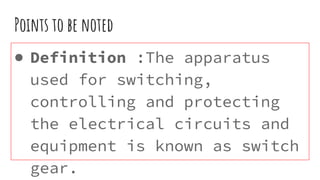
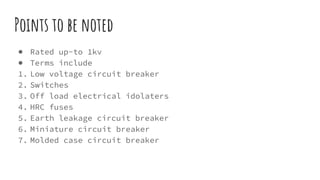
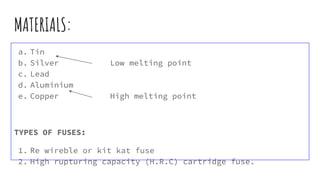
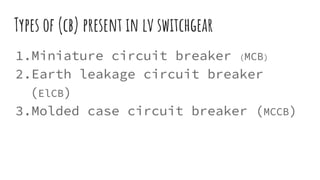
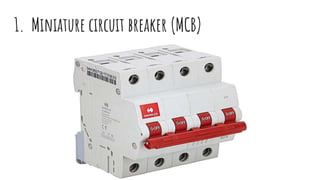
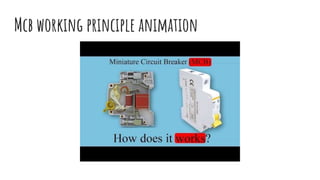
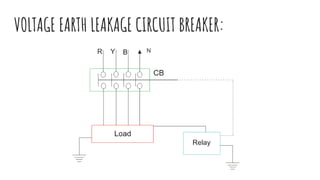
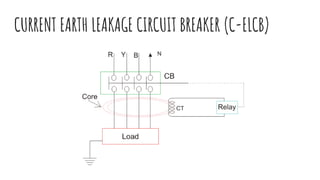
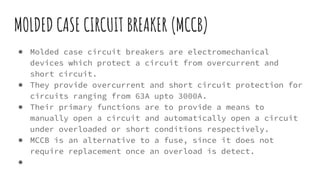
The document discusses different components of low voltage switchgear including switch fuse units, miniature circuit breakers, earth leakage circuit breakers, and molded case circuit breakers. It describes their working principles and applications. Protective devices like fuses, MCBs, ELCBs, and MCCBs are used to isolate faulty circuits and protect electrical equipment from overloads, short circuits, and earth faults. MCBs and ELCBs protect at the distribution level while MCCBs are used for high current industrial applications and main feeder protection.