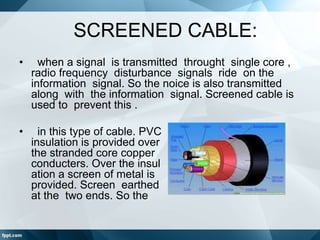
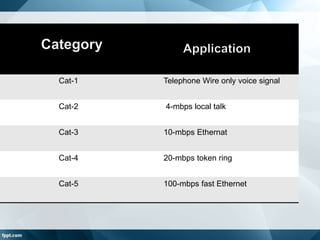
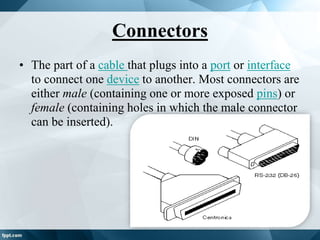
Cables are used to carry electric signals and come in different types for various applications. Cable specifications include characteristic impedance, current carrying capacity, size, and flexibility. Common cable types include ribbon, screened, coaxial, twisted pair, and fiber optic cables. Coaxial cable has an inner conductor surrounded by insulation and an outer shield, and is used for applications requiring minimal interference such as TV and radio frequency signals. Twisted pair cable has multiple insulated conductor pairs that are twisted together to reduce interference, and is used for voice and data communication. Fiber optic cable uses glass fibers to transmit data using light rather than electricity.