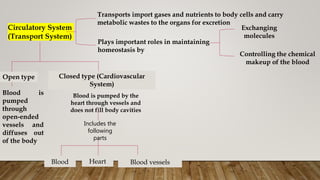
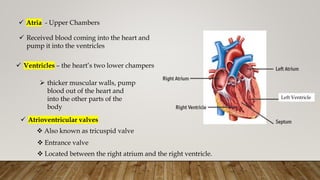
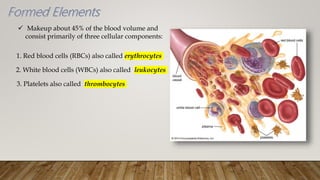
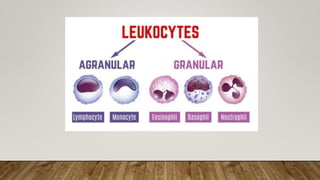
Here is a chart showing the components of human blood, their functions, and relative proportions by blood volume:
Component Function Proportion of blood volume
Plasma - Carries cells and molecules
- Maintains osmotic pressure
- Involved in clotting 55% (about 90% water)
Red blood cells - Carry oxygen to tissues
- Carry carbon dioxide from tissues 40%
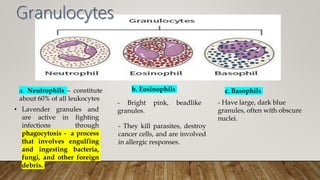
White blood cells - Fight infection and disease <1%
- Neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, etc.
Platelets - Involved in clotting process <1%
The major components that make up the formed elements (cells)