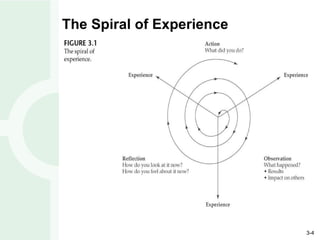
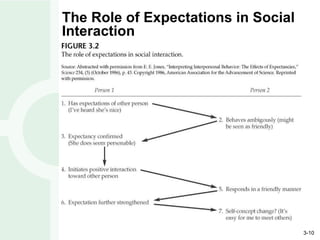
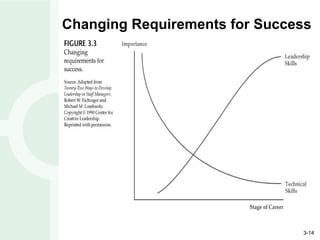
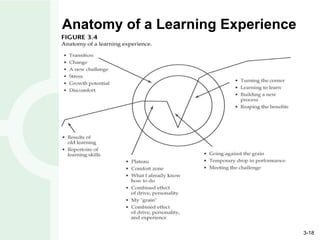
Leadership development is enhanced through experiences involving action, observation, and reflection. Perception affects all three phases and how experiences are interpreted. Reflection provides leaders insights to frame problems from multiple perspectives. Education and training programs can help people become better leaders, but leadership primarily develops through meaningful experiences over time with challenges that push individuals outside their comfort zone.