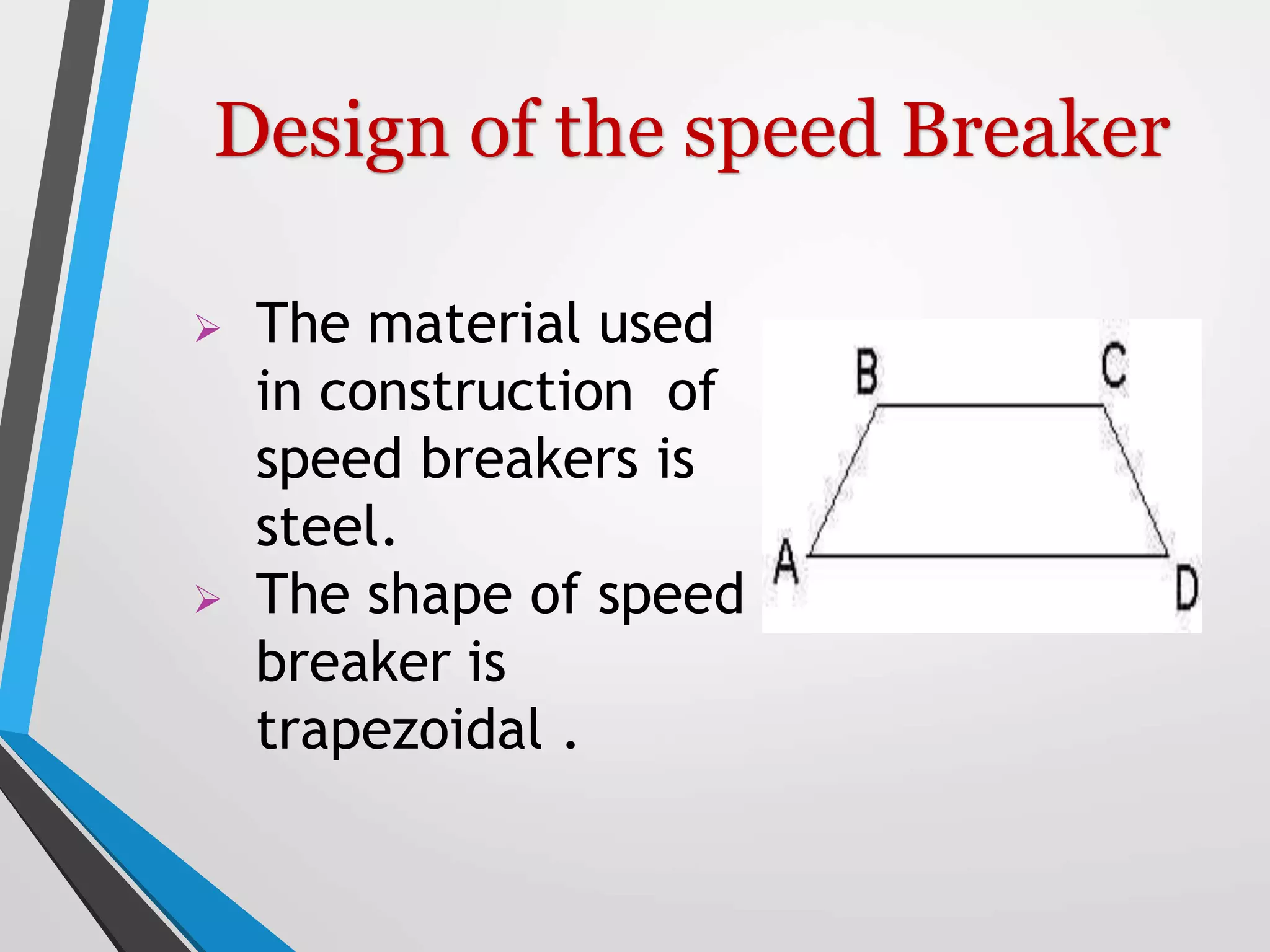
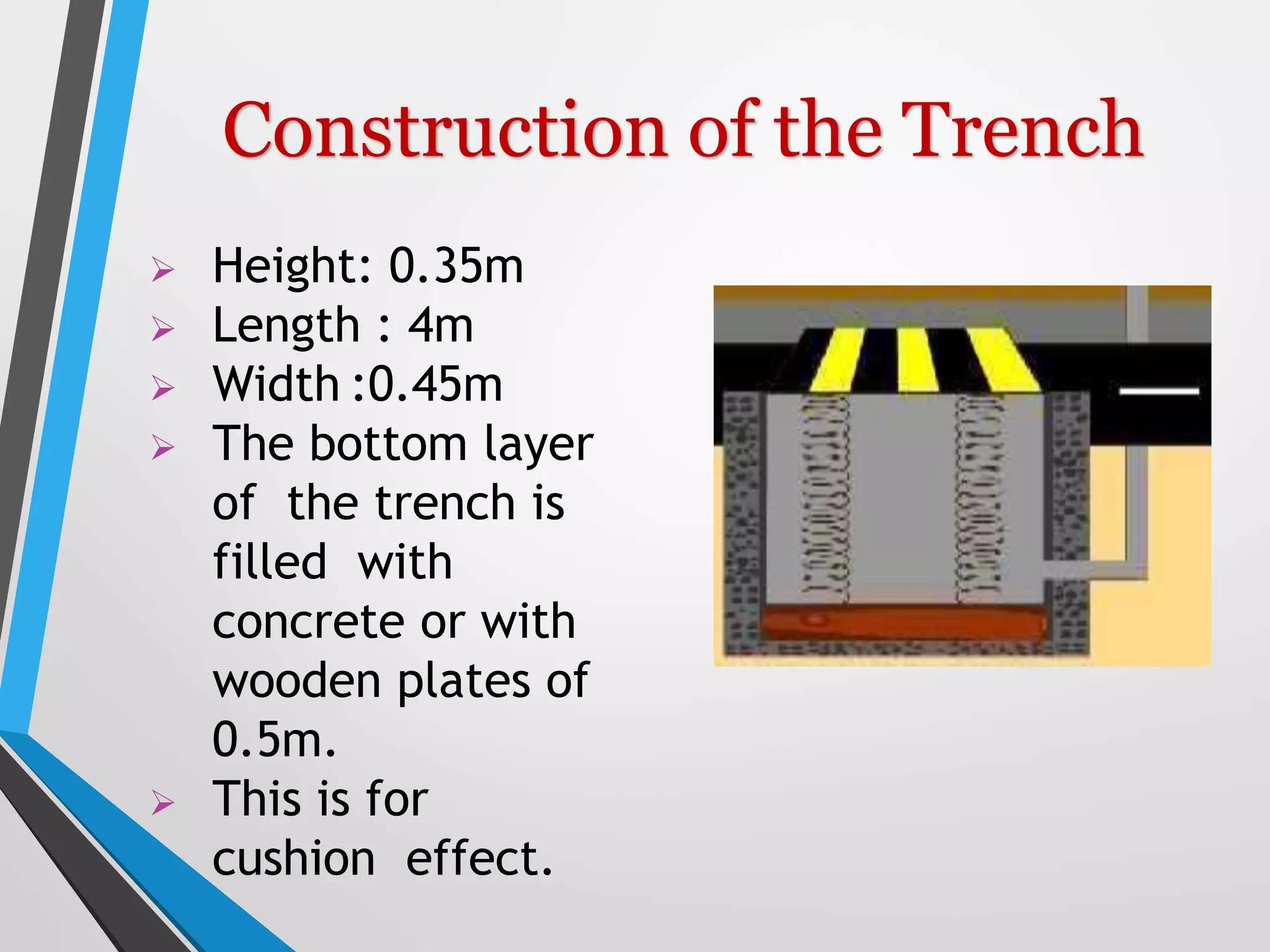
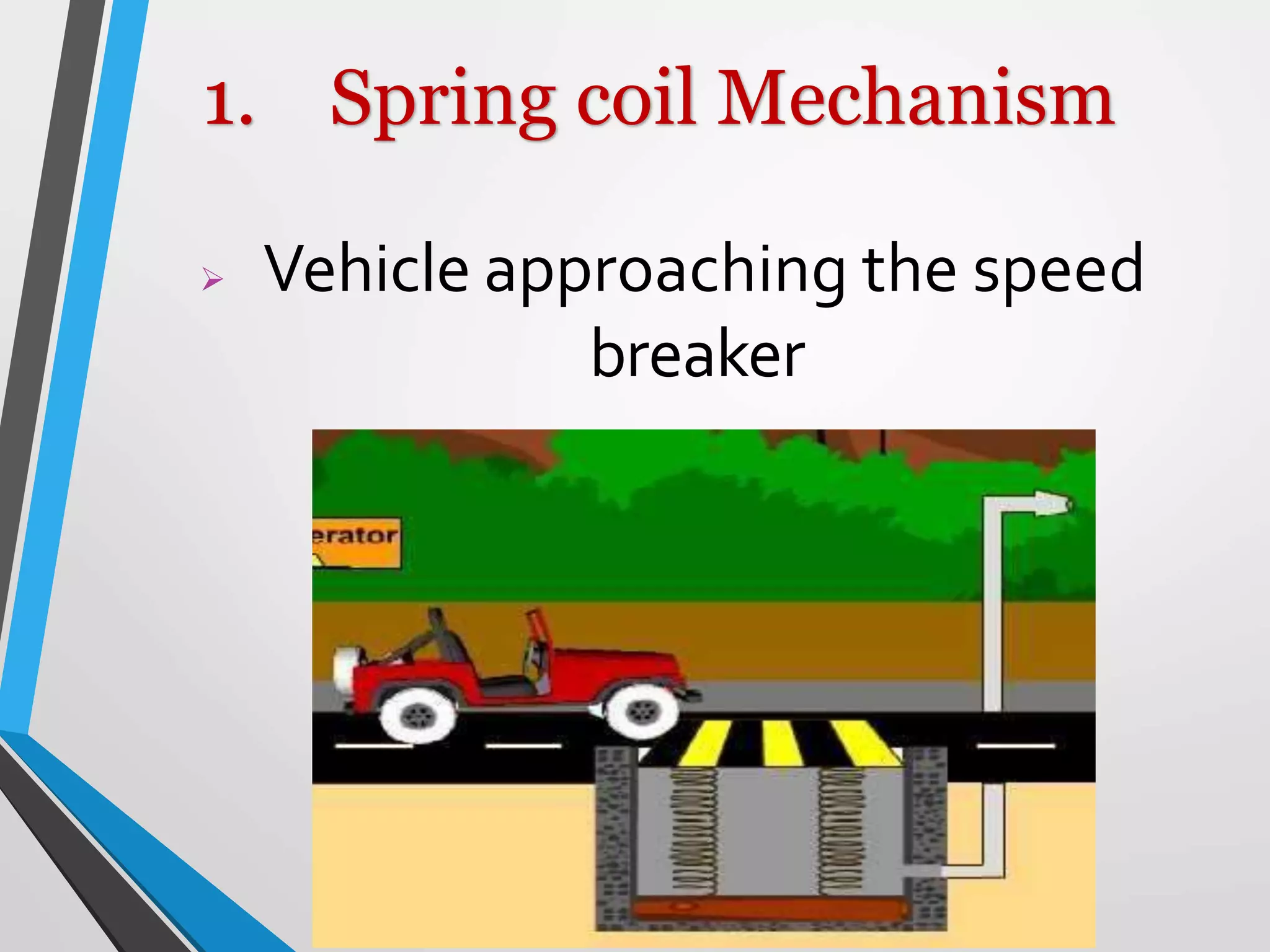
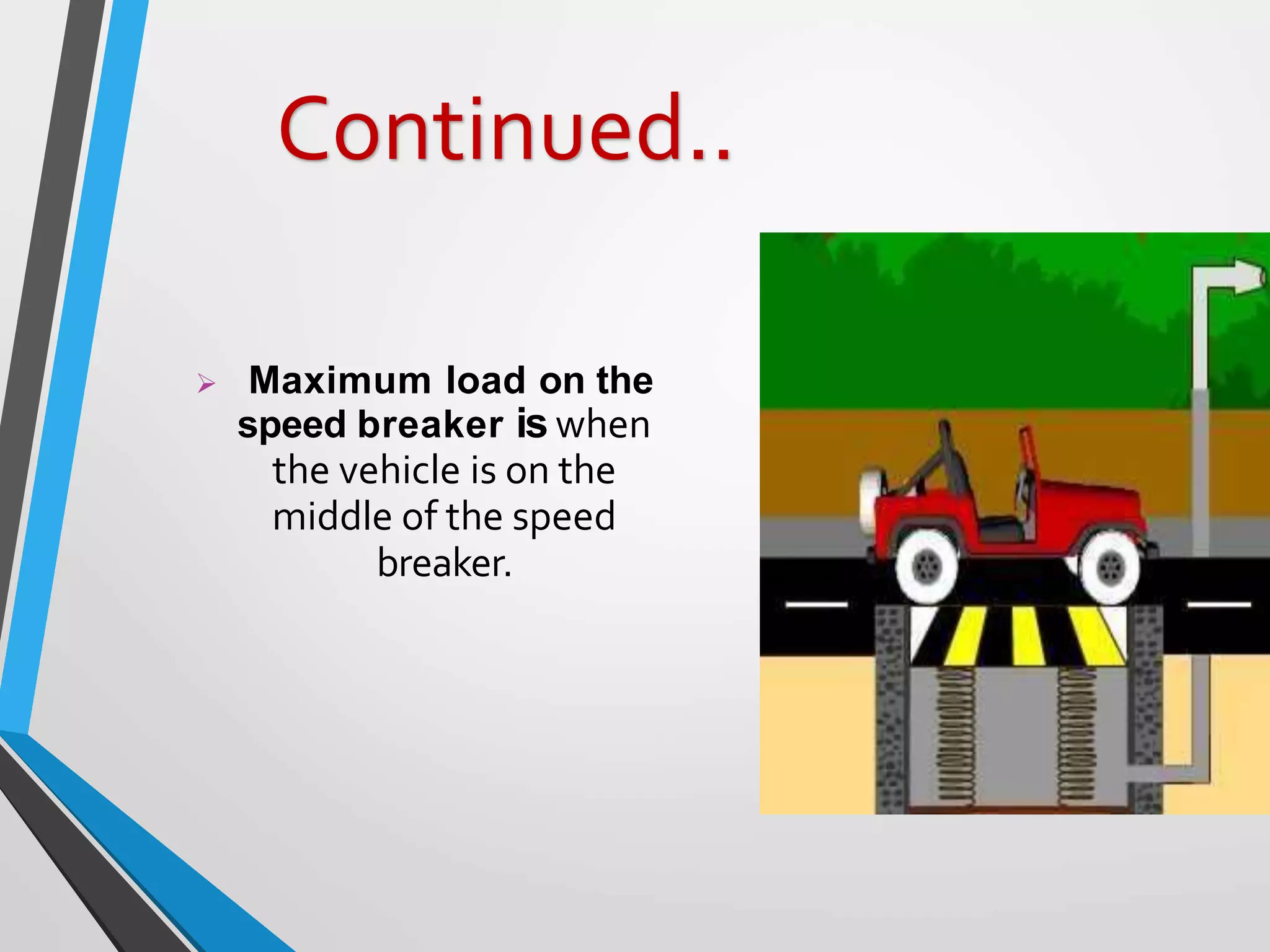
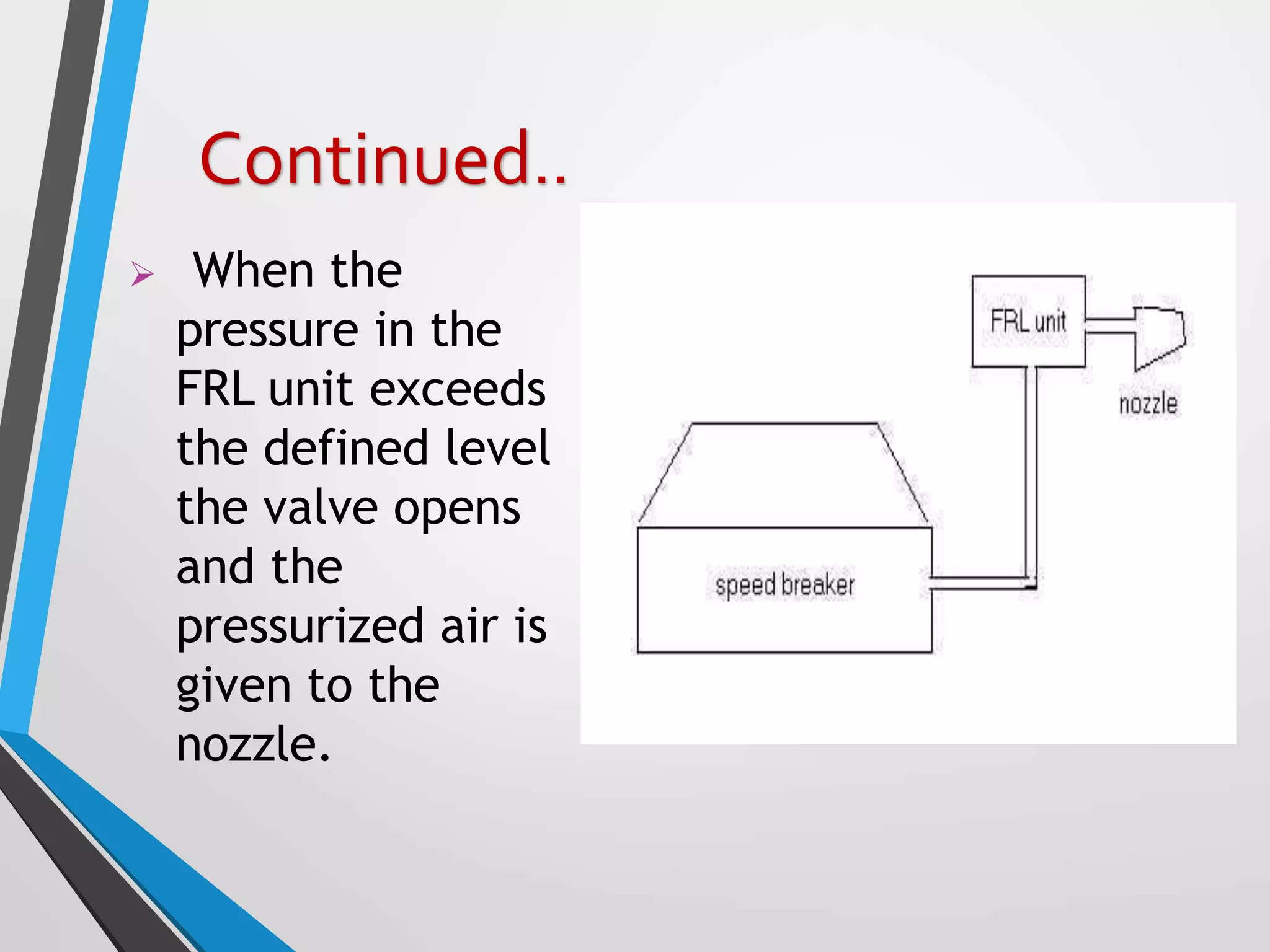
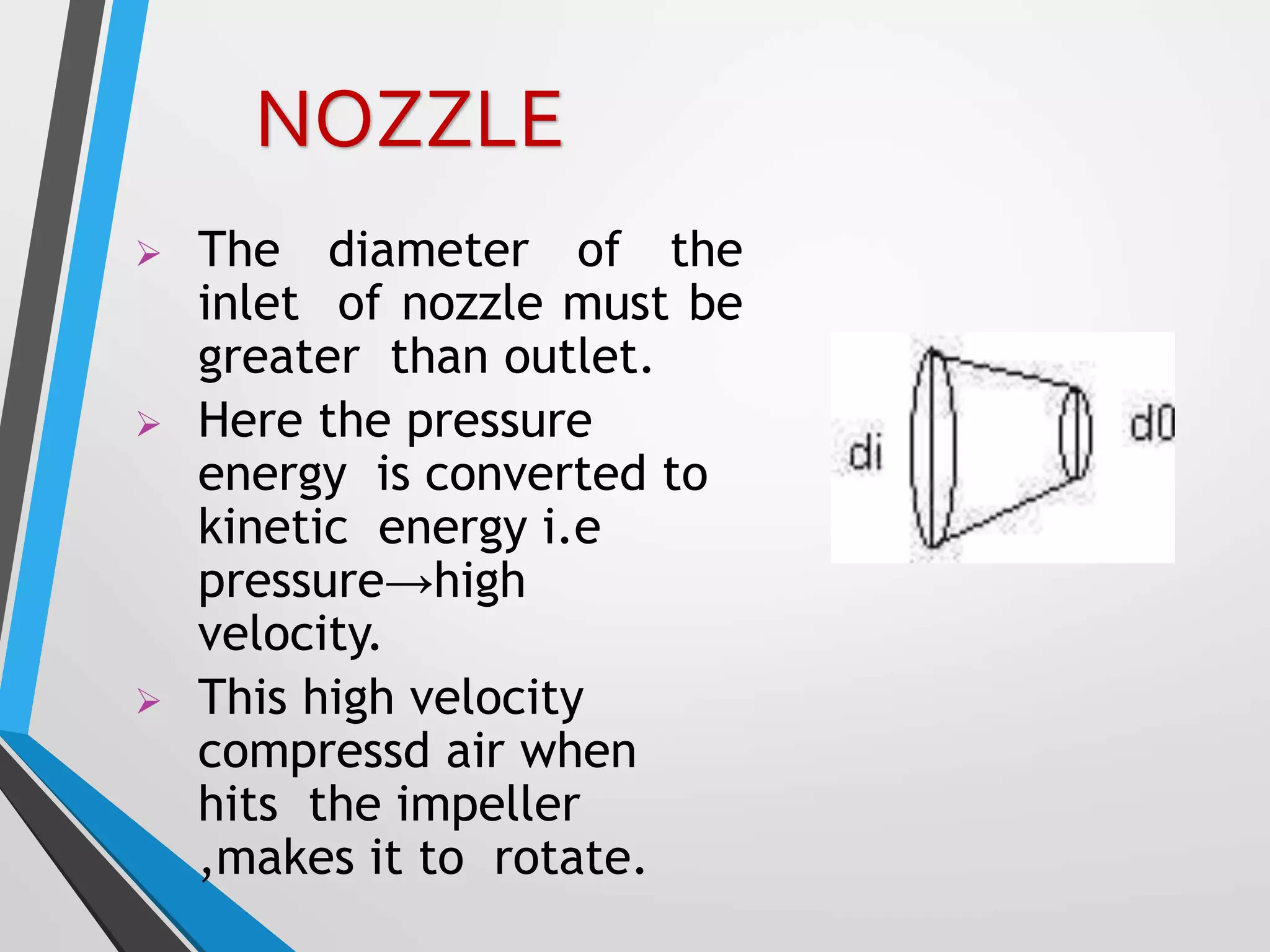
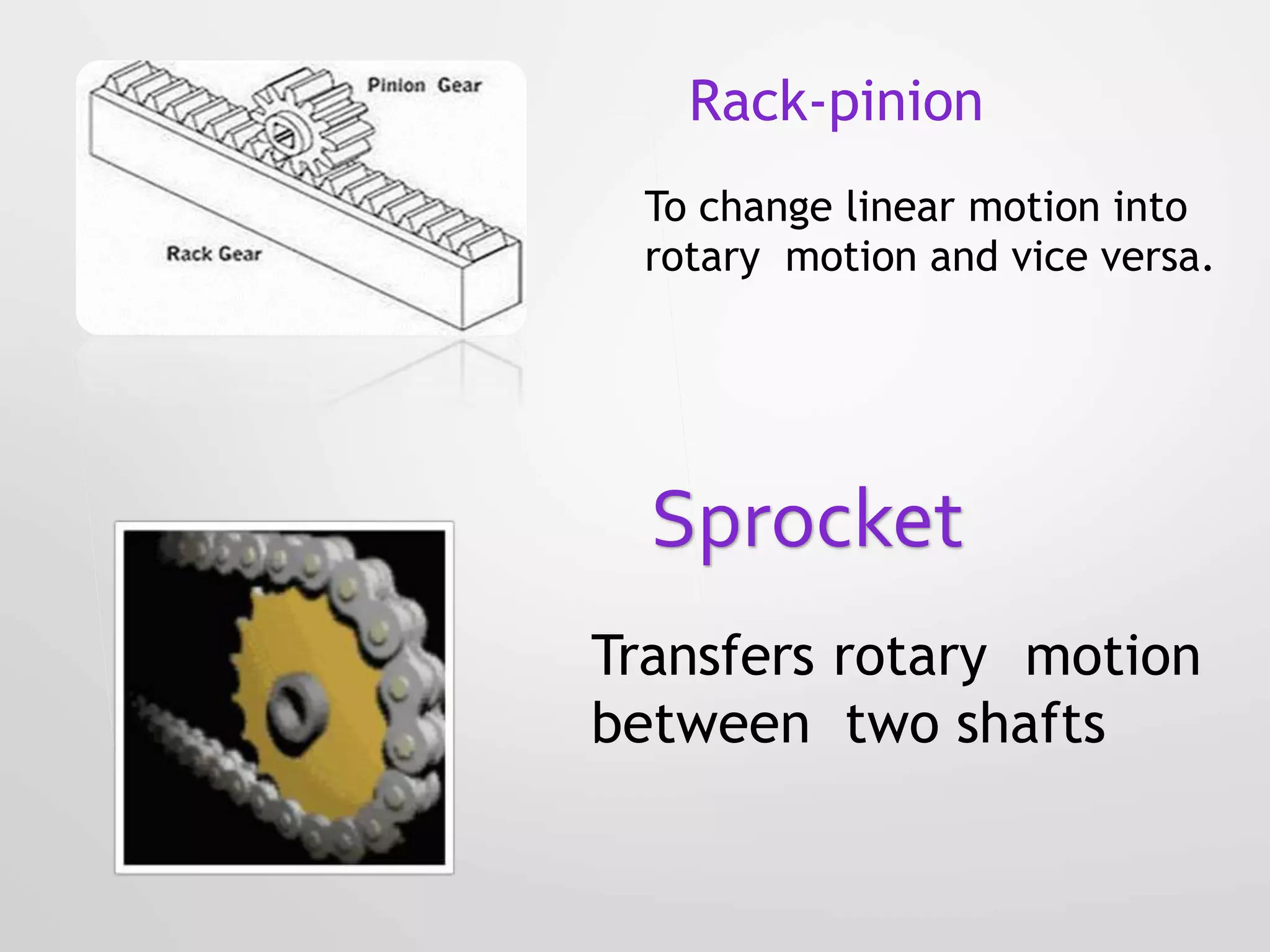
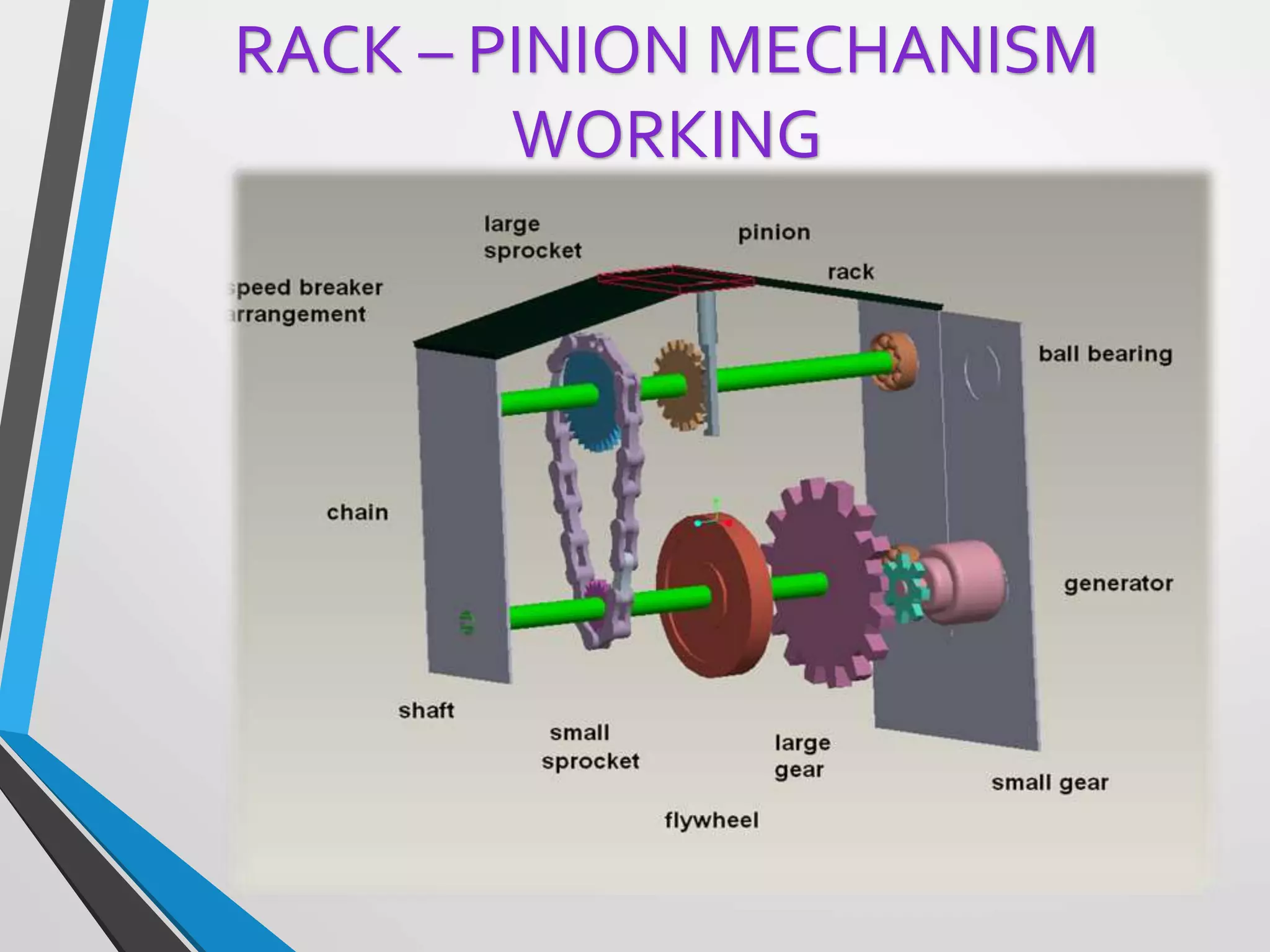
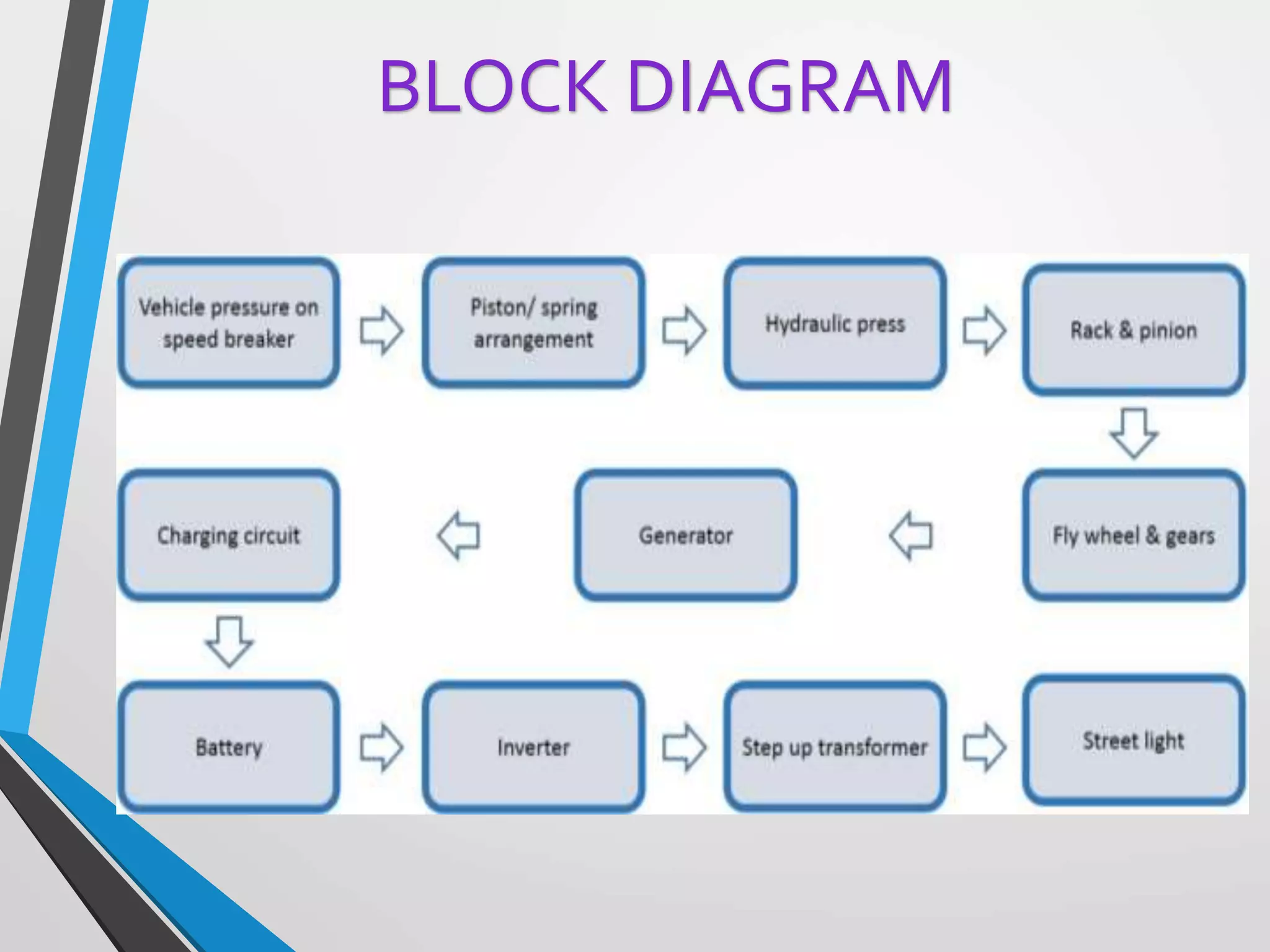
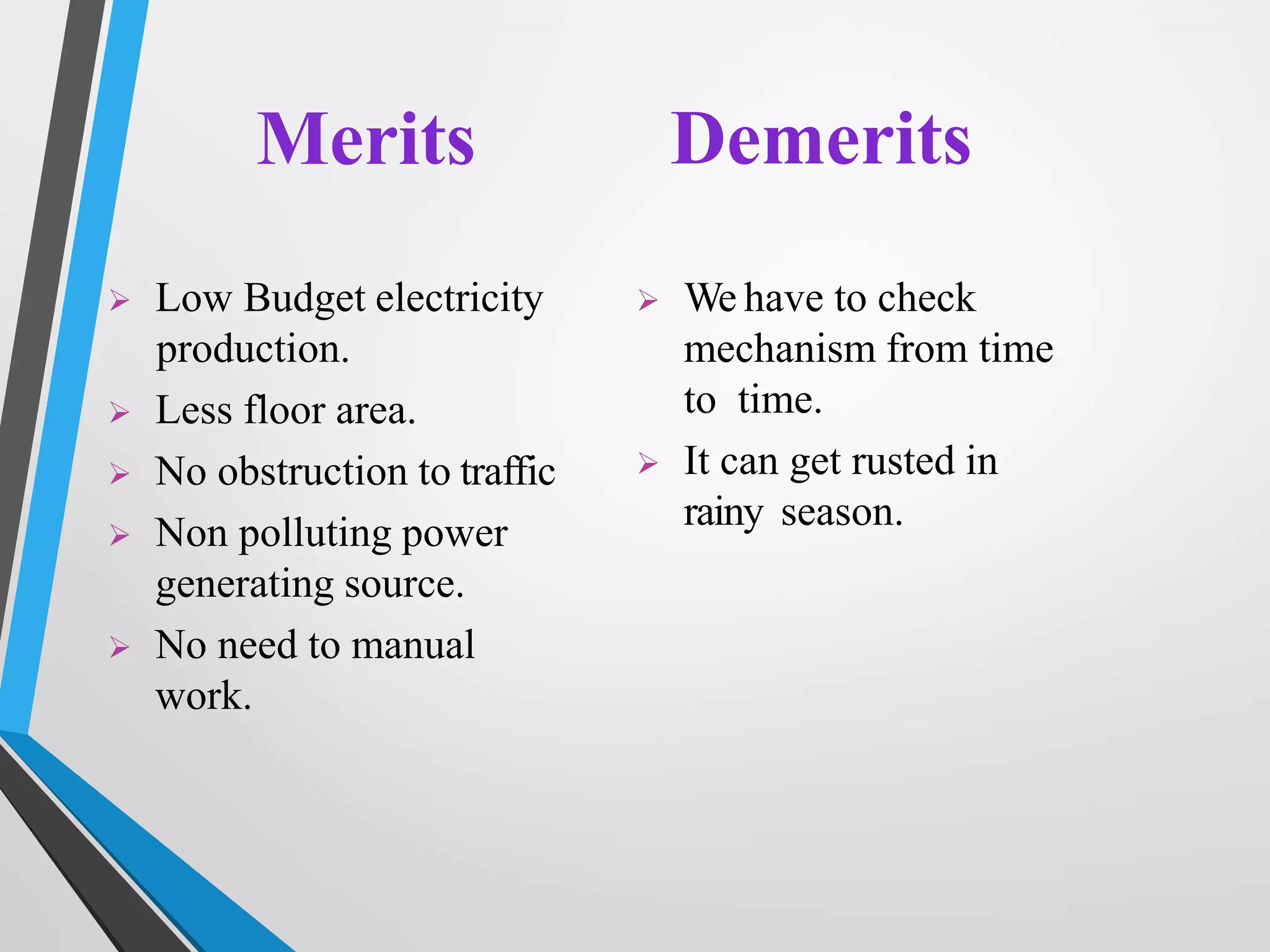
This document presents a design for a speed breaker that can generate electricity. It discusses two possible mechanisms: a spring coil mechanism and a rack-pinion mechanism. The spring coil mechanism uses the compression of a spring when a vehicle passes over the speed breaker to power a pneumatic system that converts the energy to electricity. The rack-pinion mechanism uses a rack and pinion gear setup to convert vertical motion into rotational motion to drive an electric generator. The speed breaker could help produce small amounts of electricity from kinetic energy of passing vehicles and power streetlights.