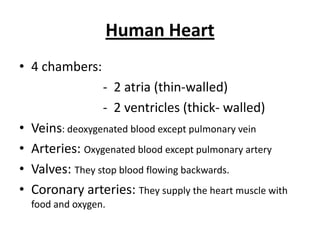
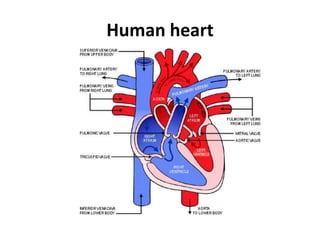
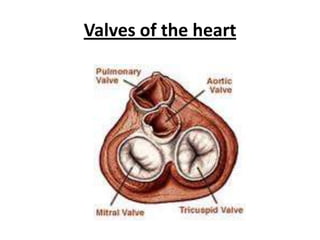
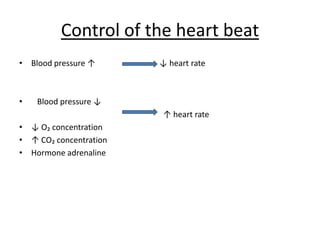
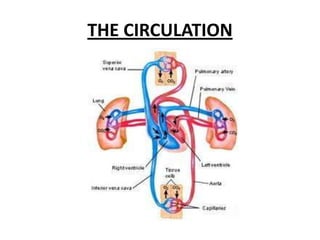
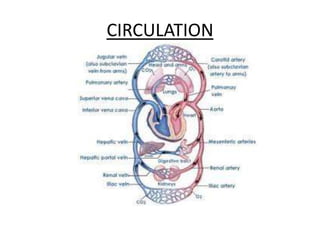
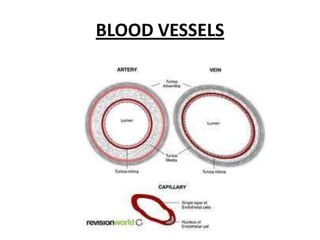
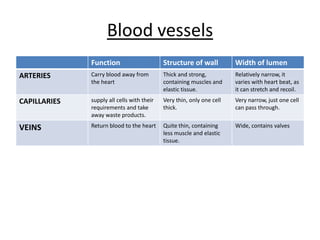
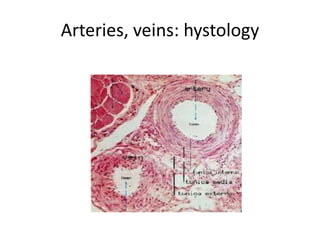
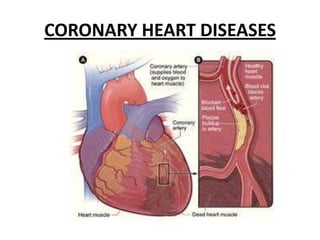
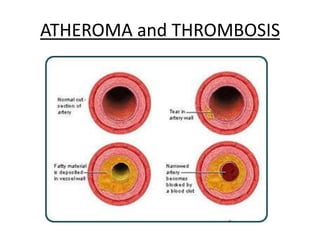
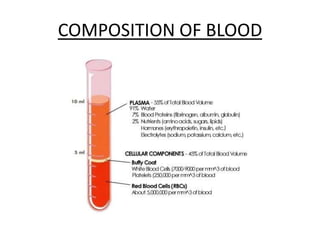
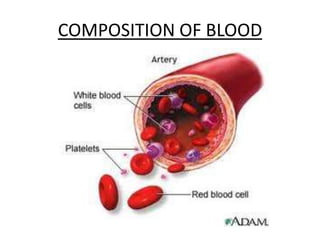
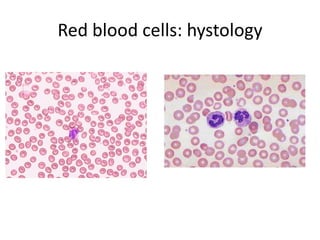
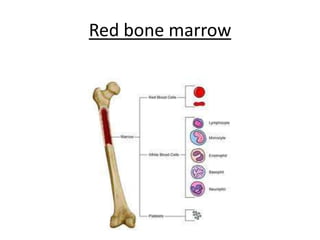
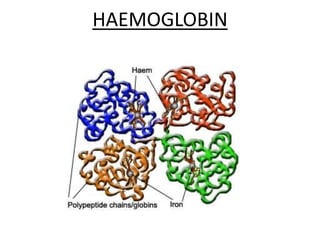
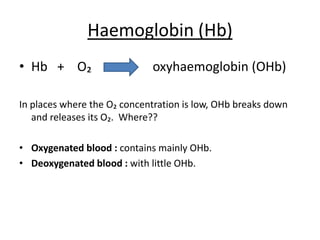
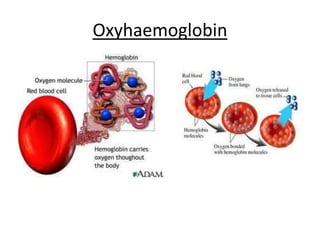
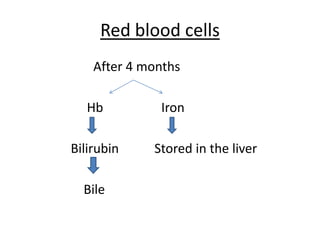
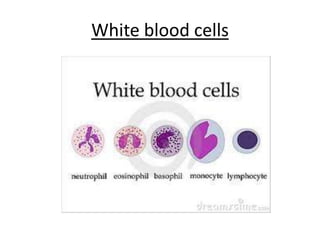
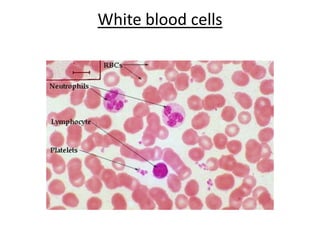
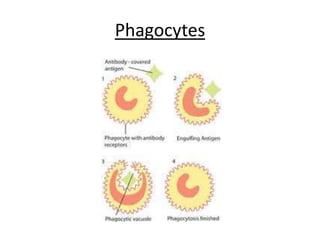
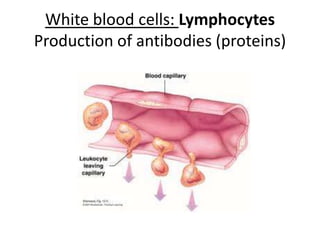
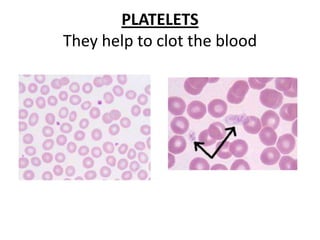
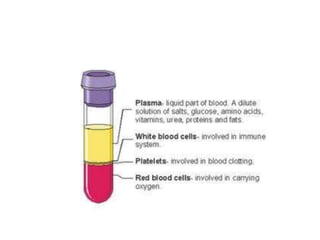
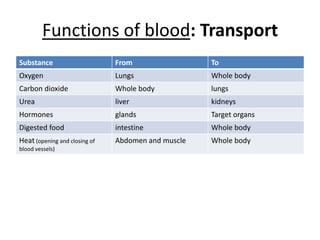
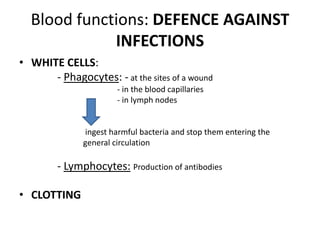
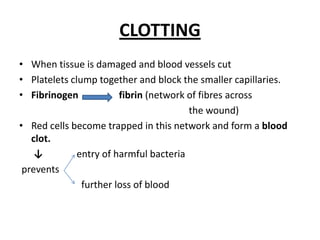
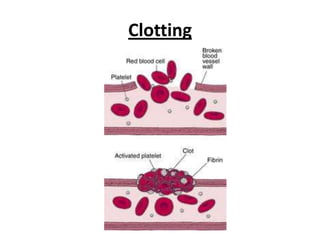
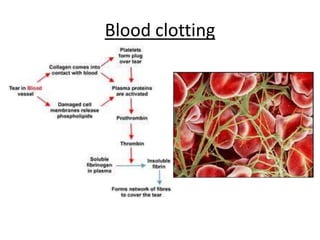
The human heart has four chambers - two atria and two ventricles - that work together to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart beats regularly due to a group of pacemaker cells in the right atrium that initiate each heartbeat. Factors like blood pressure, oxygen levels, and hormones can influence the heart rate. Blood vessels carry oxygenated and deoxygenated blood between the heart and tissues via arteries and veins. Coronary heart disease occurs when fatty deposits build up in the arteries and restrict blood flow.