The document outlines various algorithms for drawing lines and circles in computer graphics, focusing on the Digital Differential Analyzer (DDA) and Bresenham's line drawing algorithms. It describes the steps and calculations involved in each algorithm and highlights the advantages of Bresenham's algorithm over DDA due to its improved accuracy in pixel plotting. Additionally, it briefly explains the midpoint circle drawing algorithm and provides mathematical examples for implementing these algorithms.

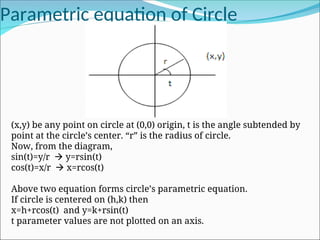
![Digital Differential Analyzer Algorithm(DDA)
Cartesian slope-intercept equation for a straight line,
y=mx+b (m=slope, b= y-intercept)
m=dy/dx= y/ x
∆ ∆
b= y1-mx1
Now, case 1:- (|m|<1)
yi=mxi+b
yi+1=m(xi+1)+b
=mxi+m+b
= yi+m
Case 2:- (|m|>1)
xi=(yi-b)/m
xi+1=(yi+1-b)/m
=[(yi-b)/m] + [1/m]
= xi+1/m](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-250102092830-04329c44/85/2-Line-circle-drawing-ppt-line-circlw-drawing-algorith-2-320.jpg)
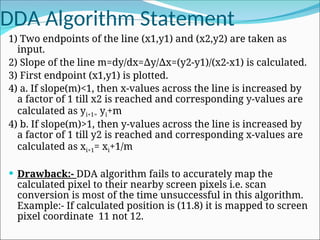
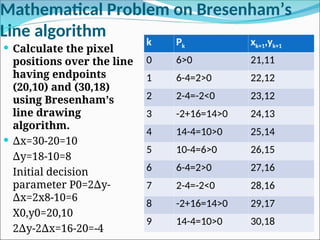
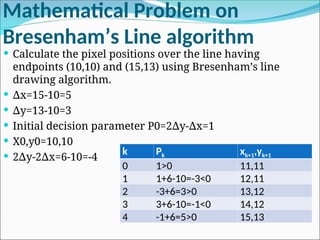
![Problem on DDA Algorithm
Problem:-
Two endpoints of line are (10,10) and (20,16). Find all
coordinates of pixels over the line using DDA algorithm.
Solution:-
Slope of line(m) = y/ x =16-10/ 20-10=6/10=0.6
∆ ∆
Points are as follows:- [xi+1= xi+1 and yi+1= yi+m]
<10,10>
<11,10+0.6>=<11,10.6>
<12,10.6+0.6>=<12,11.2>
<13,11.2+0.6>=<13,11.8>
<14,11.8+0.6>=<14.12.4>
<15,12.4+0.6>=<15,13>
<16,13+0.6>=<16,13.6>
<17,13.6+0.6>=<17,14.2>
<18,14.2+0.6>=<18,14.8>
<19,14.8+0.6>=<19,15.4>
<20,15.4+0.6>=<20,16>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-250102092830-04329c44/85/2-Line-circle-drawing-ppt-line-circlw-drawing-algorith-4-320.jpg)
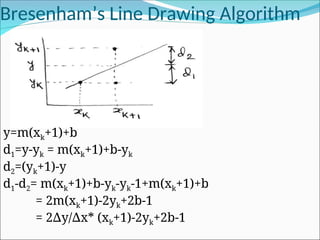
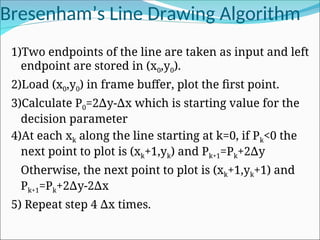
![Bresenham’s Line Drawing Algorithm
∆x(d1-d2)= 2 yx
∆ k+2 y -2 xy
∆ ∆ k+2 xb- x
∆ ∆
Now, Pk=2 yx
∆ k-2 xy
∆ k+c where, c=2 y+ x(2b-1) [P
∆ ∆ k= x(d
∆ 1-d2)]
Pk+1=2 yx
∆ k+1-2 xy
∆ k+1+c where, xk+1=xk+1
Pk+1-Pk=2 yx
∆ k+2 y-2 xy
∆ ∆ k+1-2 yx
∆ k+2 xy
∆ k
Pk+1=Pk+2 y-2 x(y
∆ ∆ k+1-yk) Now, yk+1= yk or yk+1
Either 0 or 1
P0=2 yx
∆ k-2 xy
∆ k+c y0=mx0+b= y/ x*x
∆ ∆ 0+b
=2 yx
∆ k-2 xy
∆ k+2 y+ x(2b-1)
∆ ∆ xy
∆ 0= yx
∆ 0+ xb
∆
=2 yx
∆ 0-2 xy
∆ 0+2 y+ x(2b-1)
∆ ∆
=2 yx
∆ 0-2 yx
∆ 0-2 xb+2 y+2 xb- x
∆ ∆ ∆ ∆
= 2 y- x
∆ ∆](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-250102092830-04329c44/85/2-Line-circle-drawing-ppt-line-circlw-drawing-algorith-6-320.jpg)

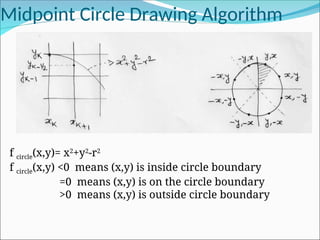
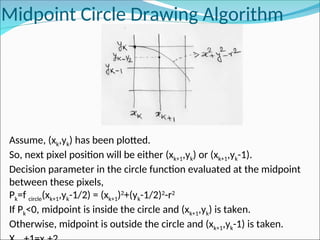
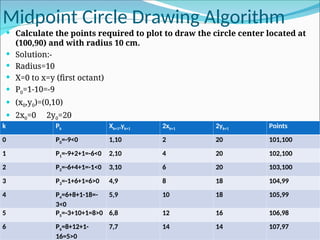
![Midpoint Circle Drawing Algorithm
Pk+1=f circle(xk+1+1, yk+1-1/2)
= [(xk+1)+1]2
+ [yk+1-1/2]2
-r2
Pk+1-Pk= (xk+1)2
+1+2(xk+1)+yk+1
2
+1/4-yk+1-r2
-(xk+1)2
-yk
2
-
1/4+yk+r2
= 2(xk+1) + (yk+1
2
-yk
2
)-(yk+1-yk)+1
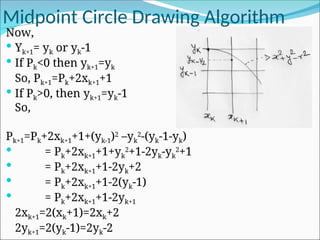
So, Pk+1=Pk+2(xk+1)+(yk+1
2
-yk
2
)-(yk+1-yk)+1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-250102092830-04329c44/85/2-Line-circle-drawing-ppt-line-circlw-drawing-algorith-13-320.jpg)