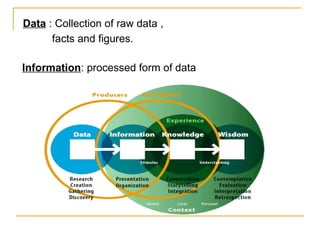
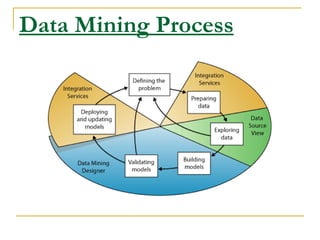
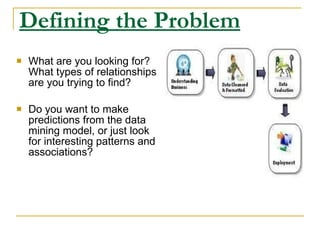
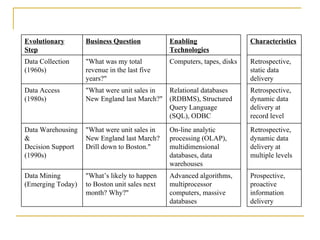
Data mining involves extracting useful patterns from large amounts of data. It involves defining a problem, preparing data, exploring data, building models, and deploying models. Some common applications of data mining include analyzing customer purchasing patterns, detecting fraud, predicting disease outbreaks, and analyzing financial/business data. While data warehousing provides insights into past trends, data mining can discover hidden patterns to predict future trends and behaviors from data.