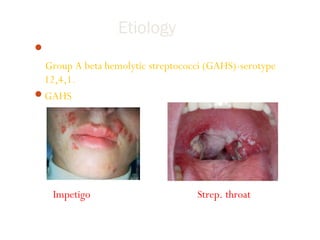
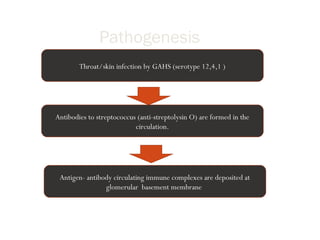
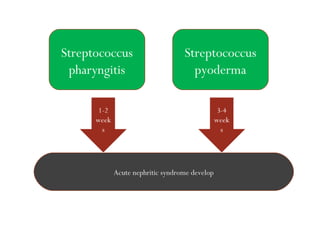
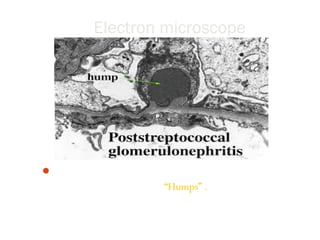
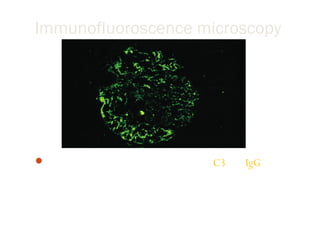
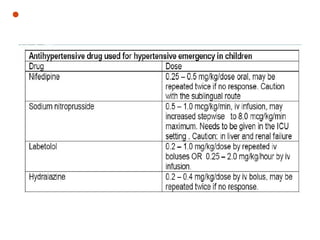
Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN) is an immune-mediated kidney disease that usually develops 1-2 weeks after a streptococcal infection. It most commonly affects children ages 6-12 and is more prevalent in males. PSGN is caused by antibodies produced in response to a Group A streptococcal infection forming immune complexes in the kidneys. This can lead to edema, hematuria, proteinuria, and hypertension. Treatment focuses on supportive care, antibiotics, controlling blood pressure and preventing clotting to minimize complications. The prognosis is generally excellent in the short term, with most patients recovering fully within weeks, though a small percentage may develop chronic kidney disease long term.