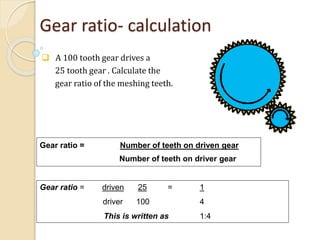
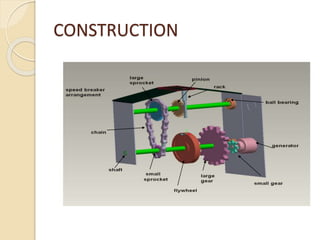
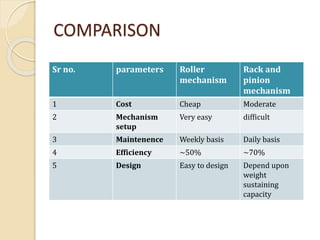
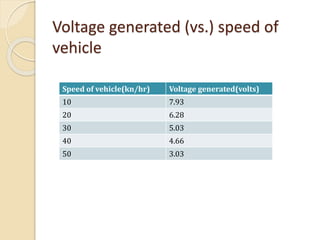
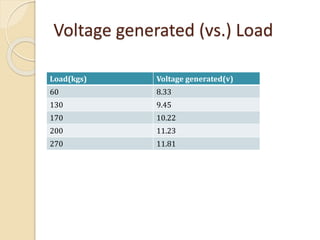
This document discusses generating electricity from speed breakers using vehicles' kinetic and potential energy. It describes two mechanisms - roller and rack/pinion mechanisms. The rack/pinion is more efficient (70% vs 50%) and easier to design for, converting the linear motion of the speed breaker into rotational motion to power a generator. Charts show voltage increasing with vehicle speed and electrical load. In conclusion, this method generates pollution-free power from vehicles at low cost, providing a solution to energy shortages.