The document describes several algorithms for drawing circles:
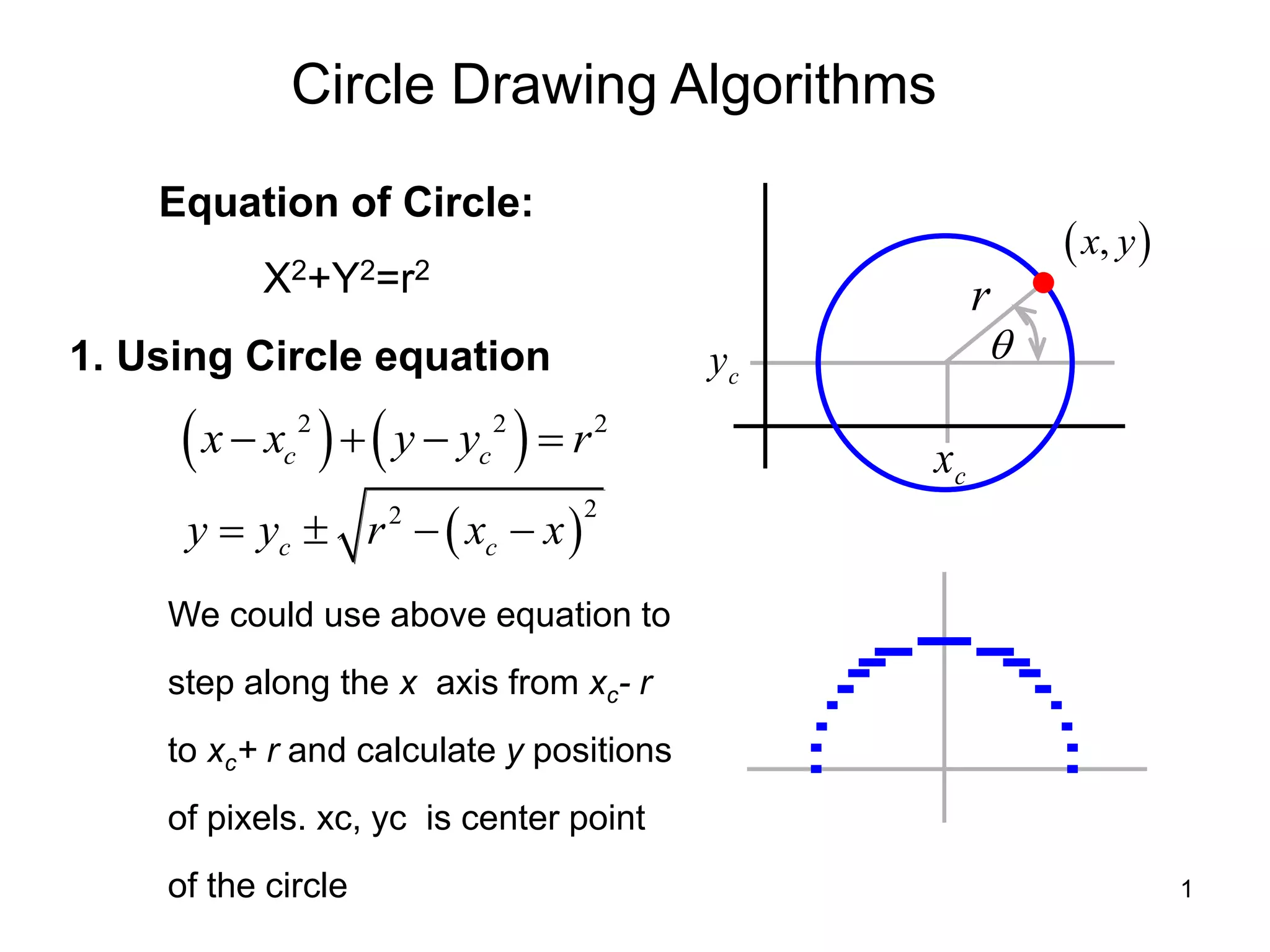
1. Using the circle equation requires significant computation and results in a poor appearance.
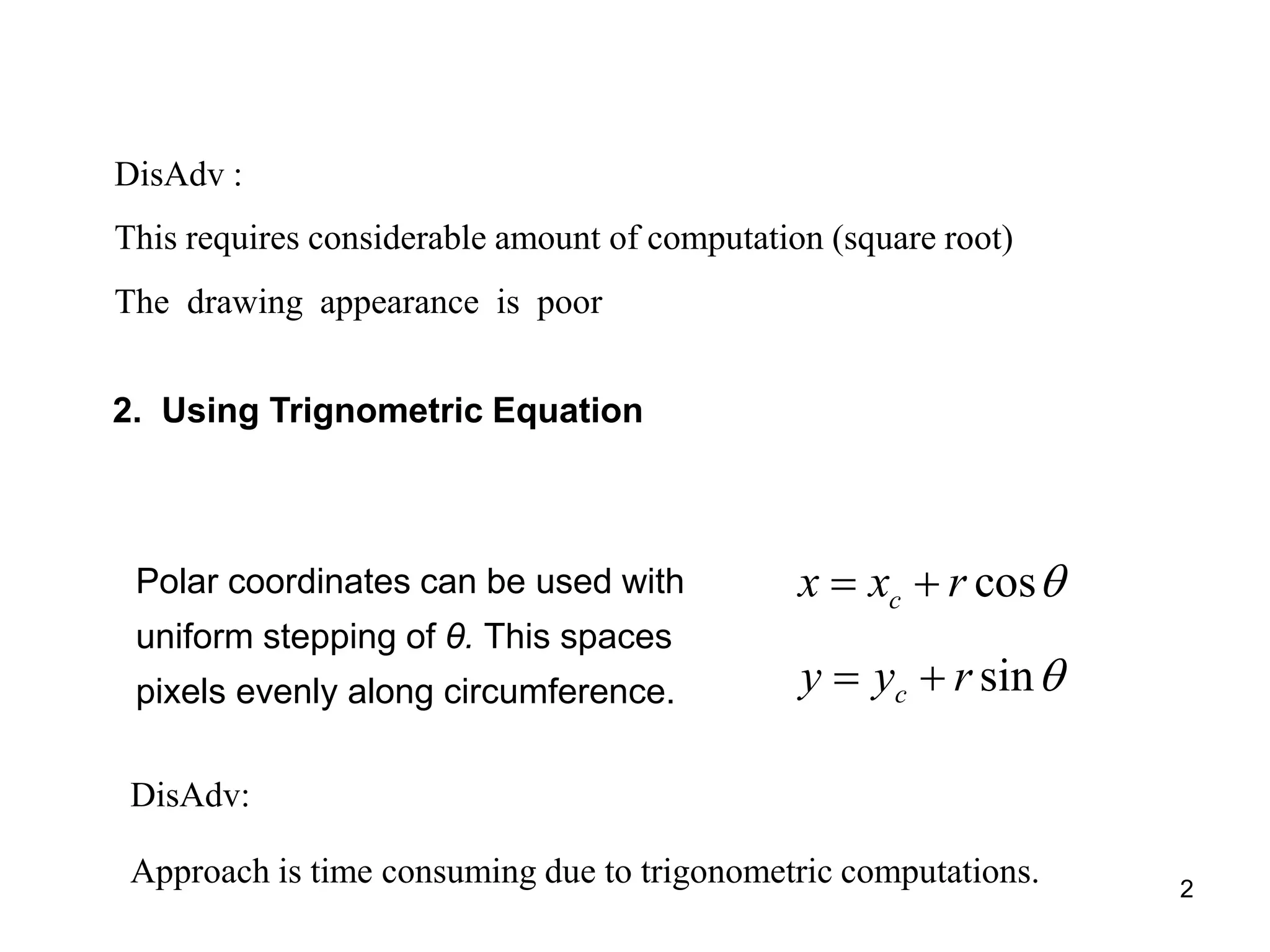
2. Using trigonometric functions is time-consuming due to trig computations.
3. The midpoint circle algorithm uses the midpoint between candidate pixels to determine which is closer to the actual circle. It has less computation than the circle equation.
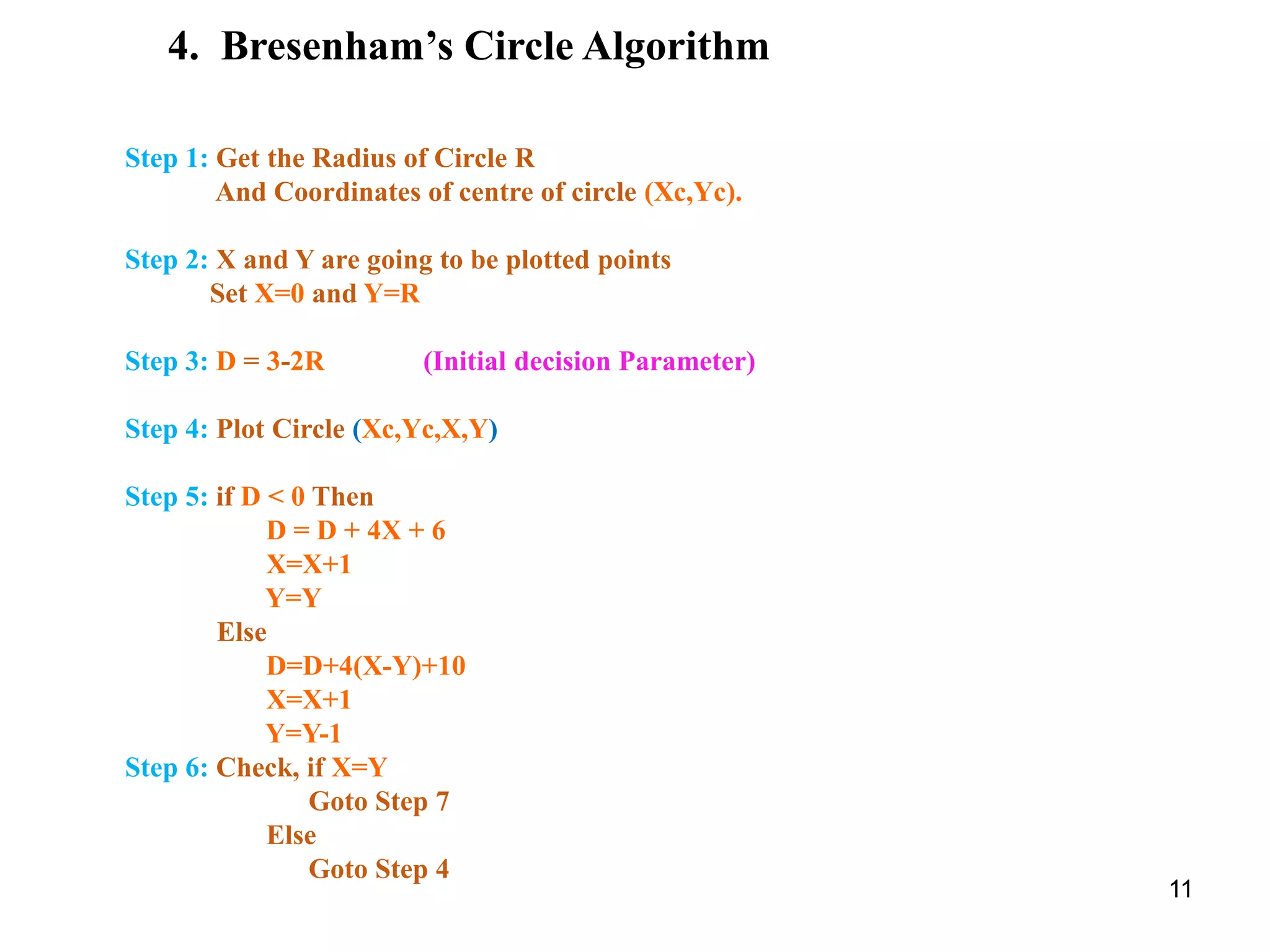
4. Bresenham's circle algorithm uses a decision parameter D to iteratively select the next pixel, requiring fewer computations than trigonometric functions.