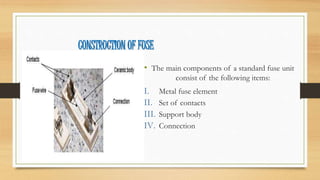
This document was prepared by a group of students and provides information on electrical circuit protection devices including fuses, MCBs, ELCBs, and relays. It describes the components, construction, advantages, disadvantages and specifications of fuses. MCBs are described as having features of both fuses and switches. ELCBs provide protection against electric shock from ground faults. Relays are used to control circuits using low power signals or to control multiple circuits with one signal, and contactors can handle high power loads. In conclusion, the document was prepared after studying these circuit protection devices from course materials and online sources.