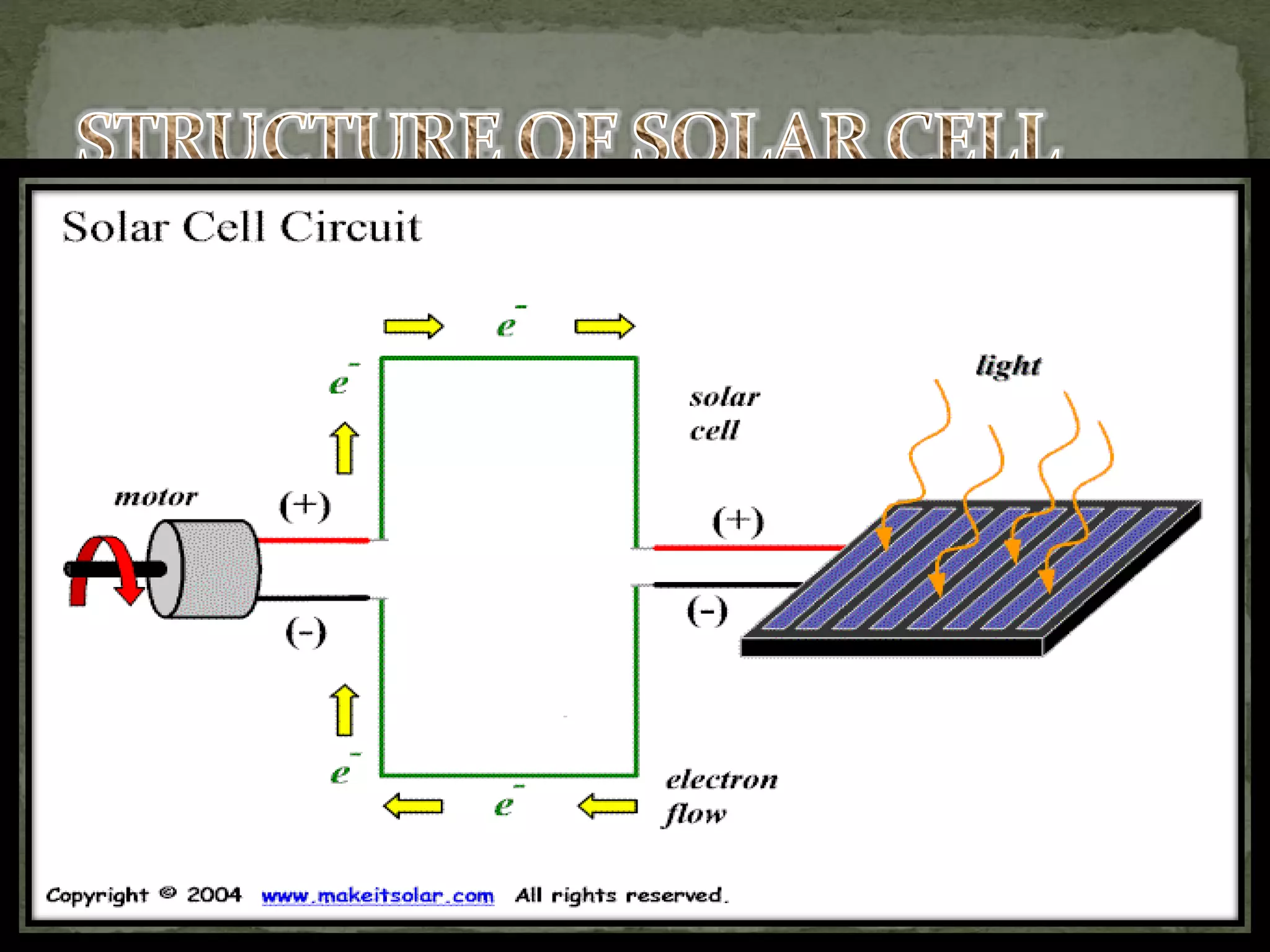
The document discusses various types of electrochemical cells, including electrolytic, fuel, galvanic, cylindrical, button, prismatic, pouch cells, and solar cells. Each type has specific uses and characteristics, such as the electrolytic cell for electrolysis, fuel cells for converting chemical energy into electricity, and solar cells for converting light into electricity. The document also covers design considerations and applications for different cell types in technology.




![ A fuel cell is a device that converts the chemical energy from a fuel
into electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen or another
oxidizing agent.[1] Hydrogen is the most common fuel, but
hydrocarbons such as natural gas and alcohols like methanol are
sometimes used.
Fuel cells are different from batteries in that they require a constant
source of fuel and oxygen/air to sustain the chemical reaction.
In 1838, German Physicist Christian Friedrich Schönbein invented
the first crude fuel cell.
The first commercial use of fuel cells was in NASA space programs to
generate power for probes, satellites and space capsules.
Fuel cells are used for primary and backup power .
They are used to power fuel cell vehicles, including automobiles,
buses, forklifts, airplanes, boats, motorcycles and submarines.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/p-160617111704/75/P-p-t-on-types-of-electric-cells-5-2048.jpg)
![ A galvanic cell, or voltaic cell, named
after Luigi Galvani, or Alessandro Volta
respectively, is an electrochemical cell
that derives electrical energy from
spontaneous redox reaction taking
place within the cell. It generally
consists of two different metals
connected by a salt bridge, or individual
half-cells separated by a porous
membrane.
Volta was the inventor of the voltaic
pile, the first electrical battery. In
common usage, the word "battery" has
come to include a single galvanic cell,
but a battery properly consists of
multiple cells.[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/p-160617111704/75/P-p-t-on-types-of-electric-cells-6-2048.jpg)