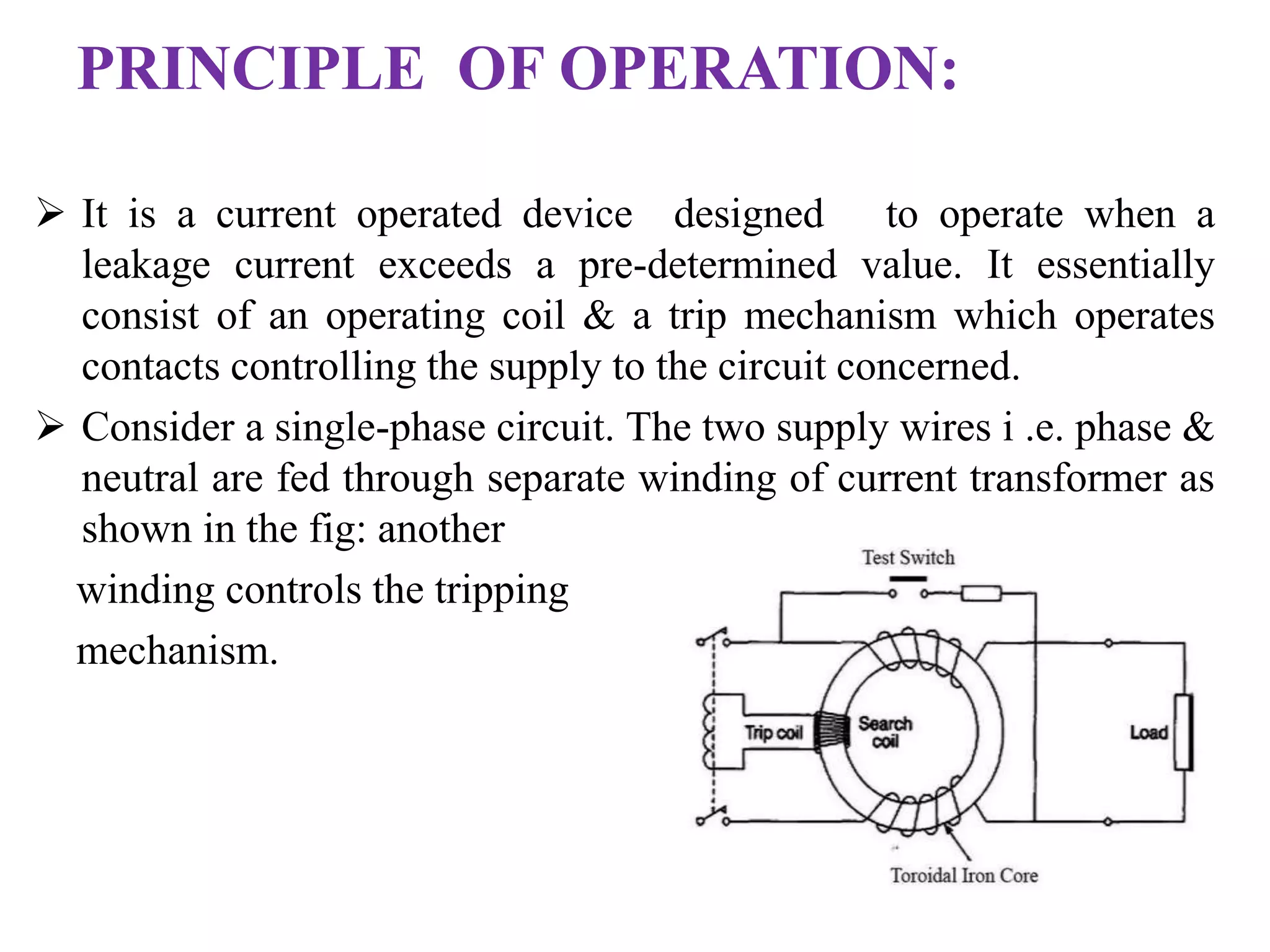
The document provides an overview of circuit breakers, detailing their definitions, working principles, types, advantages, and disadvantages. It specifically discusses various types such as oil, vacuum, air blast, SF6, miniature, and earth leakage circuit breakers. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of circuit breakers in protecting electrical networks and devices from damage, highlighting the increasing use of vacuum and SF6 circuit breakers for their reliability and efficiency.