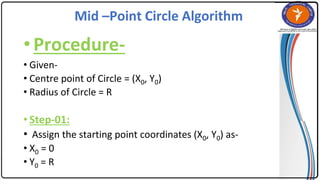
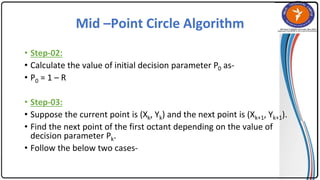
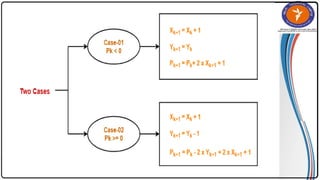
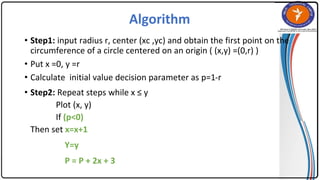
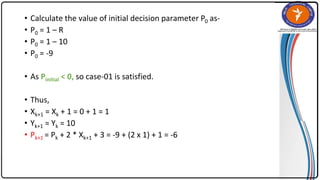
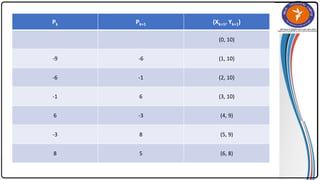
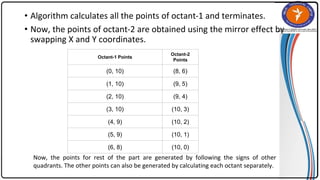
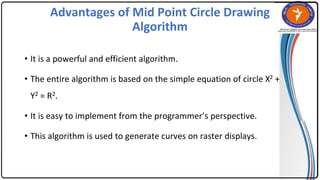
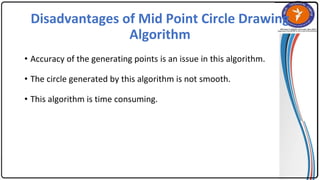
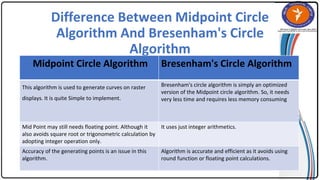
The document summarizes the midpoint circle algorithm. It explains that the algorithm takes a center point and radius as inputs and generates points on the circumference of a circle by starting at one point and using a decision parameter P to iteratively calculate the next point. It provides pseudocode for the algorithm's steps. As an example, it applies the algorithm to generate all points of a circle with center (0,0) and radius 10. The document also lists advantages like its simplicity and efficiency, and disadvantages like lower accuracy and being time consuming compared to Bresenham's circle algorithm.